![]()
 |
Mars Science Laboratory | |
| August 6, 2012 | ||
 |
Greek government debt crisis | |
| February 2012 | ||
 |
Iraqi insurgency (post U.S. withdrawal) | |
| December 15, 2011 | ||
 |
Gilad Shalit prisoner exchange | |
| October 18, 2011 | ||
 |
Occupy Wall Street | |
| September 17, 2011 - ongoing | ||
 |
2011 Thailand floods | |
| July 25, 2011 - January 16, 2012 | ||
 |
2011 Norway attacks | |
| July 22, 2011 | ||
 |
Death of Osama bin Laden | |
| May 2, 2011 | ||
 |
Second Ivorian civil war | |
| November 28, 2010 - April 11, 2011 | ||
 |
2011 Bahraini uprising | |
| February 14, 2011 - ongoing | ||
 |
Syrian civil war | |
| March 15, 2011 | ||
 |
Sendai earthquake and tsunami | |
| March 11, 2011 | ||
 |
2011 Libyan civil war | |
| Febuary 15, 2011 - October 23, 2011 | ||
 |
2011 Egyptian protests | |
| January 25, 2011 - June 30, 2012 | ||
 |
2010-2011 Tunisian uprising | |
| Janaury 14, 2011 | ||
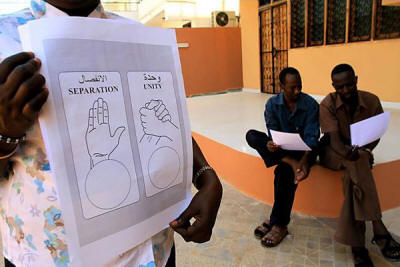 |
Southern Sudanese independence referendum | |
| Janaury 9-15, 2011 | ||
 |
WikiLeaks released a collection of more than 250,000 American diplomatic cables, including 100,000 marked "secret" or "confidential" | |
| November 28, 2010 | ||
 |
|
|
| July 29, 2010 |
|
|
 |
|
|
| July 26, 2010 | ||
 |
the Gaza flotilla raid occurred in the international waters of the Mediterranean Sea, when Israeli naval forces seized a flotilla of six ships carrying international activists, known as the "Gaza Freedom Flotilla". The activists were planning to break the Israeli blockade of Gaza and deliver humanitarian supplies. According to Israeli sources, their forces boarded the flotilla after it had refused to change its course to the port of Ashdod, where the Israeli government had said it would inspect the aid and deliver non-banned items to Gaza |
|
| May 31, 2010 | ||
 |
because of the Greek Bond Crisis, the Greek government requested that the EU/IMF bailout package (made of relatively high-interest loans) be activated |
|
| April 23, 2010 | ||
 |
a suspicious explosion on the Deepwater Horizon offshore drilling rig, operating in the Gulf of Mexico off the coast of Louisiana, resulted in a fire that sank the rig and caused a massive-scale oil spill. The spill covers a surface area of at least 2,500 square miles (6,500 km2) according to estimates reported on May 3, 2010 by CNBC. The oil spill, originating from a deepwater oil well 5,000 feet (1,500 m) below sea level, is currently discharging an estimated 5–25 thousand barrels (210,000–1,100,000 US gallons; 790,000–4,000,000 litres) of crude oil daily |
|
| April 20, 2010 | ||
 |
the 2010 Eruptions of Eyjafjallajökull started with thousands of small earthquakes (mostly of magnitude 1–2 Mw), 7 to 10 kilometres (4.3 to 6.2 mi) beneath the volcano at the end of December 2009. This led to a volcanic eruption of Volcanic Explosivity Index 1 on 20 March 2010. The plume of ash from a later eruption beginning on 14 April 2010 led to widespread disruption of air travel from 15 April, with much of the airspace in Europe closed until 20 April, causing cancellation of most flights within, to, and from Europe |
|
| April 14, 2010 | ||
 |
the 2010 Haiti earthquake was a catastrophic magnitude 7.0 Mw earthquake, with an epicentre near the town of Léogâne, approximately 25 km west of Port-au-Prince, Haiti's capital. The earthquake occurred at 16:53 local time on Tuesday, 12 January 2010. By 24 January, at least 52 aftershocks measuring 4.5 or greater had been recorded. An estimated three million people were affected by the quake; the Haitian Government reported that an estimated 230,000 people had died, 300,000 had been injured and 1,000,000 made homeless. They also estimated that 250,000 residences and 30,000 commercial buildings had collapsed or were severely damaged |
|
| January 12, 2010 | ||
 |
at the G-20 Pittsburgh summit world leaders announce that the G-20 will assume greater leverage over the world economy, replacing the role of the G-8, in an effort to prevent another financial crisis like that in 2008 |
|
| September 25, 2009 | ||
 |
||
| January 20, 2009 | ||
 |
the Gaza War was a three-week military conflict that took place in the Gaza Strip during the winter of 2008–2009. It was dubbed Operation Cast Lead by the Israeli government. The conflict has been called the Gaza massacre in the Arab world. A six-month Israel-Hamas temporary truce was set to expire on December 19. On November 4, Israel sent special forces supported by tanks and bulldozers into Gaza, which triggered sporadic violent clashes along the Gaza-Israeli border over the following six weeks. Israel stepped up the blockade of Gaza, and Palestinian rocket attacks on Israeli cities and towns resumed. On 27 December Israel began a wave of airstrikes on the Gaza Strip with the stated aim of stopping the rocket attacks from and arms smuggling into the territory, damaging or destroying tens of thousands of homes, leaving 50,000 homeless, 400,000-500,000 without running water, one million without electricity, and resulting in acute food shortages |
|
| December 2008 | ||
|
|
the 2008 Greek riots started on 6 December 2008, when Alexandros Grigoropoulos, a 15-year-old student, was fatally shot by Epaminondas Korkoneas, a police officer. Korkoneas, accompanied by another police officer on a patrol, shot Alexandros who was out to celebrate a friend's name day in Exarcheia district of central Athens. The death of Grigoropoulos resulted in large protests and demonstrations, which escalated to widespread rioting, with hundreds of rioters damaging property and engaging riot police with Molotov cocktails, stones and other objects. Demonstrations and rioting soon spread to several other cities, including Thessaloniki, the country's second-largest city. Outside Greece, solidarity demonstrations, riots and, in some cases, clashes with local police also took place in a number of European cities including Istanbul, London, Paris, Brussels, Rome, Dublin, Berlin, Frankfurt, Madrid, Barcelona, Amsterdam, The Hague, Copenhagen, Bordeaux, Seville as well as Nicosia, the capital of Cyprus, and the western Cypriot city of Paphos |
|
|
December 2008 |
||
 |
the 2008 Mumbai attacks were more than ten coordinated shooting and bombing attacks across Mumbai, India's largest city, by Muslim terrorists from Pakistan. The attacks, which drew widespread condemnation across the world, began on 26 November 2008 and lasted until 29 November, killing at least 173 people and wounding at least 308 |
|
| November 26-29, 2008 | ||
 |
when Lehman Brothers filed for bankruptcy protection the Global financial crisis was fomented |
|
| September 2008 | ||
 |
||
 |
||
| August 2008 | ||
 |
||
| March 10, 2008 | ||
 |
2008–2010 Thai political crisis is a continuation of the 2005–2006 political crisis. The PAD's followers usually dress in yellow, called 'the yellow shirts', the royal color of King Bhumibol Adulyadej. The UDD's followers dress in red, widely called 'the red shirts', known as the supporters of the deposed prime minister Thaksin Shinawatra |
|
| Jnauary 2008 | ||
 |
Arktika 2007 was an expedition in which Russia performed the first ever crewed descent to the ocean bottom at the North Pole, as part of research related to the 2001 Russian territorial claim, one of many territorial claims in the Arctic |
|
| August 2007 | ||
 |
||
| June 28 - September 3, 2007 | ||
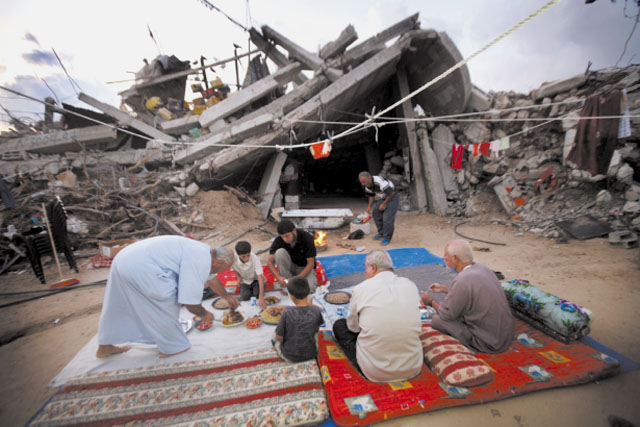 |
the Gaza Strip has been blockaded by Israel and Egypt since June 2007, when, after their 2006 victory in the Palestinian legislative election, Hamas took control of the Palestinian territory in the course of the Battle of Gaza (2007) from the Palestinian government of March 2007 |
|
| June 2007 - present | ||
 |
||
| 2006 - 2009 | ||
|
|
North Korea tested "Hwadae-ri" |
|
| October 9, 2006 | ||
 |
||
| September 19, 2006 | ||
 |
||
| September 18, 2006 | ||
|
○
|
||
| August 10, 2006 | ||
|
○
|
||
| April 24, 2006 | ||
 |
||
| July 12, 2006 | ||
 |
||
| October 27 - November 2005 | ||
 |
||
| October 8, 2005 | ||
|
○
|
||
| October 1, 2005 | ||
 |
Mass bordercrossing from Morocco to Ceuta and Melilla, Spain |
|
| September 29, 2005 | ||
 |
the 2005 Atlantic hurricane season was the most active Atlantic hurricane season in recorded history |
|
| 2005 | ||
 |
||
| August 2005 | ||
 |
Hunger crisises continue to affect most developing countries |
|
| 2005 | ||
 |
three bombs on the London Underground exploded within fifty seconds of each other |
|
| July 2005 | ||
 |
||
| March 23, 2005 | ||
 |
Rafik Hariri was assasinated |
|
| Febuary 14, 2005 | ||
 |
||
| January 2005 | ||
|
○
|
||
| December 14, 2004 | ||
 |
||
| 2004 | ||
|
○
|
Bhutan became the first country to ban tobacco sale completely |
|
| November 2004 | ||
 |
||
| November 2004-2005 | ||
 |
||
| March 11, 2004 | ||
 |
||
| February 2004 | ||
 |
the Human Genome Project announced having completed its task |
|
| April 2003 | ||
 |
the second oil-richest country on earth was invaded and occupied by the "coalition of the willing", officially, in order to rid Iraq of its alleged weapons of mass destruction |
|
| March 2003 | ||
 |
the Darfur conflict is an ongoing conflict in the Darfur region of western Sudan, mainly between the Janjaweed, a government-supported militia recruited from local Arab tribes, and the non-Arab peoples of the region |
|
| 2003 | ||
 |
||
| December 27, 2002 | ||
 |
Israel started building the Apartheid wall |
|
| 2002 | ||
 |
the United States Department of Homeland Security was established by the Homeland Security Act and officially began operation on January 24, 2003 |
|
| November 25, 2002 | ||
 |
||
| November 2002 - June 2003 | ||
|
○
|
the Bali Bombing occurred in the town of Kuta on the Indonesian island of Bali |
|
| October 12, 2002 | ||
 |
the International Criminal Court was established as a permanent tribunal to prosecute individuals for genocide, crimes against humanity, and war crimes, as defined by several international agreements, most prominently the Rome Statute of the International Criminal Court |
|
| July 1, 2002 | ||
|
○
|
||
| May 20, 2002 | ||
|
|
||
| April 2002 | ||
 |
||
| 2002 | ||
 |
the Euro was introduced as the new 'single currency' of the European Monetary Union |
|
| January 1, 2002 | ||
 |
the United States invaded Afghanistan as part of their "War on Terrorism" campaign |
|
| October 2001 | ||
 |
||
| 9.11.2001 | ||
 |
Carlo Giuliani was killed on July 20, 2001 during the demonstrations against the Group of Eight summit that was held in Genoa, Italy |
|
| 1978-2001 | ||
 |
the Shanghai Cooperation Organization is an intergovernmental organization which was founded by leaders of the People's Republic of China, Russia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan and Uzbekistan |
|
| June 14, 2001 | ||
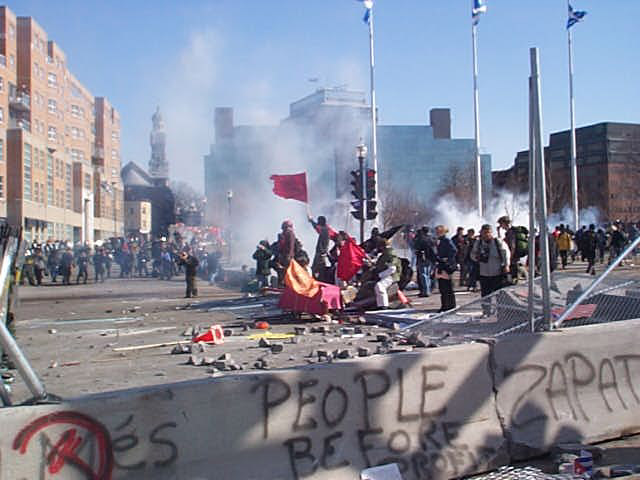 |
the Summit of the Americas held in Quebec City, Quebec, Canada, was a round of negotiations regarding a proposed Free Trade Area of the Americas |
|
| April 20, 2001 | ||
 |
||
| March 2001 | ||
 |
||
| January 2001 | ||
 |
Plan Puebla Panama is a mega project which seeks to open up the southern half of Mexico and Central America to private foreign investment and establishing the foundation for the Free Trade Area of the Americas |
|
| December 2000 | ||
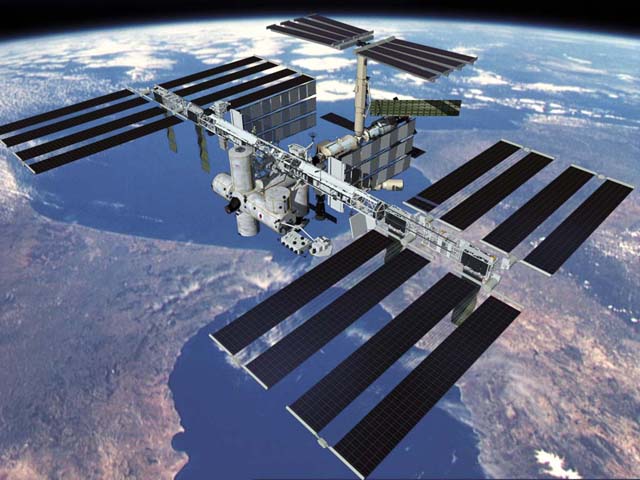 |
the international space station represents a merger of previously planned independent space stations, especially Russia's Mir 2, United States' Space Station Freedom and the planned European Columbus, representing a permanent human presence in space: it has been manned with a crew of at least two since November 2, 2000. The Russian space station Mir was launched on February 19, 1986 and de-orbited on March 23, 2001 |
|
| October 31, 2000 | ||
|
|
the second Palestinian Intifada began just after the second Camp David Summit, when Ariel Sharon and an entourage of 1,000 armed men entered the Al-Aqsa mosque compound |
|
| September 29, 2000 - 2005 | ||
|
○
|
||
| September 2000 | ||
|
○
|
Germany determined to stop producing energy in nuclear power plants by the year 2020, in favour of developing renewable energy sources |
|
| June 16, 2000 | ||
 |
humanoid robots are becoming.increasingly advanced |
|
| 2000 | ||
 |
Plan Columbia is an ambitious and controversial initiative aimed at resolving the ongoing, forty-year civil war in Colombia. The plan was conceived by the administration of President Andrés Pastrana Arango with the goals of social and economic revitalization, ending the armed conflict and creating an anti-narcotic strategy. The most controversial element of the anti-narcotic strategy is aerial fumigation to eradicate coca |
|
| 1999 | ||
 |
||
| 1999 | ||
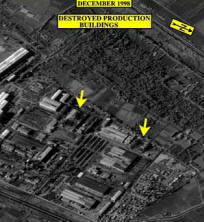 |
Operation Desert Fox was the military codename for a major three-day bombing campaign on Iraqi targets by the United States and United Kingdom |
|
| December 16-18, 1998 | ||
 |
the U.S. military launched cruise missile attacks against alleged Al-Qaeda camps in Afghanistan and a suspected chemical plant in Sudan in retaliation for the August 7 bombings of American embassies in Kenya and Tanzania. The al-Shifa pharmaceutical factory in Khartoum is destroyed in the attack |
|
| August 20, 1998 | ||
 |
U.S. embassy bombings in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, and Nairobi, Kenya |
|
| August 7, 1998 | ||
|
○
|
Pakistan tested "Chagai-I" |
|
| 1998 | ||
 |
with the Good Friday Agreement following a Provisional IRA cease-fire, attempts began to be made to restore self-government to Northern Ireland |
|
| April 10, 1998 | ||
 |
the Second Congo war officially ended in 2002. However, a true peace has been elusive and there are continuing concerns that the conflict will flare again. The widest interstate war in modern African history, it directly involved nine African nations, as well as about twenty armed groups, and earned the epithet of "African World War" |
|
| 1998 | ||
 |
the Kyoto Protocol was negotiated in Kyoto, Japan. It was opened for signature on March 16, 1998. The agreement came into force on February 16, 2005 following ratification by Russia on November 18, 2004. Countries which ratify this protocol commit to reduce their emissions of carbon dioxide and five other greenhouse gases, or engage in emissions trading if they maintain or increase emissions of these gases. A total of 141 countries have ratified the agreement. Notable exceptions include the United States and Australia |
|
| December 1997 | ||
 |
||
| 1997 | ||
|
○
|
||
| 1997 | ||
 |
Hong Kong was a British crown colony until it was returned to Chinese rule |
|
| July 1, 1997 | ||
|
○
|
riots broke out in Albania after an ostensible investment program that had attracted virtually every citizen with any money to spare was exposed as a pyramid scheme swindle |
|
| March 1997 | ||
 |
||
| 1996 | ||
 |
Yitzhak Rabin was assassinated |
|
| November 4, 1995 | ||
 |
Windows 95 was released to the public |
|
| August 24, 1995 | ||
|
|
the Sarin gas attack on the Tokyo subway |
|
| March 20, 1995 | ||
 |
||
| 1995 | ||
 |
the WTO was created to replace the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT), a series of post-war trade treaties intended to facilitate free trade |
|
| January 1, 1995 | ||
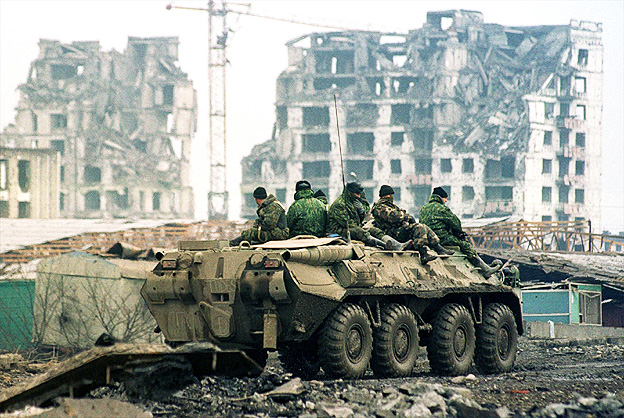 |
the Chechen Wars occurred when Russian forces attempted to recapture the breakaway southern republic of Chechnya |
|
| 1994-1996, 1999-2002 | ||
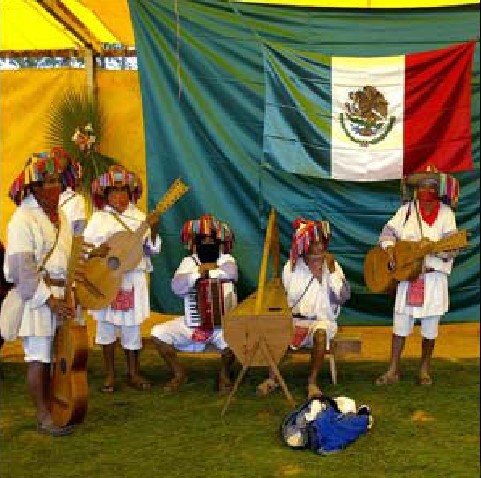 |
the Zapatista rebellion started on January 2, 1994 in response to the North American Free Trade Agreement becoming operational |
|
| 1994 | ||
 |
Yemen Civil war |
|
| 1994 | ||
 |
the Oslo Accords granted the withdrawal of Israeli forces from the Gaza Strip and the West Bank, as well as the Palestinian right to self-government within those areas through the creation of the Palestinian Authority, in exchange for a commitment on the part of the Palestinians to curb the violence of suicide bombings of the Intifada |
|
| August 20, 1993 | ||
 |
the High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program is a US Air Force, Navy and University of Alaska funded investigation to "understand, simulate and control ionospheric processes that might alter the performance of communication and surveillance systems" started in 1993 for a proposed twenty year series of experiments. It is similar to numerous existing ionospheric heaters around the world, and has a large suite of diagnostic instruments that facilitate its use to increase scientific understanding of ionospheric dynamics |
|
| 1993 | ||
 |
Operation Provide Relief was a United Nations sponsored effort to provide humanitarian relief for the people of Somalia who were facing a severe famine, initiated and exacerbated by the ongoing Somali civil war |
|
| August 1992 | ||
 |
the Earth Summit was held in Rio de Janeiro |
|
| June 3-14, 1992 | ||
 |
||
| December 10, 1991 - January 6, 1992 | ||
 |
after the Collapse of the Soviet Union the three republics that founded the USSR in 1922, Russia, Belarus and Ukraine, formed the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS). The Soviet parliament passed its final resolution, acknowledging the dissolution of the USSR, on December 26 |
|
| August 1991 | ||
 |
the Yugoslavian wars were characterized by bitter ethnic conflicts between the people of the former Yugoslavia, though the underlying cause of the conflict was political rather than ethnic - a clash over the governance of the Yugoslavian republics after the country began to fall apart following Slovenia's and Croatia's declarations of independence on June 25, 1991. On November 21, 1995, in Dayton, Ohio, presidents of Bosnia and Herzegovina (Alija Izetbegović), Croatia (Franjo Tuđman), and Serbia (Slobodan Milošević) signed a peace agreement that brought a halt to the three years of war in the Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina. Nevertheless the war flared up again in the southern Serbian province Kosovo in 1996. This conflict ended on June 10, 1999 after an intervention by NATO forces. The International Criminal Tribunal for the former Yugoslavia is a body of the United Nations established to prosecute war crimes in the former Yugoslavia. The tribunal functions as an ad-hoc independent court and is located in The Hague |
|
| June 25, 1991-2001 | ||
 |
||
| October 30, 1990 | ||
 |
||
| 1990 | ||
 |
the Rwanda Civil war began when the Tutsi Rwandese Patriotic Front invaded Rwanda from their base in neighboring Uganda. After the war had already officially ended with the signing of the Arusha accords, violence between the Hutu majority and the Tutsi rebels escalated into a genocide against theTutsi. In 1993 the rivalries between Hutu and Tutsi tribal factions led to the Burundi Civil war |
|
| 1990-1994 | ||
 |
during the Persian Gulf war George Bush declared the "New World Order" on September 11, 1991 |
|
| 1990-1991 | ||
 |
the Hubble Space Telescope was put in space by pace NASA's Space Shuttle Discovery |
|
| April 4, 1990 | ||
|
○
|
the Soviets rejected the Lithuanian claim of independence start an economic blockade, and seize strategic buildings as part of a military and political crackdown |
|
| March 11, 1990 | ||
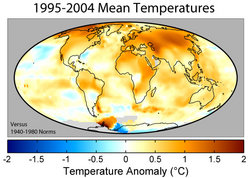 |
the scientific consensus on global warming is that the Earth is warming, and that humanity's greenhouse gas emissions are making a significant contribution |
|
| 1990 - present | ||
 |
Apartheid in South Africa was gradually removed starting with the release of Nelson Mandela from 27 years of imprisonment |
|
| February 2, 1990 | ||
 |
the Romanian Revolution was a series of riots and protests that overthrew the Communist regime of Nicolae Ceauşescu. The increasingly violent riots culminated in a cursory trial and the execution of Ceauşescu and his wife Elena. While the Romanian Revolution was unfolding, other Eastern European nations were peacefully transitioning to democracy; Romania was the only Eastern Bloc country to violently overthrow its Communist regime |
|
| December 16 - 27, 1989 | ||
 |
Operation Just Cause was the invasion of Panama by the United States that deposed general, dictator and de facto Panamanian military leader Manuel Noriega |
|
| December 1989 | ||
 |
the Berlin Wall fell after mass demonstrations against the government in East Germany began in the fall of 1989 |
|
| November 9, 1989 | ||
 |
Hungary removed its border restrictions with Austria, so that in September of that year more than 13,000 East Germans were able to escape the totalitarian system of East Germany through this country |
|
| August 23, 1989 | ||
 |
the third Tiananmen Square Protests were a series of student-led, pro-democracy, pro-socialism demonstrations, which were violently confronted by the Chinese People's Liberation Army |
|
| April 15, 1989 - June 4, 1989 | ||
|
|
in the Exxon Valdez oil spill between 11 million and 35 million U.S. gallons of crude oil spilled form the tanker hit Prince William Sound's Bligh Reef |
|
| March 24, 1989 | ||
 |
||
| 1989 | ||
 |
the first of 24 satellites that form the current GPS constellation (Block II) was placed into orbit. The 52nd GPS satellite since the beginning in 1978 was launched November 6, 2004 aboard a Delta II rocket |
|
| February 14, 1989 | ||
 |
||
| December 21, 1988 | ||
 |
||
| 1988-1993 | ||
 |
||
| 1987-1993 | ||
 |
||
| 1986-1989 | ||
 |
||
| 1986 | ||
 |
the Chernobyl nuclear power plant exploded releasing clouds of radioactive particles, and the severely damaged containment vessel started leaking radioactive matter |
|
| April 26, 1986 | ||
 |
the Challenger exploded shortly after take off |
|
| January 28, 1986 | ||
 |
Nevado del Ruiz erupted |
|
| November 13, 1985 | ||
 |
the Live Aid rock music concert was organised by Bob Geldof and Midge Ure in order to raise funds for famine relief in Ethiopia |
|
| July 13, 1985 | ||
 |
the Schengen treaty is an agreement to end border checkpoints and controls within the Schengen area. It was signed initially only by Belgium, France, Germany, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands |
|
| June 14, 1985 | ||
 |
Mikhail Gorbachev became General Secretary of the CPSU and leader of the Soviet Union. He tried to reform the stagnating state economy by introducing the concepts of glasnost ("openness"), perestroika ("restructuring"), and uskorenie ("acceleration"). But most importantly he abandoned the Brezhnev Doctrine, the Soviet Union’s policy of intervening with military force, if necessary, to preserve Communist rule in the Eastern bloc nations |
|
| March 11, 1985 | ||
 |
||
| 1984 | ||
 |
||
| December 20, 1983 | ||
 |
Black July is the commonly used name of the pogroms starting in Sri Lanka on between 1,000 - 3,000 tamils were killed, tens of thousand houses were destroyed and a wave of tamils sought refugee in other countries. "Black July" is generally seen as the start of full-scale armed struggle between the tamil minority and the sinhalese majority |
|
| July 23, 1983 | ||
 |
the core networking protocol of ARPANET was changed from NCP to TCP/IP, marking the start of the Internet as we know it today |
|
| January 1, 1983 | ||
|
|
the Falklands war was an armed conflict between Argentina and the United Kingdom over the Falkland Islands |
|
| March - June 1982 | ||
 |
||
| August 12, 1981 | ||
|
○
|
both Pope John Paul II and President Reagan were wounded in assassination attempts |
|
| 1981 | ||
|
○
|
Sweden determined to stop producing energy in nuclear power plants in favour of using wind energy |
|
| 1980 | ||
 |
the origins of the Iran-Iraq war go back to the question of sovereignty over the resource-rich province of Khuzestan |
|
| 1980-1988 | ||
 |
||
| 1979-present | ||
 |
||
| June 3, 1979 | ||
 |
with the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan the Great "Game" between the British and the Russian Empire for supremacy in Central Asia was continued, after the first and second Anglo Afghan wars (1839-1842 and 1878-1879), now with involvement form the United States who supported Mujahideen forces like the Taliban to create an anti-Soviet resistance |
|
| 1979-1989 | ||
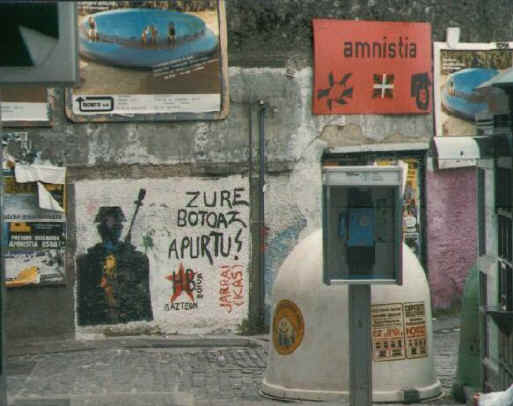 |
the Spanish state devolved into autonomous communities of which the Spanish Basque Country became the Basque Country |
|
| October 25, 1979 | ||
 |
the approval of the Spanish Constitution was the culmination of the Spanish transition to democracy. Upon the death of the dictator General Franco in November 1975, his personally-designated heir Prince Juan Carlos had assumed the position of king and head of state |
|
| October 31, 1978 | ||
 |
the Camp David Accrods were concluded six months later with the signing of the Israel-Egypt Peace Treaty |
|
| 1978 | ||
 |
the Iranian Revolution transformed Iran from an autocratic pro-west monarchy under Shah Mohammad Reza Pahlavi to an Islamic, theocratic democracy under the rule of Ayatollah Khomeini |
|
| 1978-1979 | ||
 |
the Voyager 1 is the farthest human-made object from Earth. It is an unmanned probe of the outer solar system and beyond. It contains a message from mankind engraved on the golden record |
|
| September 5, 1977 | ||
 |
||
| 1976-1983 | ||
|
○
|
||
| 1976 | ||
 |
||
| 1976 | ||
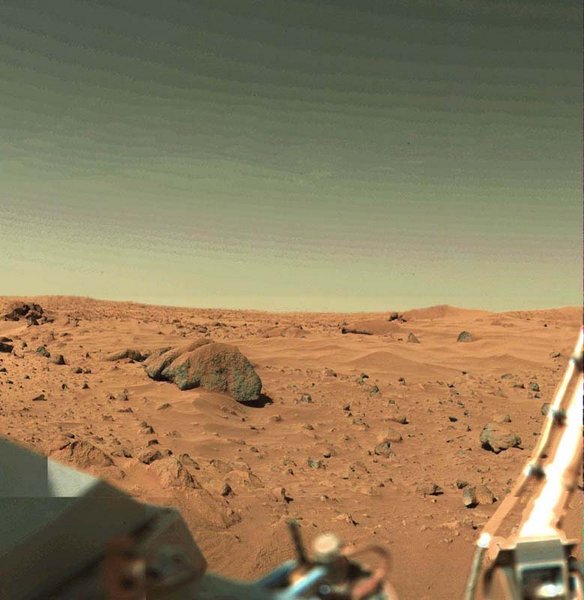 |
Viking 1 ( was the first spacecraft that returned color pictures of Mars to Earth. The first successful landing on the planet was directed by the Russian space program and their probe Mars 3 in 1971. Other successful Mars exploration spacecraft launches include NASA's Mars Global Surveyor which entered orbit on September 12, 1997. The Mars Pathfinder spacecraft also landed in 1997 and carried a tiny remote-controlled rover called Sojourner, which traveled a few meters around the landing site, exploring the conditions and sampling rocks around it. In 2001 Mars Odyssey used spectrometers and imagers to hunt for evidence of past or present water and volcanic activity, and later actually confirmed the finding of large amounts of hydrogen. The European Space Agency's probe Mars Express and its lander Beagle 2 entered Mars orbit on December 25, 2003. Shortly after the launch of Mars Express, NASA sent a pair of twin rovers toward the planet as part of the Mars Exploration Rover Mission which landed in July 2004 |
|
| July 20, 1976 | ||
 |
the so-called Green March into Western Sahara began when 300,000 unarmed Moroccans converged on the southern city of Tarfaya and waited for a signal from King Hassan II of Morocco to cross into Western Sahara. As a result, Spain abandoned Western Sahara on November 14, 1975, repatriating even the Spanish corpses from its cemeteries. Morocco later virtually annexed the northern two-thirds of Western Sahara (formerly Spanish Sahara) in 1976, and the rest of the territory in 1979, following Mauritania's withdrawal. On February 27, 1976, the Polisario Front formally proclaimed the Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), and set up a government in exile. A guerrilla war between the Polisario and Morocco ended in a 1991 cease-fire |
|
| November 6, 1975 | ||
 |
the Lebanese Civil war was fought between Lebanese Maronite Christians, led by the Phalangist party and militia, and allied initially with Syria then with Israel, which provided them with arms and training to fight against the Palestine Liberation Organization |
|
| 1975-1990 | ||
 |
the Group of Six originally consisted of France, West Germany, Italy, Japan, the United Kingdom and the United States. Only a year later Canada joined as the seventh member, Russia joined in 1998. Today the G8+5 includes China, Mexico, India, Brazil and South Africa |
|
| 1975 | ||
 |
||
| 1975 | ||
 |
||
| 1975 | ||
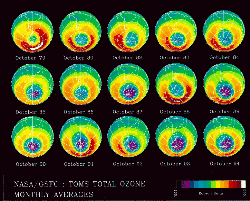 |
Ozone depletion refers to the phenomenon of reductions in the amount of ozone in the stratosphere. Since the ozone layer prevents most harmful wavelengths of ultraviolet light from passing through the Earth's atmosphere, observed and projected decreases in ozone have generated worldwideconcern and led to adoption of the Montreal Protocol banning the use of chlorofluorocarbon (CFC) compounds, as well as other ozone depleting chemicals such as carbon tetrachloride, trichloroethane and bromine compounds known as halons |
|
| 1975 - present | ||
|
○
|
||
| 1975 | ||
 |
India tested "Smiling Buddha" |
|
| 1974 | ||
 |
||
| 1974 | ||
 |
the world oil shock began when Arab members of the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), in the midst of the Yom Kippur War, announced that they would no longer ship petroleum to nations that had supported Israel in its conflict with Egypt - that is, to the United States and its allies in Western Europe |
|
| October 1973 | ||
 |
the Yom Kippur war was fought between Israel and a coalition of Egypt and Syria |
|
| October 6 - 24, 1973 | ||
 |
a military coup in Chile backed by the CIA overthrew Allende's "Popular Unity" Socialist coalition. A military government, led by General Pinochet, took over control of the country |
|
| September 11, 1973 | ||
 |
modern mobile telephony is considered to have started when Motorola employee Martin Cooper placed a call to rival AT&T's Bell Labs while walking the streets of New York City talking on Motorola DynaTAC |
|
| April 3, 1973 | ||
 |
||
| November 16, 1972 | ||
 |
the Munich massacre occurred during the 1972 Summer Olympics in Munich, West Germany |
|
| September 5 - 6, 1972 | ||
|
|
the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty was a treaty between the United States of America and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics on the limitation of the anti-ballistic missile systems used in defending areas against missile-delivered nuclear weapons. On May 26, 1972, the President of the United States, Richard Nixon and the General Secretary of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, Leonid Brezhnev signed the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty. The treaty was in force for thirty years, from 1972 until 2002. On June 13, 2002, six months after giving the required notice of intent, the US withdrew from the treaty |
|
| May 26, 1972 - June 13, 2002 | ||
 |
Pioneer 10 was the first spacecraft to travel through the asteroid belt, and was the first spacecraft to make direct observations of Jupiter. Pioneer 10 is heading in the direction of the star Aldebaran in the constellation Taurus |
|
| March 2, 1972 | ||
 |
||
| 1971 | ||
 |
||
| 1971 | ||
 |
Greenpeace is an independent, campaigning organisation which uses non-violent, creative confrontation to expose global environmental problems, and to force solutions for a green and peaceful future. Greenpeace's goal is to ensure the ability of the earth to nurture life in all its diversity |
|
| 1971 | ||
 |
the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs entered into force on August 16, 1976. Today, 175 nations are Parties to the treaty. Provisions to prevent the international trafficking of drugs covered by this Convention are contained in the United Nations Convention Against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances. The "war on drugs" was instituted by Nixon in 1972 |
|
| February 21, 1971 | ||
 |
the Woodstock Music and Art Festival represented the culmination of the counterculture of the 1960s and the high point of the "hippie era" |
|
| August 15-17, 1969 | ||
 |
the U.S. Apollo program sent twelve men to land on the Moon, the first of whom were Neil Armstrong and Buzz Aldrin in Apollo 11. The first men sent to the Moon were Frank Borman, James Lovell and William Anders, in Apollo 8. Before and since that time, the Moon has been the target of numerous landing and orbiting space probes, starting with the Soviet Luna 1 in 1959 |
|
| July 20, 1969 | ||
 |
the Football war was fought between El Salvador and Honduras |
|
| July 14, 1969 - July 18, 1969 | ||
|
○
|
||
| July 1, 1968 | ||
|
|
student protests in France led De Gaulle to dissolve the National Assembly and call for new parliamentary elections. In Germany the student Benno Ohnsorg was shot on June 2, 1967 during a demonstration against Shah Pahlewi |
|
| May 1968 | ||
 |
Civil rights leader Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. was assassinated in Memphis, Tennessee |
|
| April 4, 1968April 4, 1968 | ||
 |
||
| January 5 - August 20, 1968 | ||
 |
the Six-Day war was fought between Israel and its Arab neighbors Egypt, Jordan, and Syria. By the end of the war, Israel controlled the Gaza Strip, the Sinai Peninsula, the West Bank, and the Golan Heights |
|
| June 5 - June 11, 1967 | ||
 |
the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution in the People's Republic of China was a struggle for power within the Communist Party of China that manifested into wide-scale social, political, and economic chaos, which grew to include large sections of Chinese society and eventually brought the entire country to the brink of civil war. It was launched by the Communist Party of China's Chairman, Mao Zedong on May 16, 1966, officially as a campaign to rid China of its "liberal bourgeoisie" elements and to continue revolutionary class struggle. It is widely recognized, however, as a method to regain control of the party after the disastrous Great Leap Forward led to a significant loss of Mao's power to rivals Liu Shaoqi and Deng Xiaoping, and would eventually manifest into waves of power struggles between rival factions both nationally and locally |
|
| 1966-1976 | ||
 |
the first documented case of HIV in Europe dates to 1966 when a 20-year-old Norwegian sailor, who had traveled to Africa, checked himself into a hospital. The official date for the beginning of the AIDS epidemic is marked as June 5, 1981 |
|
| 1966 | ||
 |
||
| 1965 - present | ||
 |
||
| December 30, 1964 | ||
 |
||
| August 1964 | ||
 |
the People's Republic of China tested "596" |
|
| 1964 | ||
 |
John F. Kennedy was assassinated by Lee Harvey Oswald according to the conclusions of two government investigations into the assassination. He was replaced in office by vp Johnson |
|
| November 22, 1963 | ||
 |
||
| August 28, 1963 | ||
 |
the Partial Test Ban Treaty prohibits atmospheric testing of nuclear weapons |
|
| August 5, 1963 | ||
 |
the so-called "red telephone" that linked the White House with the Kremlin was established |
|
| June 20, 1963 | ||
 |
Norman Borlaug launched the "Green Revolution" by breeding a strain of wheat that yields three to five times than ordinary wheat. He saved millions of lives in India, which after much bureaucratic red tape, finally allowed the grain to be imported |
|
| 1963 | ||
 |
||
| 1963 | ||
 |
||
| 1961 | ||
 |
||
| October 30, 1961 | ||
 |
||
| 1960 | ||
|
○
|
France tested "Gerboise Bleue" |
|
| 1960 | ||
 |
the loss of tropical rain forest continues to progress |
|
| 1960 - present | ||
 |
the Antarctic Treaty assuring that scientific discovery will be the only human activity in the region, was signed by the 12 countries active in Antarctica during the International Geophysical Year of 1957-58 |
|
| December 1, 1959 | ||
 |
Fidel Castro's communist 'July 26 Movement' toppled the U.S.-backed dictator Fulgencio Batista. Soon after in the Bay of Pigs Invasion of 1961 the United States attempted but failed to overthrow the new Cuban government in turn |
|
| 1959 | ||
 |
||
| October 5, 1958 | ||
 |
||
| 1958 | ||
 |
Sputnik 1 was the first artificial Earth satellite. It is one of the many firsts accomplished by the Russian Space program besides Luna 1 (January 2, 1959) the first craft to orbit the Sun, Luna 2 (September 12, 1959) the first craft to land on the Moon, Luna 3 (October 4, 1959) the first craft to orbit the Moon, Yuri Gagarin (April 12, 1961) the first human to travel into space, Valentina Tereshkova (1963) the first woman to fly into space, or Aleksei Leonov (March 18, 1965) the first man to perform a spacewalk |
|
| October 4, 1957 | ||
 |
||
| July 29, 1957) | ||
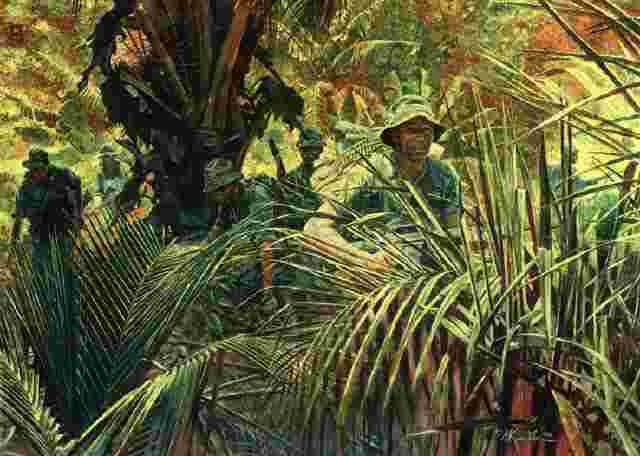 |
the Vietnam war was fought to decide whether Vietnam would be united under a Communist government, or would remain indefinitely partitioned into the separate countries of North and South Vietnam. The war ended in 1975 with a Communist victory and the unification of the country under a government controlled by the Communist Party of Vietnam. In 1979, Vietnam invaded Cambodia and removed Pol Pot from power and into hiding, thereby decisively stabilizing Cambodia. Only one month later, however, partially in retaliation, China launched a failed invasion of Vietnam: the Sino-Vietnamese War |
|
| 1957-1975 | ||
 |
||
| October 23 - November 10, 1956 | ||
 |
the Suez Crisis pitted Egypt against an alliance between France, the United Kingdom and Israel. When the Soviet Union threatened to intervene on behalf of Egypt, the United States feared a larger war, and forced the British and French to withdraw. The Crisis marked the completion of the shift in the global balance of power from European powers to the US and Russia |
|
| 1956 | ||
 |
Morocco recovered its political independence from France |
|
| March 2, 1956 | ||
 |
||
| 1950s - present | ||
 |
the Central Treaty Organization was adopted by Iraq, Turkey, Pakistan, and Iran, as well as the United Kingdom |
|
| 1955 | ||
 |
the Bandung Conference was a meeting of Asian and African states, most of which were newly independent, ultimately it led to the establishment of the Nonaligned Movement in 1961 |
|
| April 1955 | ||
 |
the Warsaw Pact was a military alliance of the Eastern European Eastern Bloc countries, who intended to organize against the perceived threat from the NATO alliance |
|
| May 14, 1955 - March 31, 1991 | ||
 |
||
| 1955 | ||
 |
||
| September 8, 1954-1977 | ||
 |
the Algerian war of Independence was a period of guerrilla strikes, mainly led by the Algerian Front de Libération Nationale against the occupation of their country by the French |
|
| 1954-1962 | ||
 |
the Central Intelligence Agency orchestrated the overthrow of the democratic Guatemalan government, known as Operation pbsuccess, triggering a civil war that would continue for more than 35 years |
|
| 1954 | ||
 |
Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay reached the summit of Mount Everest |
|
| May 29, 1953 | ||
 |
the helical structure of the DNA molecule was discovered by James D. Watson and Francis Crick together with Rosalind Franklin |
|
| April 1953 | ||
 |
Iran's prime minister Mohammed Mossadeq was removed from power in a complex plot orchestrated by British and US intelligence agencies ("Operation Ajax") |
|
| 1953 | ||
|
○
|
the United Kingdom tested "Hurricane" |
|
| 1952 | ||
 |
the first passenger flight on a jet airliner was from London Heathrow Airport to Johannesburg |
|
| May 2, 1952 | ||
|
○
|
the ANZUS Treaty is the military alliance which binds Australia and New Zealand and, separately, Australia and the United States to cooperate on defence matters in the Pacific Ocean area |
|
| September 1, 1951 | ||
 |
the European Coal and Steel Community was established with the Treaty of Paris, it was the earliest forerunner of the European Union and consisted of only six members: Belgium, the Netherlands, Luxembourg (the Benelux countries), (West) Germany, France and Italy |
|
| April 18, 1951 | ||
 |
||
| 1951 | ||
 |
||
| 1950s | ||
 |
the Korean war was a conflict between North Korea and South Korea. It was also a Cold war proxy war between the United States and its United Nations allies and the Communist powers of the People's Republic of China and the Soviet Union. The war ended in a stalemate and left the peninsula permanently divided with a garrisoned pro-Soviet, Communist party led state in North Korea and a pro-American capitalist one in the South |
|
| 1950-1953 | ||
|
○
|
the Soviet Union tested "RDS-1" |
|
| 1949 | ||
 |
the People's Republic of China was proclaimed by Mao Zedong |
|
| 1949 | ||
|
|
||
| 1949 | ||
 |
||
| 1949 | ||
 |
||
| December 10, 1948 | ||
 |
during the Arab-Israeli war David Ben Gurion proclaimed the establishment of the State of Israel on May 14, 1948. The 1949 Armistice Agreements, a set of treaties signed between Israel and its neighbors Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon and Syria ended the war. They established the armistice lines between Israel and the West Bank, also known as the Green Line, until the 1967 Six-Day war |
|
| 1948 | ||
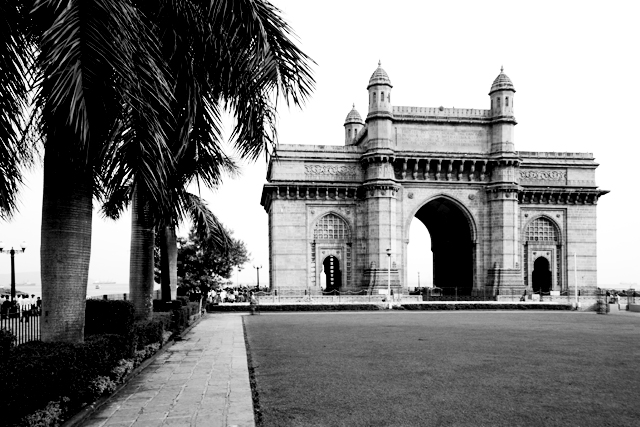 |
India and Pakistan gained independence from British rule. The Indian independence movement began with the Rebellion of 1857 but it was especially during the 1920s with the leadership of Mahatma Gandhi that the cause attracted world attention |
|
| August 15, 1947 | ||
 |
the Cold war was the open yet restricted rivalry that developed after world war II between the United States and its allies and the Soviet Union and its allies. A major feature of the Cold war was the arms race between the Soviet Union and the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation, which was established in 1949 |
|
| 1947-1991 | ||
 |
||
| 1946-1954 | ||
 |
the British mandate over Transjordan ended and the country became the independent Hashemite Kingdom of Transjordan |
|
| May 22, 1946 | ||
 |
||
| January 22, 1946 - 1947 | ||
 |
the United Nations came into existence after the Charter had been ratified by the five permanent members of the Security Council - the Republic of China, France, the Soviet Union, the United Kingdom, and the United States. The institution is the more modern version of the League of Nations which was established after the first world war. The Universal Declaration of Human Rights, though not yet legally binding, was adopted by the General Assembly in 1948 as a common standard of achievement for all member countries |
|
| October 24, 1945 | ||
 |
Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan, were destroyed by atomic bombs dropped by the United States military on August 6 and August 9, 1945, respectively, killing at least 100,000 civilians outright and many more over time. The bombs, secretly developed by the United States (with assistance from the United Kingdom and Canada) under the codename Manhattan Project, were the second and third atomic devices to be detonated, and are the only ones ever used as weapons, rather than for testing purposes. The first nuclear test explosion, designated "Trinity" (and nicknamed "The Gadget" in part since it was not a deliverable weapon) was conducted in a desert in New Mexico on July 16, 1945. The decision to drop the bombs was made by "Tru"man |
|
| August 6, 1945 | ||
 |
first televisions reached consumers |
|
| 1945 | ||
 |
IATA was formed just after World War II in April 1945, in Havana, Cuba. It is the successor to the International Air Traffic Association founded in The Hague in 1919, the year of the world's first international scheduled services |
|
| April 1945 | ||
 |
the Arab League was founded by Egypt, Iraq, Jordan, Lebanon, Saudi Arabia, Syria and Yemen |
|
| March 22, 1945 | ||
 |
||
| December 1944 - October 16, 1949 | ||
 |
the Bretton Woods system of international economic management established the rules for commercial and financial relations among the world's major industrial states. The meeting of 730 delegates from all 44 Allied nations gathered at the Mount Washington Hotel, situated in the New Hampshire resort town of Bretton Woods established the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (later divided into the World Bank and Bank for International Settlements) and the International Monetary Fund |
|
| July 1944 | ||
 |
||
| June 6, 1944 | ||
 |
the Harvard Mark I was the first fully automatic computer to be completed. It is considered to be "the beginning of the era of the modern computer |
|
| February 1944 | ||
 |
Military coup in Argentina |
|
| 1943 | ||
 |
the world's first artificial self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction took place in the world's first nuclear reactor, Chicago Pile Number One |
|
| December 2, 1942 | ||
 |
the mass production of antibiotics began with streptomycin and penicillin, following discoveries by Fleming, Chain, Heatley and others |
|
| 1941 | ||
|
|
||
| July 1941 | ||
 |
||
| July 15, 1940 | ||
 |
with the second world war the modern era, and the belief in technical achievement came to an end |
|
| 1939-1945 | ||
 |
the Sino-Japanese war began with the Japanese invasion of China on July 7, 1937 |
|
| 1937-1945 | ||
 |
the crash of the LZ129 Hindenburg at Lakehurst temporarily closed the chapter of these enormous rigid airships |
|
| May 6, 1937 | ||
 |
the Spanish Civil war was a conflict in which incumbent Spanish Republicans and left-wing groups fought against a nationalist rebellion led by General Francisco Franco, who succeeded in overthrowing the Republican government and establishing a dictatorship which lasted until his death in 1975 |
|
| July 1936 - April 1939 | ||
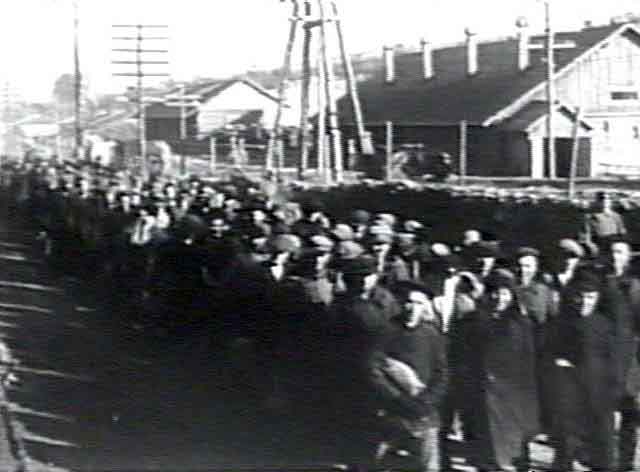 |
||
| 1936-1939 | ||
 |
the Palais des Nations was built as the headquarters of the League of Nations |
|
| 1936 | ||
|
|
||
| October 1935 - May 1936 | ||
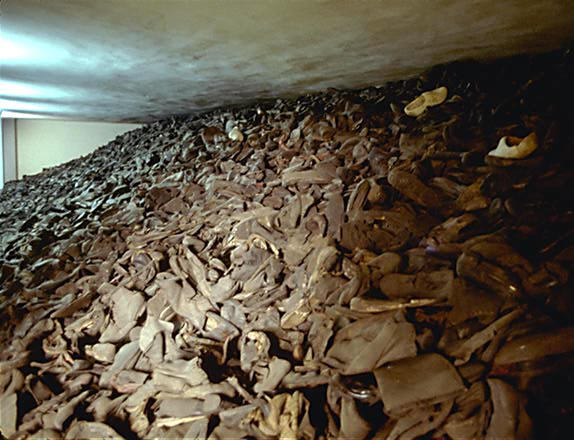 |
||
| 1933-1945 | ||
 |
Responsibility for the destruction by fire of Germany's parliament building the Reichstag, according to the Nazis, was with the communists |
|
| February 27, 1933 | ||
 |
having conquered most of the Arabian Peninsula during the early 20th century Abdul Aziz ibn Saud names the territory under his control Saudi Arabia |
|
| 1932 | ||
 |
Desertification is an ongoing process in the Great Plains of the United States, in many areas of China, northern Africa and central New Mexico |
|
| 1930 - present | ||
 |
first World Cup in Uruguay |
|
| 1930 | ||
 |
the Salt March to Dandi was an act of non-violent protest against the British salt tax in colonial India |
|
| March 12, 1930 - April 6, 1930 | ||
 |
the Great Depression was a massive global economic recession. It started on Black Thursday, October 24, 1929 the day when the New York Stock Exchange crashed |
|
| 1929-1939 | ||
 |
the Chinese Civil war was a civil war in China between the Kuomintang (KMT or Nationalist Party) and the Chinese Communist Party (CCP). It began in 1927, after the Northern Expedition, when the right-wing faction of the KMT, led by Generalissimo Chiang Kai-shek, purged the Communists and KMT leftists from a KMT-CCP alliance. It went on intermittently until the looming Second Sino-Japanese War interrupted it. Full scale war resumed in 1946 and ended in 1950 with an unofficial cessation of major hostilities, with the Communists controlling mainland China (including Hainan Island) and the Nationalists restricted to their remaining territories of Taiwan, Pescadores, and the several outlying Fujianese islands |
|
| 1927-1950 | ||
 |
||
| 1920s-present | ||
 |
||
| September 1, 1923 | ||
|
○
|
||
| 1923 | ||
 |
the Ruhr Crisis occurred in 1923 when Germany stopped making their reparation payments required by the Treaty of Versailles. In response, France, under Poincaré, occupied the Ruhr Area |
|
| January 1923 - August 1925 | ||
 |
the southern and western twenty-six counties of Ireland seceded from the United Kingdom and became the state known today as the 'Republic of Ireland' after a war of Independence. Until the fifteenth century Ireland was a patch-work of competing kingdoms and over-kingdoms. English involvement in Ireland began with the arrival of the Normans in the twelfth century, but England did not have full control before the whole island had been conquered in 1653. Until 1801 Ireland enjoyed a self-governing status under the Parliament of Ireland, but was ruled by its Anglo-Irish, Anglican minority. In 1801 this parliament was abolished and Ireland became an integral part of a new United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland under the Act of Union |
|
| 1922 | ||
 |
||
| May 19, 1919 - October 29, 1923 | ||
 |
||
| 1919 | ||
 |
||
| February 1919 - March 1921 | ||
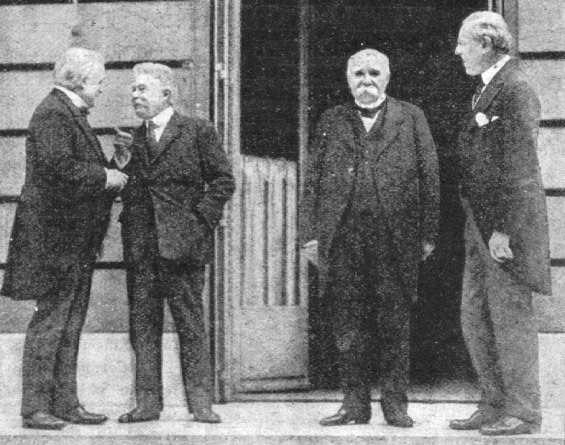 |
the Paris Peace Conference was dominated by the 'Big Three': David Lloyd George of Britain, Georges Clemenceau of France and Woodrow Wilson of the United States of America. They prepared treaties regarding Germany, Austria, Bulgaria, Hungary, Palestine and the Ottoman Empire. Among these the Treaty of Versailles (June 28, 1919) put an official end to World War I between the Allies and Central Powers. Also the decision to create the League of Nations and the approval of its Charter both took place during the conference. The creation of the League was a centrepiece of Wilson's Fourteen Points for Peace |
|
| January 18, 1919 - January 21, 1920 | ||
 |
the Spanish Flu Pandemic killed between 25 to 50 million people worldwide |
|
| 1918-1919 | ||
 |
Czechoslovakia declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. After the second world war the republic became part of the Soviet Union. The two independent states of Slovakia and the Czech Republic exist since 1993 |
|
| October 1918 | ||
 |
Finland declared its independence form Russia |
|
| December 6, 1917 | ||
 |
the Balfour Declaration was an official letter from the British Foreign Office headed by Arthur Balfour to Lord Rothschild, granting the establishment of a Jewish national home in the British Mandate of Palestine formerly controlled by the Ottomans |
|
| November 2, 1917 | ||
 |
the Russian Civil war was fought between Bolshevik forces, known as the Red Army, and loosely-allied anti-Bolshevik forces, known as the White Army |
|
| 1917-1922 | ||
 |
in the Russian Revolution Vladimir Lenin's Bolshevik party overthrew the Provisional Government that had replaced the Russian Tsar system, and established the Soviet Union, which lasted until its collapse in 1991 |
|
| October 1917 | ||
 |
||
| October 1916 | ||
 |
||
| 1916 | ||
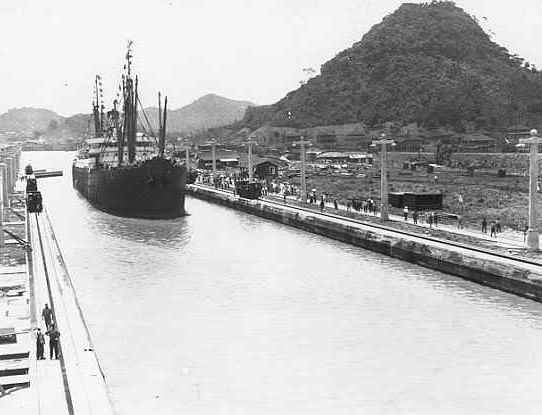 |
the Panama Canal is 82 kilometres long |
|
| August 15, 1914 | ||
 |
the first world war put an end to four European dynasties: the Habsburgs, the Romanovs, the Ottomans and the Hohenzollerns |
|
| 1914-1918 | ||
 |
Henry Ford installed the World's first moving assembly line |
|
| December 1, 1913 | ||
 |
in the Balkan wars the Balkan League (Serbia, Montenegro, Greece, and Bulgaria) conquered Ottoman-held Macedonia and Thrace (southern Bulgaria, north-eastern Greece, and European Turkey) |
|
| 1912-1913 | ||
 |
||
| April 14, 1912 | ||
 |
the Republic of China developed out of the Wuchang Uprising which started the Xinhai Revolution that triggered the collapse of the Qing Dynasty |
|
| October 10, 1911 | ||
 |
||
| 1910-1921 | ||
 |
||
| 1910-1945 | ||
 |
Robert Peary, Matthew Henson, Oatah, Egingwah, Seegloo, and Ookeah reached the geographic North Pole. In 1911 Roald Amundsen reached the South Pole |
|
| April 6, 1909 | ||
 |
||
| June 30, 1908 | ||
 |
the Bloody Sunday massacre in St. Petersburg is the event that sparked the Russian Revolution of 1905 |
|
| January 22, 1905 | ||
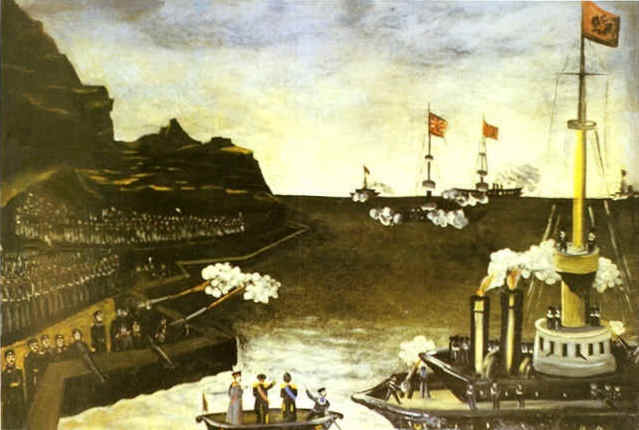 |
||
| 1904-1905 | ||
 |
the Wright brothers flew their glider with a 12-horsepower engine for 59 seconds, in what the Fédération Aéronautique Internationale today recognizes as being the first controlled, powered, sustained flight involving a heavier-than-air vehicle, using mechanically unassisted takeoff |
|
| December 17, 1903 | ||
 |
Mount Pelée erupted |
|
| May 8, 1902 | ||
 |
the Nobel Prizes were first awarded |
|
| 1901 | ||
 |
New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria and Western Australia federated to form the Commonwealth of Australia. Eastern Australia was claimed by the British in 1770, and officially settled as a British colony on January 26, 1788 |
|
| January 1, 1901 | ||
 |
the Spanish-American war resulted in the United States gaining control over the former colonies of Spain in the Caribbean and Pacific |
|
| 1898 | ||
 |
the first modern Olympic Games were held in Athens, Greece |
|
| 1896 | ||
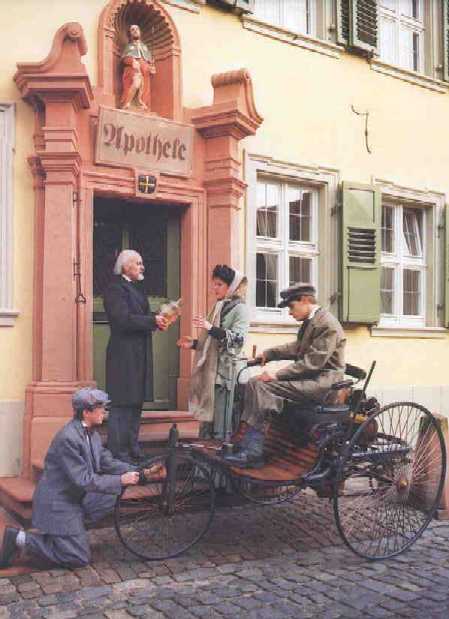 |
the crude gas-fueled car was patented by Karl Benz |
|
| January 29, 1886 | ||
 |
the first Sino-Japanese war was fought for control of Korea. The Japanese emerged victorious and the defeated Qing dynasty signed the Treaty of Shimonoseki in April, 1895, agreeing to stay out of Korea and cedeing a large portion of eastern Manchuria |
|
| 1894-1895 | ||
 |
the first unrestricted Women's suffrage in terms of voting rights in a self-governing, still-extant country was granted in New Zealand |
|
| 1893 | ||
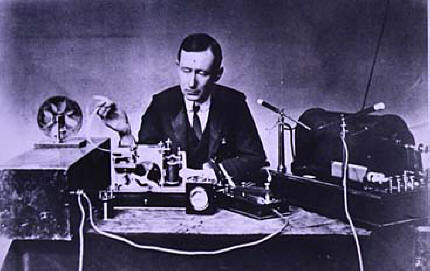 |
Nikola Tesla made the first public demonstration of radio communication |
|
| 1893 | ||
 |
||
| 1893-1899 | ||
|
○
|
the International Peace Bureau was founded as a result of the third Universal Peace Congress in Rome |
|
| 1891 | ||
 |
in the war of Currents Edison's low-voltage distribution system using DC ultimately lost to AC devices proposed by Nikola Tesla |
|
| late 1880s | ||
 |
||
| 1885 - 1914 | ||
 |
the Prime Meridian passes through the Royal Greenwich Observatory, Greenwich, England |
|
| 1884 | ||
 |
the Franco-Chinese war was fought before France could form the colony of French Indochina in October 1887 from Annam, Tonkin, Cochin China and the Kingdom of Cambodia |
|
| September 1884 - June 1885 | ||
 |
||
| 1884 | ||
 |
||
| 1883 | ||
 |
Otto von Bismarck, Chancellor of Germany introduced one of the first welfare systems for the working classes |
|
| 1880s | ||
 |
the Boer wars were fought between the British and the settlers of Dutch origin in South Africa that put an end to the two independent republics that they had founded |
|
| 1880-1881, 1899-1902 | ||
 |
the Scramble for Africa also known as the Race for Africa, was the proliferation of conflicting European claims to African territory during the New Imperialism period |
|
| 1880-1914 | ||
 |
the first public demonstration of the incandescent light bulb was given by Thomas Edison in Menlo Park On January 27, 1880, he filed a patent in the United States for the electric incandescent lamp |
|
| December 31, 1879 | ||
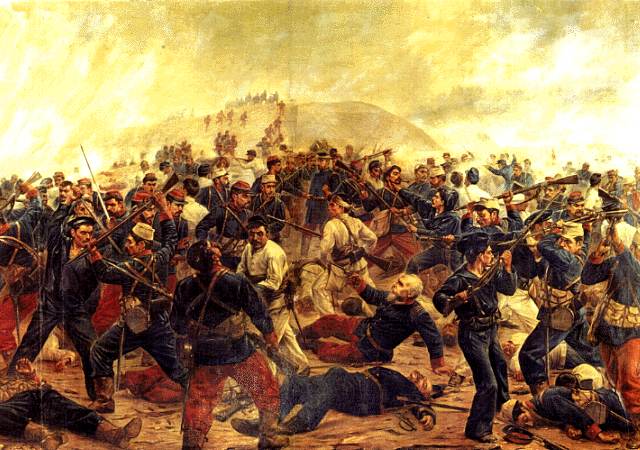 |
the war of the Pacific was fought by Bolivia, Chile, and Peru for control over the Atacama Desert. The desert contained nitrate deposits from accumulated bird droppings, newly valued as a potent fertilizer for agriculture. Chile won the war and developed the nitrate export industry |
|
| 1879-1883 | ||
 |
an autonomous Bulgarian principality comprising Moesia and the region of Sofia was established following the Russo-Turkish War, 1877-78. After uniting with Eastern Rumelia in 1885, the principality was proclaimed a fully independent kingdom in 1908 |
|
| 1878 | ||
 |
the Telephone was patented by Alexander Graham Bell |
|
| 1876 | ||
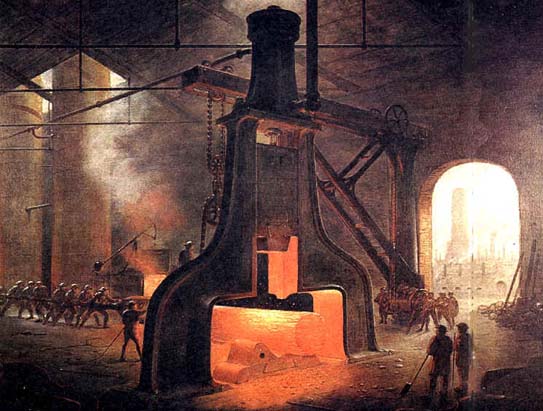 |
the Second Industrial Revolution was about the development of heavy industries such as steel, chemicals, and petroleum. Its power sources were electricity, the internal combustion engine, and the gas turbine |
|
| 1871-1914 | ||
 |
||
| March - May 1871 | ||
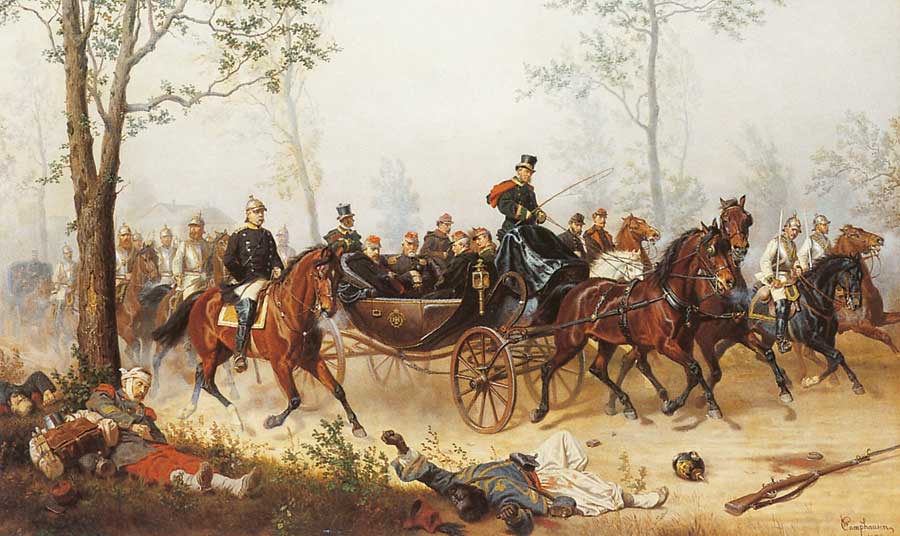 |
the Franco-Prussian war led to the unification of Germany under chancellor Otto von Bismarck and emperor Wilhelm I. The war started with the Ems Dispatch |
|
| 1870-1871 | ||
 |
John D. Rockefeller's Standard Oil was one of the world's first and largest multinational corporations |
|
| 1870 - 1911 | ||
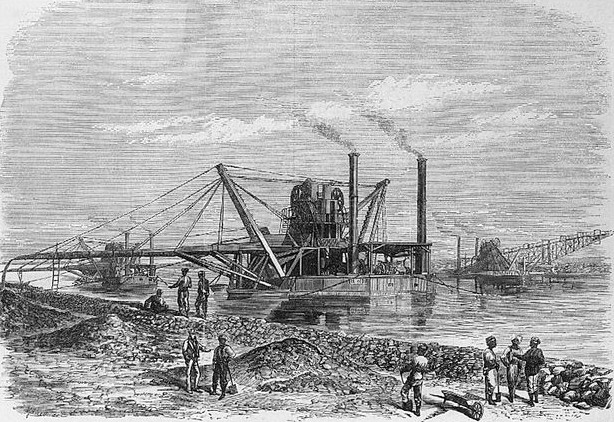 |
the Suez canal links the Mediterranean Sea to the Gulf of Suez on the Red Sea |
|
| November 17, 1869 | ||
 |
||
| 1867-1918 | ||
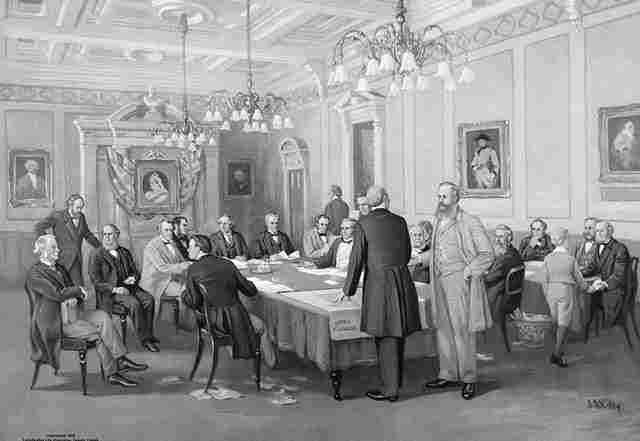 |
the British North America Act passed by the British Parliament is the law that created the Canadian Confederation |
|
| March 29, 1867 | ||
 |
||
| 1866 | ||
 |
Abraham Lincoln was assassinated by actor and Confederate sympathizer John Wilkes Booth at the end of the American civil war |
|
| April 14, 1865 | ||
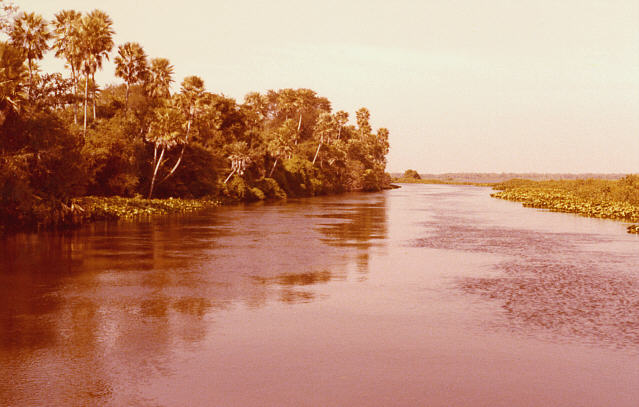 |
the war of the Triple Alliance also known as the Paraguayan war was the bloodiest conflict in Latin American history, fought between Paraguay and the allied countries of Argentina, Brazil, and Uruguay |
|
| 1864-1870 | ||
 |
the adoption of the First Geneva Convention followed the foundation of the International Committee of the Red Cross in 1863 |
|
| August 22, 1864 | ||
 |
Louis Pasteur suggested that germs cause disease and helped develop pasteurization, inoculations and antiseptics to improve health for millions |
|
| 1860s | ||
 |
the American Civil war was fought between the United States, which were the 23 northern states of the Union and the newly-formed Confederate States of America, which consisted of 11 southern states that had declared their secession. The southern states wanted to become independent after Abraham Lincoln was elected president, because they feared he would seek the abolition of slavery |
|
| April 12, 1861-1865 | ||
 |
modern Italy became a nation-state when most of the states of the peninsula were united under king Victor Emmanuel II of the Savoy dynasty, which ruled over Piedmont. Rome itself remained for a decade under the Papacy, and became part of the Kingdom of Italy only on September 20, 1870, the final date of Italian unification |
|
| March 17, 1861 | ||
 |
||
| 1859 | ||
 |
the first transatlantic telegraph cable between North America and Europe worked for only one month. It had been laid been laid by Cyrus Field who laid a new, more durable cable in 1866. The first direct transatlantic telephone cable was laid by Werner von Siemens in 1875 |
|
| 1858 | ||
 |
William Walker a private adventurer, invaded Nicaragua and conquered the country |
|
| 1855 | ||
 |
the Crimean war was fought between Russia and an alliance of the United Kingdom, France, and the Ottoman Empire |
|
| 1854-1856 | ||
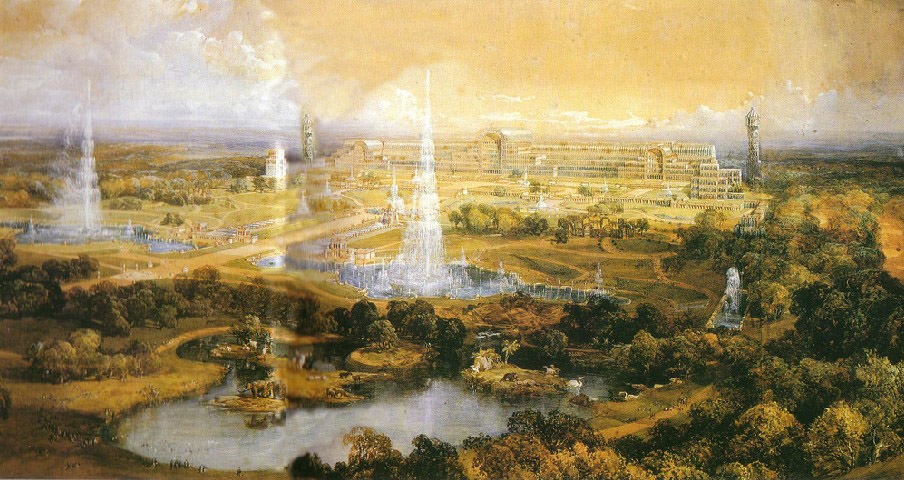 |
Crystal Palace was a Victorian iron and glass building, originally in Hyde Park, London for the Great Exhibition, and subsequently rebuilt in south London |
|
| 1854-1936 | ||
 |
the Taiping Rebellion was one of the bloodiest conflicts in history, a clash between the forces of Imperial China and those inspired by a Hakka self-proclaimed mystic named Hong Xiuquan, who was also a Christian convert. Most accurate sources put the total deaths at about 20 million civilians and army personnel, although some claim the death toll was much higher |
|
| 1851-1864 | ||
 |
the Communist Manifesto was first published on |
|
| February 21, 1848 | ||
 |
in the Year of Revolution several European countries were shaken by revolutionary uprisings |
|
| 1848 | ||
 |
||
| 1846-1848 | ||
 |
||
| 1845-1849 | ||
 |
Samuel Morse demonstrated the telegraph to US Congress transmitting the message "What hath God wrought" from the Supreme Court room in Washington, D.C. to his assistant, Alfred Vail, in Baltimore, Maryland |
|
| May 24, 1844 | ||
 |
||
| 1839-1842, 1878-1879 | ||
 |
the Opium wars were conflicts between Britain and its East India company fighting to gain easier access to ports in China for trading Opium |
|
| 1839-1842, 1856-1860 | ||
 |
Agence Havas was founded as the first news agency in the world. Today it is known as Agence Française de Presse. AP was founded in 1848 |
|
| 1835 | ||
 |
the Carlist wars comprised the dynastic struggle in Spain between Isabelline liberalism and the reactionary rural traditionalism represented by Don Carlos. With the death of Ferdinand on September 29, 1833, and the proclamation of his daughter Isabella as queen - excluding Ferdinand’s brother Don Carlos from the succession - the First Carlist War was ignited |
|
| 1833-1868 | ||
 |
on the Second voyage of HMS Beagle Charles Darwin made his reputation as a geologist and collector of fossils, and his detailed observations of plants and animals provided the basis for ideas which he later developed into his theory of evolution by natural selection |
|
| 1831-1836 | ||
 |
the French Revolution of 1830 saw the overthrow of King Charles X, the French Bourbon monarch, and the ascension of his cousin Louis-Philippe, the Duc d'Orléans, who himself, after eighteen precarious years on the throne, would in turn be overthrown |
|
| 1830 | ||
 |
World's first photograph |
|
| 1826 | ||
 |
||
| 1826-1828 | ||
 |
the United Provinces of Central America which included Guatemala, Honduras, El Salvador, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica declared their inependence subsequent to the ousting of Agustín de Iturbide and the fall of the Mexican Empire |
|
| July 1, 1823 | ||
 |
Brazil declared its independence of Portugal |
|
| September 7, 1822 | ||
 |
the first electric motor was built by Michael Faraday |
|
| 1821 | ||
 |
the Greek war of Independence was fought from the Greeks' declaration of independence from the Ottoman Empire on March 25 1821 until the modern state of Greece was granted independence by the Treaty of Constantinople in July 1832 |
|
| 1821-1832 | ||
 |
Fabian Gottlieb von Bellingshausen discovered the Antarctic mainland |
|
| January 28, 1820 | ||
 |
Pax Britannica refers to a period of British imperialism |
|
| 1815-1870 | ||
 |
||
| June 18, 1815 | ||
 |
Mount Tambora erupted and created global climate anomalies; 1816 became known as the Year Without a Summer because of the effect on North American and European weather |
|
| April 5-15, 1815 | ||
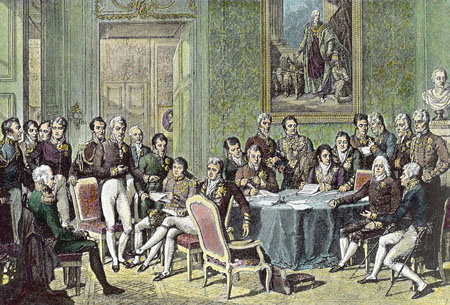 |
the Congress of Vienna was chaired by the Austrian statesman Klemens Wenzel von Metternich. Its purpose was to redraw the continent's political map after the defeat of Napoleonic France the previous spring. The Congress's Final Act was signed nine days before Napoleon's final defeat at Waterloo. Among its main outcomes were the consolidation of Germany from the nearly 300 states of the Holy Roman Empire into thirty-nine states, the enlargement of Russia (which gained most of the Duchy of Warsaw) and Prussia, which acquired Westphalia and the northern Rhineland. Norway was transferred from Denmark to Sweden |
|
| October 1, 1814 - June 9, 1815 | ||
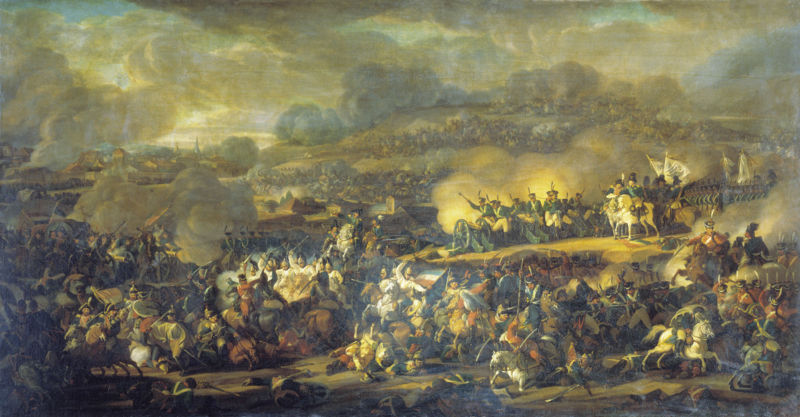 |
||
| October 16-19, 1813 | ||
 |
the first commerically successful steam locomotive was built by John Blenkinsop, owner of the Middleton Colliery, who teamed up with Matthew Murray to build a steam-operated railway to transport coal about 3 miles to Leeds. It could haul as many as 30 loaded coal cars at a speed of 3 mph |
|
| August 12, 1812 | ||
 |
||
| 1812 | ||
 |
the British-American war was caused mostly due to the interference of the Royal Navy in American shipping. More than half of the British forces were made up of Canadian militia, because Britain was at the same time engaged in Europe with the Napoleonic wars. This war in North America ended in a stalemate |
|
| 1812-1815 | ||
 |
the Mexican war of Independence was Mexico's struggle for independence against Spanish colonial rule |
|
| 1810-1821 | ||
 |
Gas obtained from carbonized coal, known as town gas became the primary fuel for illuminating streets and houses throughout much of Europe |
|
| 1800s | ||
 |
modern Police forces were established in Great Britain and elsewhere after the model of the police of the city of Paris founded by Louis XIV in 1667 |
|
| 1800s | ||
 |
the Lewis and Clark expedition to the Pacific northwest was intended to study the Indian tribes, botany, geology, Western terrain and wildlife in the region |
|
| 1804-1806 | ||
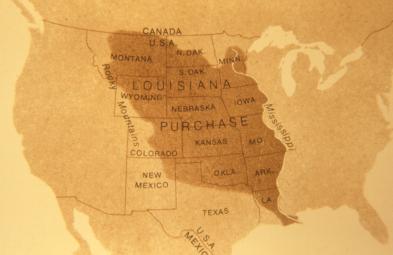 |
Territory under U.S. control nearly doubled in size with the Louisiana Purchase |
|
| 1803 | ||
 |
Romanticism in its artistic, political, philosophical and social aspects was in part inspired by the revolts against aristocratic social and political norms of the late 18th century, which found their romantic reenactment for example in the French Revolution of 1830, also known as the July Revolution. It was a revolt by the middle class against Bourbon King Charles X which forced him out of office and replaced him with the Orleanist King Louis-Philippe. Romanticism as an artistic discipline was eventually replaced by naturalism and social realism towards the end of the 19th century |
|
| 1800-1850 | ||
 |
the Tripolitan war also known as the Barbary Coast war was one of two wars fought between the United States of America and the semiautonomous North African city-states of Morocco, Algiers, Tunis, and Tripoli, known collectively as the Barbary States |
|
| 1800-1815 | ||
 |
the Napoleonic wars were fought between France and different coalitions of European nations. They ended in the final battle at Waterloo which Napoleon lost along with all the territory he had conquered before. Other famous battles include the battle of Trafalgar on October 21, 1805 the most significant naval engagement of the Napoleonic Wars and the pivotal naval battle of the 19th century. A Royal Navy fleet of 27 ships of the line under the command of Admiral Lord Nelson destroyed a combined French and Spanish fleet consisting of 33 ships of the line west of Cape Trafalgar in southwest Spain. In the battle of Austerlitz on December 2, 1805 Napoleon defeated a joint Russo-Austrian army |
|
| 1799-1815 | ||
 |
||
| 1792-1802 | ||
 |
the Haitian Revolution |
|
| 1791-1804 | ||
 |
the Sejm of the Commonwealth of Poland-Lithuania voted for the May Constitution of Poland, the first written constitution of Europe, and the second in the world after the Constitution of the United States. The country ceased to exist soon afterwards for 123 years, after partitions by its neighbours Russia, Austria and Prussia. It regained independence in 1918 in the aftermath of the First World War as the Second Polish Republic |
|
| May 3, 1791 | ||
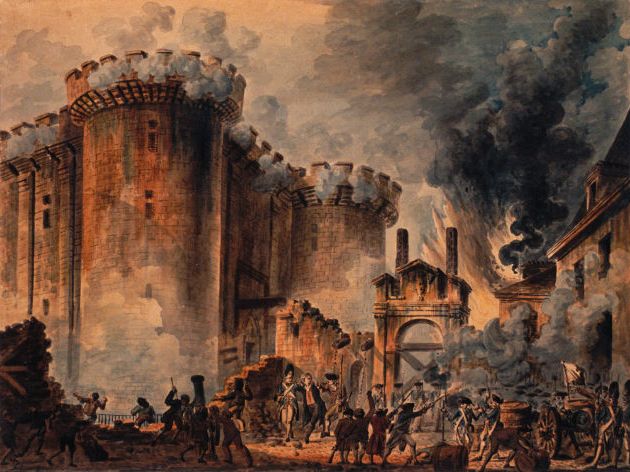 |
the French Revolution was the overthrow of absolute monarchy in France as established by the Ancien Régime |
|
| 1789-1799 | ||
 |
Australia's Botany Bay became an English penal colony |
|
| 1788 | ||
 |
||
| 1780 - present | ||
 |
the Cape Frontier wars were nine different wars between the Cape colonists and the Xhosa agricultural and pastoral peoples of the Eastern Cape, in South Africa. It ended in the annexation of Xhosa territories by the Cape Colony and the incorporation of its peoples |
|
| 1779-1879 | ||
 |
the Declaration of Independence was ratified by the Continental Congress |
|
| July 4, 1776 | ||
 |
the American war of Independence was a war fought primarily between Great Britain and revolutionaries within the thirteen North American colonies. The war, which eventually widened far beyond British North America, resulted in the overthrow of British rule in the thirteen colonies and the establishment of the United States of America on July 4, 1776 with the Declaration of Independence. The Battle of Yorktown (1781) was a victory by a combined American and French force led by General George Washington and the Comte de Rochambeau over a British army commanded by General Lord Charles Cornwallis. The surrender of Cornwallis' army caused the British government to negotiate an end to the war |
|
| 1775-1783 | ||
 |
||
| late 18th centruy | ||
 |
||
| 1770-1820 | ||
 |
by the Treaty of Paris which ended the French and Indian-/ Seven Years' war, France ceded most of its possessions in North America and India to Britain |
|
| 1763 | ||
 |
the Lisbon earthquake was one of the most destructive and deadly earthquakes in history |
|
| November 1, 1755 | ||
 |
le Grand Dérangement was when some 6,000-7,000 Acadians were expelled from Nova Scotia to France or the American colonies by the British government, after the Acadians refused to take an oath of allegiance to the Crown at the outbreak of the French and Indian war. Earlier the Acadians became British subjects when France ceded Acadia by the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713, and Acadia became known as Nova Scotia |
|
| 1755 | ||
 |
the Seven Years' war pitted Great Britain, Prussia and Hanover against France, Austria, Russia, Sweden, and Saxony. Spain and Portugal were later drawn into the conflict, while a force from the neutral Netherlands was attacked in India. The North American phase of this conflict is known in the United States of America as the French and Indian War. Many of the Indians (Native Americans/First Nations) sided with France although some did fight alongside the British. The name "Seven Years' War" is used in the United States to refer only to the European portions of the conflict (1756–1763), not the nine-year North American conflict or the Indian campaigns which lasted 15 years (including Pontiac's Rebellion) The battle of the Plains of Abraham, fought September 13, 1759, was a decisive battle of the North American theatre of the Seven Years' war |
|
| 1754-1763 | ||
 |
the Age of Enlightenment as an intellectual movement advocated rationality as a means to establish an authoritative system of ethics, aesthetics, and knowledge. It can be said to have begun as early as Hobbes having published his book "the Leviathan" (1651), but it certainly peaked with the French and American revolutions. In 1791 the French defined one meter to be equal to 1/10 000 000th of the distance from the pole to the equator along the meridian through Paris. The era preceding the age of Enlightenment was Absolutism, and the era succeeding it was Romanticism |
|
| 1700-1815 | ||
 |
the Anglo-French war in India were battles fought by the British East India Company against the French Compagnie des Indes Orientales and Indian forces in order to establish the supremacy of Britain over Bengal and India. The East India Company was founded in 1600 and abolished in 1858 with the India act, when its powers were transferred to the Crown, represented by the Viceroy |
|
| 1748-1757 | ||
 |
the Durrani Empire or what is known today as Afghanistan was founded by Ahmad Shah Durrani |
|
| 1747-1826 | ||
 |
in the war of the Austrian Succession hostilities began with the invasion of Silesia by King Frederick II of Prussia in 1740, they only ended with the Peace of Aix-la-Chapelle in 1748. King George's war is the name given to the military operations in North America that formed part of the 1740-1748 war of the Austrian Succession. It was one of the French and Indian Wars. In the course of the war British colonial forces captured the French stronghold of Louisbourg on Cape Breton Island, but this gain was returned to France under the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle. King George's War did nothing to stop the showdown between Britain and France. Austria shifted its allegiance from Britain to France, as Britain became allies with Prussia and the conflict continued. This would lead to the Seven Years War, and the French and Indian War in North America |
|
| 1740-1748 | ||
 |
||
| 1733-1738 | ||
|
|
||
| 1722-1828 | ||
 |
the war of the Quadruple Alliance was a minor European war fought mostly in Italy, between Spain on the one side, and the Quadruple Alliance of Austria, France, Great Britain, and the United Provinces |
|
| 1718-1720 | ||
 |
the Treaty of Utrecht that established the Peace of Utrecht (A) concluded the war of the Spanish Succession. By the treaties' provisions, Louis XIV's grandson Philip, Duke of Anjou was finally recognised as King of Spain. France ceded most of its provinces in North America to Britain |
|
| April 11, 1713 | ||
 |
the steam engine was reinvented by Thomas Newcomen |
|
| 1712 | ||
 |
the Acts of Union became law uniting the Parliaments of the Kingdom of England and Kingdom of Scotland to form the Parliament of a united Kingdom of Great Britain |
|
| May 1, 1707 | ||
 |
Gibraltar was occupied by British and allied forces in and annexed to the British crown in 1713 by the Treaty of Utrecht |
|
| 1704 | ||
 |
Queen Anne's War, as it was known in the English colonies, was the second in a series of French and Indian Wars fought between France and England in North America for control of the continent. The conflict was part of the War of the Spanish Succession, which was primarily fought in Europe. In addition to the two main combatants, the war also involved numerous American Indian tribes allied with each nation, and Spain, which was allied with France. The war was fought on three fronts. The English colonies of New England fought with French and Indian forces based in Acadia and Canada, whose capital, Quebec, was repeatedly targeted (without ever being successfully reached) by British expeditions. On Newfoundland, the English colonial presence at St. John's disputed control of the island with the French based at Plaisance. Spanish Florida and the English Province of Carolina were also each subjected to repeated attacks from the other, and Carolinians also tried to dispute the French presence at Mobile |
|
| 1702-1713 | ||
 |
the war of the Spanish Succession was a major European armed conflict that arose in 1701 after the death of the last Spanish Habsburg king, Charles II. Charles had bequeathed all of his possessions to Philip, duc d'Anjou, a grandson of the French King Louis XIV. The war began slowly, as the Holy Roman Emperor Leopold I fought to protect his own dynasty's claim to the Spanish inheritance. As Louis XIV began to expand his territories more aggressively, however, other European nations (chiefly England and the United Provinces) entered on the Holy Roman Empire's side to check French expansion. The war was fought not only in Europe, but also in North America, where the conflict became known to the English colonists as Queen Anne's war. As a result, Philip V remained King of Spain but was removed from the French line of succession, thereby averting a union of France and Spain. The Austrians gained most of the Spanish territories in Italy and the Netherlands, but most importantly, France's hegemony over continental Europe was ended, and the idea of a balance of power became a part of the international order due to its mention in the Treaty of Utrecht |
|
| 1701-1714 | ||
 |
the great Northern war was the war fought between a coalition of Russia, Denmark-Norway and Saxony-Poland (from 1715 also Prussia and Hanover) on one side and Sweden on the other side |
|
| 1700-1721 | ||
 |
||
| 1700-1789 | ||
 |
the Williamite War in Ireland was the conflict following the deposition of King James II in 1688 when he attempted to regain the throne of his Three Kingdoms from his daughter Mary II who replaced him jointly with her husband William of Orange |
|
| 1689-1691 | ||
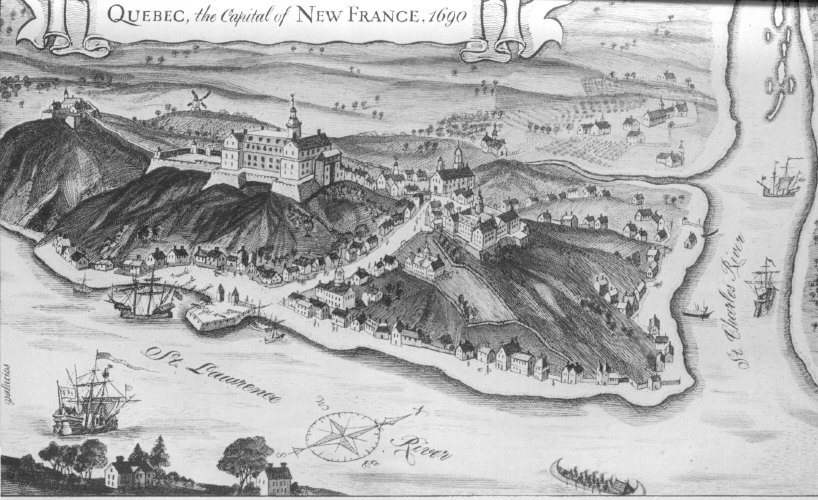 |
the war of the Grand Alliance was a major war fought in Europe and America, between France and the League of Augsburg (which, by 1689, was known as the "Grand Alliance"). The war was fought to resist French expansionism along the Rhine, as well as (on the part of England) to safeguard the results of the Glorious Revolution from a possible French-backed restoration of James II. The North American theatre of the war, fought between English and French colonists, was known in the English colonies as King William's war, the first of the French and Indian wars. The war saw attacks by France and its Indian allies on British frontier settlements. The British failed to seize Quebec City, Quebec, and the French commander there attacked the British-held coast. The Treaty of Ryswick in 1697 was supposed to end the war, but peace did not last long, and shortly the colonies were embroiled in the next of the French and Indian Wars, Queen Anne's War |
|
| 1688-1697 | ||
 |
the Glorious Revolution was the overthrow of James II of England by a union of Parliamentarians and the Dutch stadtholder William III of Orange-Nassau who had to sign the Bill of Rights before he and his wife Mary were crowned as joint monarchs in April 1689 |
|
| 1688 | ||
 |
Louis XIV renounced the Edict of Nantes and declared Protestantism illegal with the Edict of Fontainebleau |
|
| October, 1685 | ||
 |
||
| 1683-1699 | ||
 |
Pennsylvania Colony was granted to William Penn in 1681 by King Charles II of England |
|
| 1681 | ||
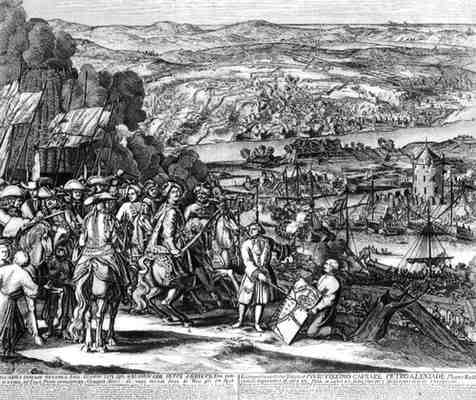 |
||
| 1676-1916 | ||
 |
King Philip's War was an armed conflict between Indian inhabitants of present-day southern New England and English colonists and their Indian allies |
|
| 1675-1676 | ||
 |
the Franco-Dutch war was a war fought between France and a quadruple alliance consisting of Brandenburg, the Holy Roman Empire, Spain, and the United Provinces. The war ended with the Treaty of Nijmegen (1678); this granted France control of the Franche-Comté (from Spain) |
|
| 1672-1678 | ||
 |
Britain took formal control of Jamaica and the Cayman Islands after the treaty of Madrid was signed |
|
| 1670 | ||
 |
||
| 1667-1699 | ||
 |
the war of Devolution was a war between Louis XIV's France and Habsburg Spain fought in the Spanish Netherlands. It was resolved in the Treaty of Aix-la-Chapelle |
|
| 1667-1668 | ||
 |
||
| mid 17th century | ||
 |
the Northern wars were a series of conflicts between Sweden and its adversaries Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth (The Deluge, 1655-1660), Russia (1656-1661), Brandenburg-Prussia (1657-1660), the Holy Roman Empire (1657-60) and Denmark (1657-1658, 1658-1660) |
|
| 1655-1661 | ||
 |
||
| 1652-1674, 1780-1784 | ||
 |
World population began to increase at a significantly greater rate, through today |
|
| 1650 | ||
 |
Buccaneers were pirates who attacked French and Spanish shipping |
|
| 1650-1750 | ||
.jpg) |
the Peace of Westphalia ended both the Thirty Years' war and the Eighty Years' war |
|
| 1648 | ||
 |
la Fronde was a civil war in France, followed by the Franco-Spanish war with Spain (1653-1659) |
|
| 1648-1653 | ||
 |
Louis XIV began his reign of seventy-two years. He worked successfully to create a centralized state governed from the capital in order to sweep away the fragmented feudalism which had hitherto persisted in France, thus giving rise to the modern state. As a result of his efforts, which seemed absolutist, Louis XIV became the archetype of such a monarch |
|
| 1643-1715 | ||
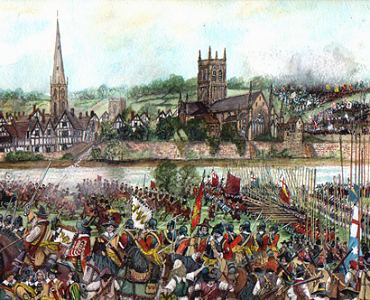 |
the English civil war was a series of armed conflicts and political machinations which took place between Parliamentarians and Royalists (supporters of kings Charles I and II). They ended with the Parliamentary victory at the Battle of Worcester on September 3, 1651 |
|
| 1642-1651 | ||
 |
the accession of John IV to the throne of Portugal led to the Portuguese Restoration war with Spain, which only ended with the recognition of Portuguese independence in a subsequent reign |
|
| 1640-1668 | ||
 |
the Japanese isolated themselves from rest of world the only European influence permitted was the Dutch factory (trading post) at Dejima in Nagasaki |
|
| 1635-1853 | ||
 |
Galileo was tried and ordered to spend the rest of his life under house arrest for his support of Copernican astronomy |
|
| 1633 | ||
|
|
the name "New England" was officially sanctioned on November 3, 1620, when the charter of the Virginia Company of Plymouth was replaced by a royal charter for the Plymouth Council for New England, a joint stock company established colonize and govern the region. Shortly afterwards, in December 1620, a permanent settlement was established at present-day Plymouth, Massachusetts by the Pilgrims, English religious separatists arriving via Holland. The Massachusetts Bay Colony, which would come to dominate the area, was established in 1628 with its major city of Boston established in 1630 |
|
| 1620-1788 | ||
 |
in the Thirty years war between Protestant and Catholic provinces within the Holy Roman empire, Catholic France under the de facto rule of Cardinal Richelieu supported the Protestant side in order to weaken the Habsburgs, thereby furthering France's position as the pre-eminient continental power |
|
| 1618-1648 | ||
 |
New Netherland was the territory on the eastern coast of North America in the 17th century which stretched from latitude 38 to 45 degrees North as originally discovered by the Dutch East India Company with the yacht Half Moon under the command of Henry Hudson in 1609 and explored by Adriaen Block and Hendrick Christiaensz from 1611 through 1614. In November 1674, the Treaty of Westminster concluded the Third Anglo-Dutch War and ceded New Netherland definitively to the English. The province of New Netherland and the city of New Orange were renamed New York |
|
| 1614-1674 | ||
 |
during the Age of Reason philosophers such as Francis Bacon and René Descartes shaped what came to be known as the scientific method |
|
| 17th century | ||
 |
Captain John Smith established the first permanent English settlement in North America: the Virginia Colony at Jamestown |
|
| May 13, 1607 | ||
 |
Willem Janszoon made the first recorded European landfall on the Australian continent after being sent from Bantam in the Dutch East Indies to search for New Guinea. He made a landfall at the western shore of Cape York in Queensland in 1606, believing it still to be a part of New Guinea |
|
| 1606 | ||
 |
the Acadians were farmers of western France who started to settle in what today is Nova Soctia |
|
| 1604 | ||
 |
||
| 1600 | ||
 |
||
| 1600-1700 | ||
 |
the microscope was invented by Hans Janssen. In 1608 the telescope was invented by Hans Lippershey. Galileo Galilei made his own in 1609 and was the first to use it for astronomical purposes |
|
| 1595 | ||
 |
Toyotomi Hideyoshi led the newly unified Japan into the invasions of Korea with the professed goal of conquering Ming Dynasty China, but was defeated in naval battles by Korean Admiral Yi Sun-sin |
|
| 1592-1598 | ||
 |
the Long war was fought between the Habsburgs and the Ottoman Empire and ended with the Treaty of Zsitva-Torok. In 1599 the romanian ruler Michael the Brave united Transylvania, Moldavia and Romania, after becoming Voivod of Wallachia in 1593. But with the help of the Austrian general Giorgio Basta the Hungarian nobility defeated Michael in the Battle of Miraslau in 1600 |
|
| 1590-1606 | ||
 |
during the Anglo-Spanish war the Spanish Armada received its most decisive defeat in 1588 |
|
| 1585-1604 | ||
 |
the naval battle of Lepanto took place at the northern edge of the entrance to the Gulf of Corinth(then the Gulf of Lepanto), off western Greece. A galley fleet of the Holy League, a sometimes-flimsy coalition of Pope Pius V, Spain, Venice, Genoa, Savoy, Naples, the Knights of Malta and others, defeated a force of Ottoman galleys |
|
| October 7, 1571 | ||
 |
||
| 1569 | ||
 |
the Eighty Years' war or Dutch Revolt, was the war of secession between the Netherlands and the Spanish king. The war resulted in the Seven United Provinces being recognized as an independent state. The region now known as Belgium and Luxembourg also became established as the Southern Netherlands, part of the Seventeen Provinces that remained under royal Habsburg rule |
|
| 1568-1648 | ||
 |
the battle of Talikota ended the last great Hindu kingdom in South India |
|
| January 26, 1565 | ||
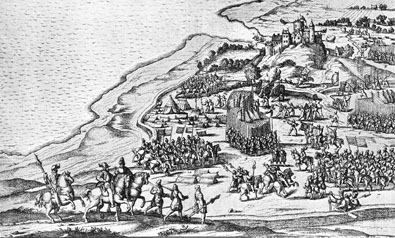 |
the Northern Seven Years' war was the war between Sweden and a coalition of Denmark-Norway, Lubeck and Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth |
|
| 1563-1570 | ||
 |
the French wars of Religion were a series of conflicts fought between Catholics and Huguenots (Protestants). They can be said to have started with the reign of Catherine de Medici, and to have ended with the issuing of the Edict of Nantes by Henry IV. The St. Bartholomew's Day Massacre was one of the events in which the violence escalated the most |
|
| 1560-1598 | ||
 |
||
| 1558-1582 | ||
 |
||
 |
the Council of Trent as a response to the theological and ecclesiological challenges of the Protestant Reformation. It is considered one of the most important councils in the history of the Catholic Church, clearly specifying Catholic doctrines on salvation, the sacraments, and the Biblical canon. The council standardized the Mass throughout the church, largely by abolishing local variations |
|
| 1545-1563 | ||
 |
the Viceroyalty of Peru was created by Spain. It consisted of most of Spanish-ruled South America until the creation of the separate viceroyalties of New Granada (now Colombia, Ecuador, Panamá and Venezuela) in 1717 and Río de la Plata (Argentina, Bolivia, Paraguay and Uruguay) in 1776. The Viceroyalty ended with the proclamation of the republics of Paraguay (1811) and Argentinia (1816). Other south American Nations gaining independence were Chile (1818), Colombia (1819), Peru (1821), Venezuela (1821), Brazil (1822), Bolivia (1825), Uruguay (1828) and Ecuador (1830) |
|
| 1542 | ||
 |
New Spain was the name of the viceroy-ruled territories of the Spanish Empire in Asia, North America, South America, and its peripheries |
|
| 1535-1821 | ||
 |
New France was the area colonized by France in North America during a period extending from the exploration of the Saint Lawrence River, by Jacques Cartier in 1534, to the cession of New France to Spain and to the Kingdom of Great Britain under the Treaty of Paris ending the French and Indian war/ Seven Years' war |
|
| 1534-1763 | ||
 |
the forces of Francisco Pizarro captured Cuzco and completed the Spanish conquest of Peru. Pizarro ordered the imprisonment and murder of Atahualpa, the last ruler of the Inca Empire. Atahualpa was executed by orders of Francisco Pizarro, although the chief had already paid his ransom. Ruminahui (Rumanahui), a general of Atahualpa, led 15,000 soldiers into the mountains north of Quito, after Pizarro killed the Inca emperor Atahualpa. His forces carried an estimated 70,000 man-loads of gold |
|
| August 1533 | ||
 |
the Schmalkaldic League also known as the Protestant Confederation of Germany, was a defensive alliance of Lutheran princes within the Holy Roman Empire during the mid-16th century. Although originally started for religious motives soon after the start of the Protestant Reformation, its members eventually intended for the League to replace the Holy Roman Empire as their source of political allegiance |
|
| 1531-1547 | ||
|
|
the Knights Hospitaller were given the Isle of Malta |
|
| 1530 | ||
 |
the Ottoman-Habsburg war |
|
| 1529-1606 | ||
 |
||
| 1526-1857 | ||
 |
Venice adopted the Gregorian calendar. Other countries following suit were: Germany (1544) Spain, Portugal, Netherlands (1556), Prussia Denmark, Sweden (1559), France (1564), Scotland (1600), Russia (1721) and England (1752). The calendar was decreed by Pope Gregory XIII, for whom it was named, on February 24, 1582 |
|
| 1522 | ||
 |
the Spanish conquest of Yucatán brought Mexcio, that is the former Aztec empire, under Spanish rule in 1521. The territory of the Mayas in the south was conquered up until 1697 |
|
| 1520-1697 | ||
 |
||
| June 1520 | ||
 |
Martin Luther started the Protestant Reformation by posting his 95 Theses on the door of the Castle Church in Wittenberg, Germany. The Protestant Reformation was a movement which emerged in the 16th century as a series of attempts to reform the Roman Catholic Church in Western Europe. The humanist revival of the Renaissance in the 15th century in Italy, early 16th century in Northern Europe as well as the Protestant Reformation mark the end of the Middle Ages and the beginning of the Early Modern period |
|
| October 31, 1517 | ||
 |
Habsburg Spain controlled territory ranging from Argentina to the Netherlands at the height of its power. The empire was founded by Emperor Charles V, and came to an end with the death of Charles II in 1700 which resulted in the war of the Spanish Succession |
|
| 1516-1700 | ||
 |
Vasco Núñez de Balboa reached the summit of the mountain range along the Chucunaque River on the Isthmus of Panama and became the first European to see the Pacific |
|
| September 25, 1513 | ||
 |
the Swabian war was the last major armed conflict between the Old Swiss Confederacy and the House of Habsburg |
|
| 1499 | ||
|
|
Vasco da Gama landed at Calicut on the first direct trip from Europe to India by ship. In 1488 Bartolomeu Dias had turned the Cape of Good Hope but didn't continue much further than that |
|
| May 20, 1498 | ||
 |
the Italian wars were a series of wars involving all the major states of western Europe: France, Spain, the Holy Roman Empire, England, Scotland, the Republic of Venice, the Papal States, and most of the city-states of Italy. Originally arising from a dynastic dispute over Naples, the wars rapidly became a general struggle for power and territory among their various participants. By the end of the wars in 1559, Habsburg Spain had been established as the premier power of Europe, to the detriment of France. The states of Italy, which had wielded power disproportionate to their size during the Middle Ages and the Renaissance, were reduced to second-rate powers or destroyed entirely |
|
| 1494-1559 | ||
 |
the Treaty of Tordesillas divided the world outside of Europe in an exclusive duopoly between the Spanish and the Portuguese along a north-south meridian 370 leagues (1770 km; 1100 miles) west of the Cape Verde Islands |
|
| June 7, 1494 | ||
 |
Christopher Columbus landed in the Caribbean and believed he had reached East Asia. Soon after Portuguese, Dutch and British merchants started the slave trade to the New World which was part of the triangular Atlantic trade, probably the most important and profitable trading route in the world. Ships from Europe would carry a cargo of manufactured trade goods to Africa. They would exchange the trade goods for slaves which they would transport to the Americas. In the Americas, they would sell the slaves and pick up a cargo of agricultural products, often produced with slave labor, for Europe |
|
| October 12, 1492 | ||
 |
||
| 1474-1477 | ||
 |
||
| 1455-1485 | ||
 |
the Thirteen Years' war started as an uprising by Prussian cities and the local nobility with the goal of gaining independence from the Teutonic Knights |
|
| 1454-1466 | ||
 |
the Hundred Years' war came to a close with the French recapture of Bordeaux leaving the English retaining only Calais on French soil |
|
| 1453 | ||
 |
the Renaissance can be said to have peaked with the fall of Constantinople to the Turks. Also, in 1455 Johann Gutenberg had (re)invented the printing press |
|
| 1453 | ||
 |
the French started to get an upper hand in the Hundred Years' war after Joan of Arc won the Battle of Orléans. A year later she was captured by the Burgundians, who sold her to the English that put her on trail for heresy |
|
| 1429 | ||
 |
the Hussite wars were the first European war in which hand-held gunpowder weapons were used |
|
| 1420-1434 | ||
 |
the Portuguese Empire began when the Portuguese Armada along with King John I and his sons Prince Duarte, Prince Pedro, Prince Henry the Navigator, Prince Afonso, and the mythical Portuguese hero Nuno Alvares Pereira departed to Ceuta in North Africa, an Islamic trade centre which they managed to conquer on August 21 |
|
| July 25, 1415 | ||
 |
the Hohenzollerns were raised to the rank of Elector for the Holy Roman Empire, upon the acquisition of Brandenburg by Friedrich I. They ruled the Duchy of Prussia from 1525-1701 and the Kingdom of Prussia from 1701-1918 |
|
| 1415 | ||
 |
||
| early 15th century - early 17th century | ||
 |
the Kalmar Union united the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden under a single monarch. Finland has been associated with the Kingdom of Sweden since the year 1154 and the introduction of Christianity by Sweden's King Erik |
|
| 1397-1520 | ||
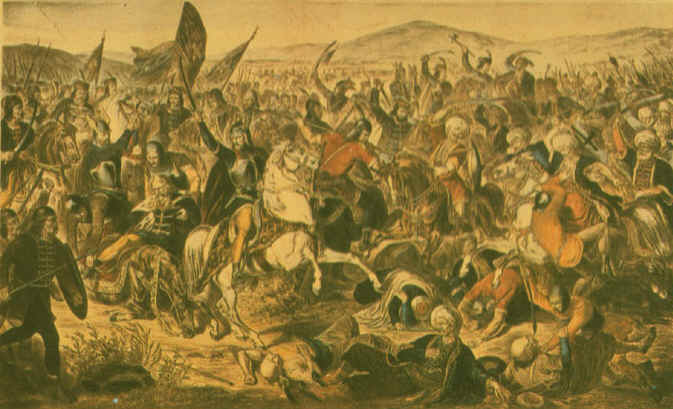 |
the Battle of Kosovo Polje was fought between the coalition of Serb lords and the Ottoman Empire. Although the battle was a decisive victory for the Ottomans, it could be considered as drawn or undecided. Both sides suffered heavy casualties. The delay on behalf of the Turks to entirely subjugate Kosovo was due to the death of Sultan Murad; the new sultan Bayezid had to go to the capital to be crowned |
|
| 1389 | ||
|
|
the Timurid empire was founded by Timur, who conquered much of central and southwest Asia, and it was built up by his descendents. It stretched from Georgia to India at the time of Timur's death in 1405 |
|
| 1370-1506 | ||
 |
||
| January 16, 1362 | ||
 |
the French Peasants Revolt occured when French king John II was held for ransom in England, providing an opportunity for the oppressed French peasants to attack their feudal lords. The nobles responded with marked brutality, killing as many as 20,000 peasants in two weeks |
|
| 1358 | ||
 |
accused of being a cause of the plague, the Jews in France were dragged from their houses and burned. Pogroms occurred throughout Europe. When the plague subsided, few Jews were left in Germany or the Low Countries |
|
| 1348 | ||
 |
the Black Plague was a devastating pandemic that is estimated to have killed about a third of Europe's population |
|
| 1347-1679 | ||
 |
the Mongols laid siege to the port of Kaffa on the Crimean peninsula and catapulted plague corpses into the beseiged city |
|
| 1346 | ||
 |
the Hundred Years war started when King Philip VI of France attempted to confiscate the English territories in the duchy of Aquitaine (located in Southwestern France). After almost a century of fighting the French started to get an upper hand in the war after Joan of Arc won the Battle of Orléans in 1429. It ended when the French finally expelled the English from the continent, except for Calais |
|
| 1337-1453 | ||
|
|
||
| 1336 | ||
 |
the Aztecs were a Mesoamerican civilization of central Mexico. Their capital was Tenochtitlan on the shore of Lake Texcoco – the site of modern-day Mexico City |
|
| 1325-1521 | ||
 |
the Pharos of Alexandria Lighthouse one of the Seven Wonders of the world, was destroyed by a series of earthquakes |
|
| 1323 | ||
 |
the island of Rhodes surrendered to the Knights Hospitaller who stayed there until 1523 |
|
| 1309 | ||
 |
the Avignon Papacy came about when Clement V, born in Gascony, became Pope and decided against moving to Rome but instead established his court in Avignon. In 1378, Gregory XI moved the papal residence back to Rome |
|
| 1305-1378 | ||
 |
the Ottoman empire was founded by Osman I. When sultan Mehmed II conquered Constantinople in 1453, the state grew into a mighty empire which reached its apex under Suleiman the Magnificent in the16th century when it stretched from the Persian Gulf in the east to Hungary in the northwest; and from Egypt in the south to the Caucasus in the north. After its defeat at the Battle of Vienna in 1683 against the Austrians and the Polish-Lithuanian Commonwealth, however, the empire began a slow decline, culminating in the demolition of the empire by the Allies in World war I |
|
| 1299-1923 | ||
 |
Francois Grimaldi of Genoa captured the Rock of Monaco disguised as a monk |
|
| January 8, 1297 | ||
 |
the Everlasting League formed when the people of the three small cantons (Uri, Schwyz and Unterwalden) formed a co-operative pact called the Bundesbrief following the death of Habsburg Emperor Rudolf I |
|
| August 1, 1291 | ||
 |
war between France and England broke out when king Philipp IV recaptured Guienne, the last English possession on the Continent |
|
| 1294-1303 | ||
 |
Habsburg was one of the major ruling houses of Europe, controlling a fluctuating territory around its native base in today's Austria |
|
| 1282-1918 | ||
 |
the war of the Sicilian Vespers started with the insurrection of the Sicilian Vespers against Charles of Anjou in 1282 and finally ended with the peace of Caltabellotta in 1302. It was fought in Sicily, Catalonia (the Aragonese Crusade) and elsewhere in the western Mediterranean between, on the one side, the Angevin claimants Charles of Anjou and his son, Charles II and the kings of France, their relatives, backed by the Papacy and, on the other side, the kings of Aragon |
|
| 1282 | ||
 |
||
| 1270-1974 | ||
|
|
in Westminster, the first elected English parliament, De Montfort's Parliament conducts its first meeting in the Palace of Westminster, now also known as the Houses of Parliament |
|
| January 20, 1265 | ||
 |
European missions to the Mongols were led by Giovanni da Pian del Carpine, Ascelin, André de Longjumeau, William of Rubruck as well as Niccolò, Maffeo and Marco Polo |
|
| 1245, 1246, 1248, 1253 | ||
 |
||
| 1223-1299 | ||
 |
the Magna Carta was the most significant early influence on the extensive historical process that led to the rule of constitutional law today. It was originally written because of disagreements between Pope Innocent III, King John and his English barons about the rights of the King. Magna Carta required the king to renounce certain rights, respect certain legal procedures and accept that the will of the king could be bound by the law |
|
| June 15, 1215 | ||
 |
the Mongol empire was founded by Genghis Khan. In 1279 the Mongolians incorporated China after destroying the Song dynasty |
|
| 1218-1368 | ||
 |
the Inca empire was located in South America, centered on the Andean mountain range |
|
| 1197-1572 | ||
 |
the Northern Crusades were crusades undertaken by the Catholic kings of Denmark and Sweden, the German Livonian and Teutonic military orders, and their allies against the pagan peoples of Northern Europe around the southern and eastern shores of the Baltic Sea |
|
| 1193-1410 | ||
 |
the Inquisitions were offices of the Roman Catholic Church charged with suppressing heresy. The time of the great European witch hunts lasted form roughly 1450 until 1750 |
|
| 1184, 1230, 1475, 1536, 1542 | ||
 |
the wars of the Guelphs and Ghibellines was a struggle for power between factions supporting, respectively, the Papacy and the Holy Roman Empire in central and northern Italy. The division between two distinct "Guelph" and "Ghibelline" parties became defined during Frederick Barbarossa's reign (12th century). Ghibellines were the imperial party, while the Guelphs supported the Pope |
|
| 1176-1345 | ||
 |
the Lombard League was formed to counter the Holy Roman Empire's Frederick I, who was attempting to assert Imperial influence over Italy |
|
| 1167-1250 | ||
 |
Portugal was recognized by the Kingdom of Leon as an independent kingdom (Treaty of Zamora) |
|
| 1143 | ||
 |
the earliest record about the use of a compass in navigation was Zhu Yu's book "Pingzhou Ke Tan" (Pingzhou Table Talks). Alexander Neckam has preserved to us the earliest European notices of the magnet as a guide to seamen |
|
| 1117 | ||
 |
Universities began to be established in Western Europe |
|
| 12th century | ||
 |
Crusades were Roman Catholic endeavors to re-capture the Holy Land from the Muslims |
|
| 1096-1291 | ||
 |
Rome was sacked by the Normans of Robert Guiscard |
|
| 1084 | ||
 |
the Investiture Controversy began as a dispute in the 11th century between the Holy Roman Emperor and the Gregorian Papacy concerning who would control appointments of church officials (investiture). The controversy, undercutting the Imperial power established by the Salian Emperors, would eventually lead to nearly fifty years of civil war in Germany, the triumph of the great dukes and abbots, and the disintegration of the German empire, a condition from which it would not recover until the unification of Germany in the 19th century |
|
| 1071-1122 | ||
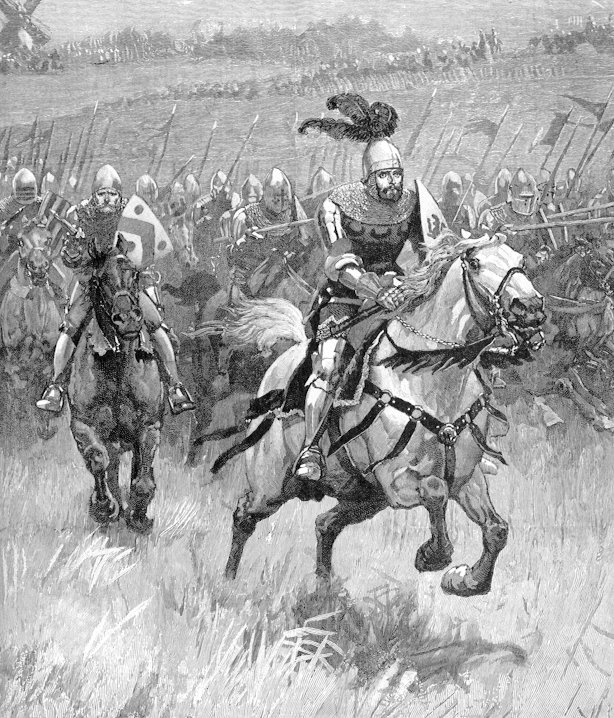 |
the Norman Conquest was the conquest of the kingdom of England by Guillaume le Conquérant, at the battle of Hastings |
|
| 1066 | ||
 |
the East-West Schism was the event that divided Chalcedonian Christianity into Western Catholicism and Eastern Orthodoxy, when Pope Leo IX and Patriarch Michael I excommunicated each other. In the second schism within the Catholic Church, the Western Schism in 1378 three claimant popes were elected at the same time. In 1965 Pope Paul VI and Patriarch Athenagoras nullified the condemnations and anathemas of 1054 |
|
| 1054 | ||
|
|
||
| 1000-1300 | ||
 |
the Roma people left India |
|
| 1000 | ||
 |
the House of Capet succeeded the Carolingian dynasty as rulers of France |
|
| 987-1328 | ||
 |
Prince Vladimir united Russia he adopted Christianity and allied with Byzantium, destroying pagan art and forcing the conversion of his subjects |
|
| 978-1015 | ||
 |
the Battle of Lechfeld was a decisive victory by Otto the Great, King of the Germans, over the Magyar leaders |
|
| August 10, 955 | ||
 |
the Ashkenazic Jewish tradition emerged in Germany and spread to eastern Europe |
|
| 950 | ||
 |
the Normans were granted the small lower Seine area, which expanded over time to become the Duchy of Normandy, by Charles III "the Simple" |
|
| 911 | ||
 |
the Magyars destroyed Great Moravia |
|
| 907 | ||
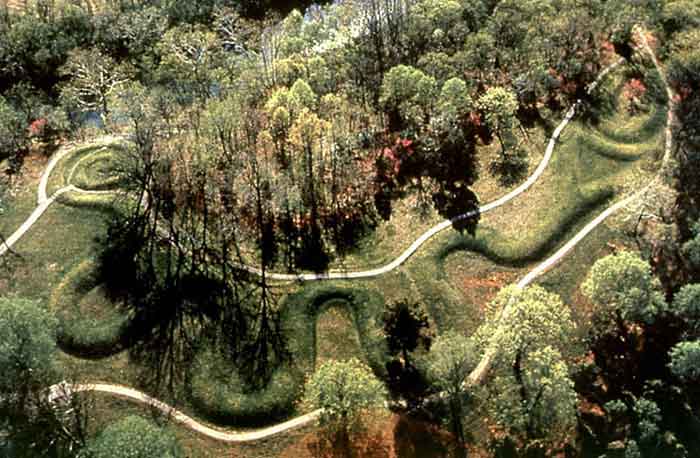 |
the Mississippian culture was a Mound-building Native American culture that flourished in the Midwestern, Eastern, and Southeastern United States in the centuries leading up to European contact |
|
| 900 | ||
 |
||
| 885-886 | ||
 |
Kievan Rus′ was the early, mostly East Slavic state dominated by the city of Kiev |
|
| 880 - middle of the 12th century | ||
 |
under the Peace of Wedmore eastern England fell under Danish rule (Danelaw), while the English ruled in the east and south |
|
| 878 | ||
 |
the Kingdom of Scotland was united by King Cináed I |
|
| 843 | ||
 |
||
| 9th century | ||
 |
Prince Mojmír from the Moravian principality, and his army, attacked the principality of Nitra, conquered it and created the first united Slav State |
|
| 833 | ||
 |
Egbert of Wessex became the first king of England by accepting the submission of the Northumbrian army |
|
| 829 | ||
 |
||
| 811-1797 | ||
 |
Viking raiders conquered the eastern Baltic Sea region and establish a settlement at Lake Ladoga. Drawn toward the Volga River trade, the Varangian chief Ryurik becomes Prince of the Slavic city-state of Novgorod in 862, founding a dynasty of Russian princes |
|
| 800 | ||
 |
the Holy Roman empire was founded by Charlemagne and became finally established with the treaty of Verdun in 843, when the Carolingian Empire was divided into three parts which correspond roughly to what today are Italy, France and Germany |
|
| 800-1806 | ||
 |
||
| 790 | ||
 |
the Vikings were seafaring warriors who raided the coasts of Scandinavia, the British Isles, and other parts of Europe |
|
| 780-1000 | ||
 |
at the battle of the Roncevaux Pass Roland, prefect of Brittany March was defeated by the Basques |
|
| 778 | ||
 |
the Donation of Pepin provided the legal basis for the erection of the Papal States, which extended papal temporal rule beyond the traditional diocese and duchy of Rome |
|
| 754 | ||
 |
the Carolingians succeeded the Merovingian dynasty when Pepin the Younger became king. The Carolingians initially were Mayors of the Palace under Merovingian kings in the sub-kingdom of Austrasia |
|
| 751 | ||
 |
the last Umayyad Caliph Marwan II was overthrown and executed by the first Abbasid Caliph, Abu al-Abbas al-Saffah. The Caliphate was moved to Baghdad, within the territory of the former Persian Empire; this would prove to be a momentous event for Baghdad which developed into a centre of world trade and culture |
|
| 744–750 | ||
 |
in the Battle of Tours Frankish leader Charles Martel defeated an Islamic army led by Emir Abd er Rahman |
|
| 732 | ||
 |
the Reconquista was the military reconquest of the Iberian Peninsula by Christian rulers, after the Muslim invasion of Iberia in 711 |
|
| 718-1492 | ||
 |
Al-Andalus is the Arabic name given to the southern parts of the Iberian Peninsula by its Muslim conquerors; it refers to both the Emirate (ca 750-929) and Caliphate of Córdoba (929-1031) and its taifa successor kingdoms specifically, and in general to territories under Muslim rule |
|
| 711-1492 | ||
 |
during the Islamic Golden Age among other sciences, modern mathematics, especially algebra and calculus were developed |
|
| 700-1400 | ||
 |
the kingdom of Champa controlled what is now south and central Vietnam |
|
| 7th century - 1832 | ||
 |
Khan Asparukh and his Bulgar tribes subjugate the Slavs and establish the Kingdom of Bulgaria |
|
| 681 | ||
 |
the Islamic empire began after Mohammed settled in Yathrib (now known as Medina) and won a war against Mecca. The Muslims, that is the religious community he founded, then succeeded to conquer the rest of Arabia. After Mohammed's death rival dynasties took turns making claims to the caliphate, or leadership of the Muslim world |
|
| 622 | ||
 |
the Tibetan Empire was founded at the castle named Stag-rtse. There, According to the Old Tibetan Chronicle "A group of conspirators convinced Stag-bu snya-gzigs to rebel against Dgu-gri Zing-po-rje. Zing po rje was in turn a vassal of the Zhang-zhung empire under the Lig myi dynasty. Zing-po-rje died before the conspiracy could get underway, and his son Gnam ri slon mtshan instead led the conspiracy after extracting an oath of fielty from the conspirators" |
|
| 608 | ||
 |
Alboin led the Lombards to cross the Julian Alps and to invade northern Italy, together with other Germanic tribes living with them (Bavarians, Gepidae, Saxons) and Bulgars |
|
| 568 | ||
 |
Justinian's Plague killed 40% of Constantinople by 544 and 25% of Europe south of the Alps |
|
| 541 | ||
 |
the Gothic war is commonly divided in two phases, the first (535-540) which ended with the fall of Ravenna and the apparent conquest of Italy by the Romans, and the second phase (540/541-553), where the Gothic resistance was reinvigorated under Totila and was put down only after long struggle by Narses, who also defeated the Frankish-Alamannic invasion of 554 |
|
| 535–554 | ||
 |
the Benedictines were the first major Chistian monastic order that arose in ther western world. They made so great contributions to religion, econcomics, education, and government in their day that the years from 550 to 1150 can be called the Benedictine centuries |
|
| 529 | ||
 |
Dionysius Exiguus recorded in his Easter Tables Jesus of Nazareth's birthday as December 25, 753 years after Rome was founded. The error, an incorrect year and date, was repeated in all Christian calendars |
|
| 525 | ||
 |
the Thule are the ancestors of the modern Canadian Inuits |
|
| 500 | ||
 |
the Ostrogothic Kingdom in Italy reached its zenith under the rule of its first king, Theodoric the Great |
|
| 476-553 | ||
 |
||
| 476-1000 | ||
 |
||
| 449 | ||
 |
the Merovingians were a dynasty of Frankish kings who ruled a frequently fluctuating area in parts of present-day France and Germany |
|
| 447-751 | ||
 |
the Munhumutapa empire was a kingdom located in Southern Africa covering mainly the modern states of Zimbabwe and Mozambique. Its capital city was the Great Zimbabwe |
|
| 400-1440 | ||
 |
the Vandals were an east Germanic tribe which started to move westward to conquer Gaul, Spain, North Africa and finally Rome in 455 |
|
| 400 | ||
 |
the battle of Adrianople was fought between a Roman army led by the Emperor Valens and Germanic tribes (mainly Visigoths and Ostrogoths, assisted by some non-Germanic Alans) commanded by Fritigern. It ended with an overwhelming victory for the Germanic tribes. Historians see the Battle of Adrianople as the end of Antiquity and the beginning of the Middle Ages |
|
| August 9, 378 | ||
|
|
the Huns originated from lands between modern-day Siberia and Korea, and then migrated progressively westward. A group led by Attila the Hun first conquered the Germanic Ostrogoths and Visigoths tribes and then Rome. Eventually they settled Hungary, a country that derives its name from them |
|
| 375 | ||
 |
||
| 369-721 | ||
 |
the Council of Nicaea which took place during the reign of the roman emperor Constantine, was the first ecumenical (from Greek oikumene, "worldwide") conference of bishops of the Christian Church |
|
| 325 | ||
 |
Constantine won the battle of the Milvian Bridge with his troops fighting under the Labarum, a standard bearing a cross. A year later he issued the Edict of Milan, which proclaimed religious toleration in the Roman Empire |
|
| October 28, 312 | ||
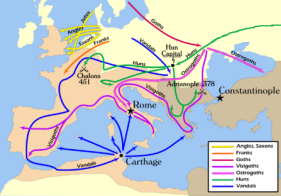 |
||
| 300-900 | ||
 |
Polynesia started to become inhabited initially form the Marquesas, and later extended to the Easter Islands in 400, Hawaii in 500, the Society Islands in 800 and to New Zealand around the year 1000 |
|
| 300 | ||
 |
the Byzantine empire is also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire. It originated with Diocletian who divided the Roman empire into a pars Orientis and a pars Occidentis. The empire's capital was the city of Constantinople, formerly known as Byzantium and today known as Istanbul. Constantine I, the emperor who ended all government-sanctioned persecution of religion and especially of Christianity, made Byzantium the capital of the Roman Empire on May 11, 330 |
|
| 284-1453 | ||
 |
the Shinto shrine in Ise, Japan, was built it is the main shrine of the Japanese royal family |
|
| 250 | ||
 |
||
| 240-600 | ||
 |
Sassanid dynasty was the name of the second Persian Empire |
|
| 224-651 | ||
 |
||
| 184-280 | ||
 |
the Chola empire was a Tamil dynasty that ruled primarily in southern India |
|
| 150-1200 | ||
 |
the Kingdom of Aksum became the country of Ethiopia |
|
| 1st century - 7th century ad | ||
 |
the city of Pompeii along with Herculaneum and many smaller places around the Bay of Naples, were Roman municipalities destroyed during an eruption of the volcano Mount Vesuvius. The ruins of Pompeii were discovered in 1748 |
|
| 79 | ||
 |
the Great Jewish Revolt was the first of two major rebellions by the Jews of Judea against the Roman Empire. It was followed up by Bar Kokhba's revolt in 132. The first revolt was unsuccessful, but the second revolt led to the establishment of an independent state of Israel, which was conquered again by the Romans in 135 |
|
| 66-73 | ||
 |
||
 |
||
| 64 | ||
 |
||
| 32 | ||
 |
||
| 9-260 | ||
 |
in the battle of the Teutoburg Forest an alliance of Germanic tribes led by Arminius wiped out three Legions of unsuspecting Roman allies. The battle established the Rhine as the boundary of the Roman Empire for the next few hundred years, until the decline of the Roman influence in the West |
|
| 9 | ||
 |
the Roman empire was officially founded by Octavian, adopted son of Julius Caesar who had conquered and added large parts of north western Europe to Rome's sphere of influence. The Julian calendar was introduced by Caesar in 46 bc, taking force in 45 bc |
|
| 31 bc - 461 ad | ||
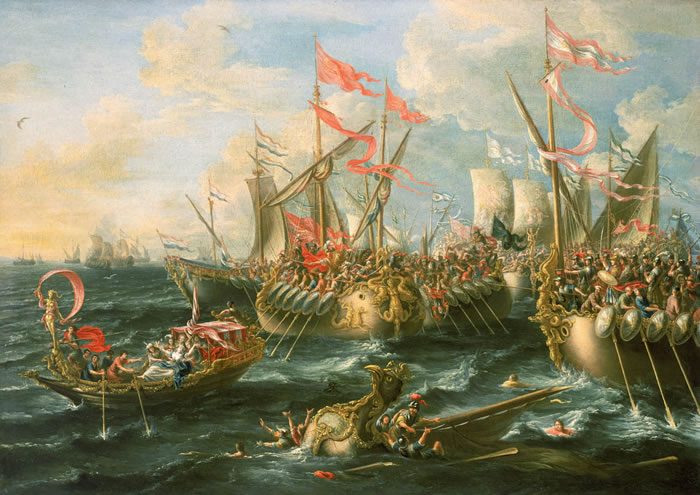 |
the naval battle of Actium was the decisive engagement in the Roman civil war between the forces supporting Octavian and those supporting Mark Antony. The fleet of Octavian was commanded by Marcus Vipsanius Agrippa, and the fleet of Antony supported by the fleet of his wife, Cleopatra, the queen of Egypt. The battle was won by the forces of Octavian and the date is now used to mark the beginning of the Roman empire |
|
| September 2, 31 bc | ||
 |
Julius Caesar was assassinated |
|
| March 44 bc | ||
 |
||
| 58-49 bc | ||
 |
Attalus bequeathed Pergamum to his roman allies in 96 bc. Ptolemy Apion followed suit and bequeathed Cyrenaica in north Africa to Rome |
|
| 133 bc | ||
 |
the Servile wars were a series of slave revolts that plagued the late Roman Republic |
|
| 135-132, 104-103, 73-71 bc | ||
 |
||
| 140 - 37 bc | ||
 |
the Maccabean revolt against the Seleucid Empire was led by Judah the Maccabee |
|
| 167 - 160 bc | ||
 |
Armenia emerged as an independent state after the destruction of the Seleucid Empire. Rome gained control over the state in 66 bc, but in 301 ad Armenia became the first nation to adopt Christianity as a state religion. Between the 4th and 19th centuries, Armenia was conquered and ruled by, among others, Persians, Byzantines, Arabs, Mongols, Turks and Russia. World war I saw the depopulation of large parts of Historic Armenia ruled by the Ottoman Turks during the Armenian Genocide |
|
| 190 bc | ||
 |
the Parthian empire was the dominating force on the Iranian plateau beginning in the late 3rd century bc, a little later Parthia controlled Mesopotamia and became the arch-enemy of the Roman Empire in the east |
|
| 190 bc - 224 ad | ||
 |
the Rhodos earthquake destroyed the Colossus of Rhodos |
|
| 226 bc | ||
 |
the Punic wars were a series of wars fought between Rome and the Phoenician city of Carthage |
|
| 264-241, 218-202, 149-146 bc | ||
 |
the Syrian wars were a series of six wars between the Seleucid Empire and the Ptolemaic Kingdom during the 3rd and 2nd centuries BC over the region of Coele-Syria, one of the few avenues into Egypt. These conflicts drained the strength of both parties involved and led to their eventual destruction at the hands of Rome and Parthia |
|
| 274-168 bc | ||
 |
King Pyrrhus of Epirus won a battle against the Romans but his casualties were very high |
|
| 280 bc | ||
 |
||
| 300 bc - 800 ad | ||
 |
||
| 305-30 bc | ||
 |
the Seleucid empire in the Near East and Central Asia was founded by Seleucus I Nicator with Babylon as its capital city. He was one of the three generals who inherited a part of the territory that Alexander the Great had conquered |
|
| 312 - 60 bc | ||
 |
the Mauryan Empire was India's first great unified empire |
|
| 321-185 bc | ||
 |
the Diadochi wars followed Alexander's death |
|
| 322 - 315 bc | ||
 |
in the Battle of Issus Alexander the Great of Macedonia defeated Darius III of Persia. Alexander´s campaign had started one year earlier and reached its eastern most part at the Beas River in 326 bc |
|
| 333 bc | ||
 |
Logic was developed and defined by Aristotle |
|
| 335 bc | ||
 |
Philip of Macedonia conquered Greece in the battle of Chaeronea |
|
| 338 bc | ||
|
|
the Samnite wars were three wars between the early Roman Republic and the tribes of Samnium |
|
| 343-290 bc | ||
 |
||
| 353 bc | ||
 |
the Gallic Senones tribesmen sacked Rome and occupied it for seven months |
|
| 386 bc | ||
 |
Rome defeated the Etruscan city of Veii after 80 years of war |
|
| 396 bc | ||
 |
||
| 4th century bc | ||
 |
||
| 399 bc | ||
|
|
on the Silk route trade began mostly with lapis lazuli, later also jade and silk became goods of exchange |
|
| 400 bc | ||
 |
Kurds are the world's largest ethnic group without their own state. The earliest historical account of their presence was given by Xenophon the ancient Greek historian who recorded the Kurds in the Anabasis as "Khardukhi", a fierce and protective mountain dwelling peoples who attacked his armies |
|
| 400 bc | ||
 |
the Peloponnesian war between the Athenian empire and the Peloponnesian league which included Sparta and Corinth lasted 27 years, with a 6-year truce in the middle, and ended with Athens' surrender |
|
| 431-404 bc | ||
 |
the magnificent temple of Zeus was designed by the architect Libon |
|
| 450 bc | ||
 |
at the battle of Thermopylae 300 Spartans were able to hold off a vastly larger Persian army for three days before nearly a million Persian soldiers and all of the Spartan warriors were killed |
|
| 480 bc | ||
 |
||
| 500-448 bc | ||
 |
Cleisthenes started what will become democracy in Athens |
|
| 505 bc | ||
 |
Pythagoras founded a school in Croton which can be said to have been the first university in history. He was also the first to coin the terms philosophy and mathematics. Plato founded the Academy in 387 bc and Aristotle started the Lyceum in 335 bc, but it is the Mosque of al-Qarawiyyin in Fez al-Bali, Morroco (857 ad) and the Al-Azhar University in Cairo, Egypt (969 ad) which are the oldest still existing universities on earth. Europe's oldest university was founded in 1088 in the northern Italian city of Bologna. The United States's oldest university, Harvard, opened in Cambridge, Massachusetts, in 1636 |
|
| 523 bc | ||
 |
Siddhartha Gautama sitting under a Peepal tree, attained Enlightenment |
|
| 528 bc | ||
 |
China started building walls around its territory |
|
| 6th century bc | ||
 |
the Achaemenid Empire was properly founded by Cyrus the Great who conquered Media, Lydia and Babylon |
|
| 546 bc | ||
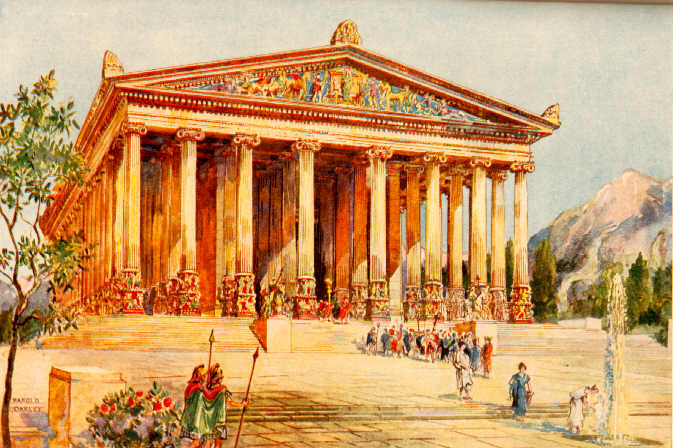 |
||
| 550 bc | ||
 |
Babylonian captivity is the name generally given to the deportation and exile of the Jews of the ancient Kingdom of Judah to Babylon by Nebuchadnezzar |
|
| 597 bc | ||
|
|
at the battle of Carcemish the Babylonians defeated a joint army of Egyptians and Assyrians |
|
| 607 bc | ||
 |
in the Neo-Babylonian or Chaldean period king Nebuchadnezzar II is the best known ruler. He annexed Judah and destroyed Solomon's temple on his conquest of Jerusalem |
|
| 626-538 bc | ||
|
|
Assyrians under Ashurbanipal captured and destroyed Babylon |
|
| 649 bc | ||
 |
Coins were invented in Lydia |
|
| around 660 bc | ||
 |
Thracians were an Indo-European people, inhabitants of Thrace and adjacent lands (present-day Bulgaria, Romania, Republic of Moldova, northeastern Greece, European Turkey and northwestern asiatic Turkey, eastern Serbia and parts of Republic of Macedonia) |
|
| 700 bc | ||
 |
Scythians inhabited an area in Eurasia which ranged from the Altai region where Mongolia, China, Russia, and Kazakhstan come together, across the South of Ukraine to the lower Danube river area and Bulgaria |
|
| 700 bc | ||
 |
the Lelantine war was a long war between Eretria and Chalcis in ancient Greece |
|
| 710-650 bc | ||
 |
the Hebrews were unable to resist the revived Assyrian empire under Sargon II who conquered Israel, the Northern kingdom, in Judah |
|
| 722 bc | ||
 |
||
| 728-550 bc | ||
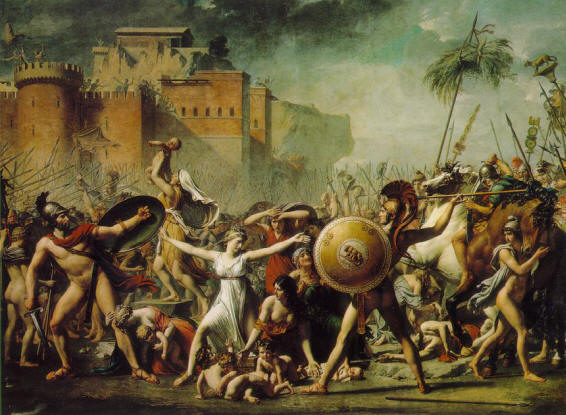 |
||
| 750 bc | ||
 |
Rome started to be a Republic after the expulsion of the last Etruscan king in 510 bc. Rome as a city was founded in 753 by Romulus and his twin brother Remus |
|
| 753-27 bc | ||
 |
Ancient Greece was also called the Delian League which was formed after a coalition of Greek states thwarted an attempted invasion of the Greek peninsula by the Persian empire in 478 bc. Under Alexander the Great Greece was able to extent its boundaries as far as India and included Persia, Egypt and Mesopotamia. However, the Greek era known as the Hellenistic Age came to end with the annexation of Greece by Rome in 146 bc. The year 776 bc is the date when the first Olympic games were held in Olympia, a tradition that was continued until 393 ad, and then taken up again in 1896 |
|
| 776-146 bc | ||
 |
Samnium was a region of the southern Apennines in Italy that was home to the Samnites, a group of Sabellic tribes |
|
| 800-290 bc | ||
 |
||
| 814 bc - 698 ad | ||
 |
the Sabaeans lived in what is today Yemen |
|
| 1st millenium bc | ||
 |
Illyrians were an Indo-European people who inhabited the western Balkans (from northern Epirus to southern Pannonia) and parts of Southern Italy |
|
| 1000 bc | ||
 |
the Celts originated in an area around western Austria and central Switzerland. They migrated to Iberia, and expanded north to the British Isles during the first millenium bc |
|
| 1000-50 bc | ||
 |
Etruscans existed in Etruria and the Po valley in the northern part of what is now Italy, prior to the formation of the Roman Republic |
|
| 1000-400 bc | ||
 |
Germanic and Slavic tribes left southern Scandinavia and moved south |
|
| 1000-500 bc | ||
 |
the kingdom of Israel was formed after the Israelites left Goshen, Egypt during the Exodus (the departure of the Hebrew slaves from Egypt under the leadership of Moses) during the late 13th century bc. The fist king, who united the twelve tribes of Israel was Saul. David, the second king of Israel, established Jerusalem as Israel's national capital. Before then, Shilo (modern day Tel Shilo) had been capital of Israel. The third King of Israel, Solomon, constructed the first Temple in Jerusalem |
|
| 1050 bc | ||
|
|
the Villanovan culture was the earliest Iron Age culture of central and northern Italy, abruptly following the Bronze Age Terramare culture |
|
| 1100-700 bc | ||
 |
the Dorian invasion of Greece led to the end of the Bronze Age Mycenaean civilization |
|
| 1150 bc | ||
 |
Elamites, under Shutruk-Nahhunte attacked Babylon and stole the stele contining the Law Code of Hammurabi |
|
| 1168 bc | ||
 |
the Philistines are the ancestors of the Palestinians |
|
| 1185 bc | ||
 |
the Trojan war was waged by the armies of the Achaeans (Mycenaean Greeks), after Paris of Troy stole Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta and brother of Agamemnon |
|
| 1193-1183 bc | ||
 |
the Phoenician Alphabet is the predecessor of several other alphabets: Hebrew, Arabic, Greek, Latin (via the Old Italic alphabet), and Cyrillic |
|
| 1200 bc | ||
 |
the Olmec lived in the tropical lowlands of south-central Mexico. Today they are understood to be the progenitors and mother culture of every primary element common to later Mesoamerican civilizations |
|
| 1200-400 bc | ||
 |
the Sea Peoples were a confederacy of seafaring raiders who sailed into the eastern shores of the Mediterranean caused political unrest, and attempted to enter or control Egyptian territory during the late 19th dynasty |
|
| 1200 bc | ||
 |
||
| 1300-100 bc | ||
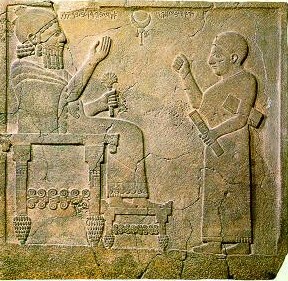 |
||
| 14th century bc | ||
 |
Iron began to be used for weapons and tools |
|
| 1300 bc | ||
 |
Phoenicians called themselves Canaanites, and founded, among others, the cities of Tyre and Sidon in what today is Lebanon, as well as Carthage and Tripoli in northern Africa |
|
| 1400-287 bc | ||
 |
||
| 1446 bc | ||
 |
the golden calf was worshipped by the Israelites during Moses's stay on Mount Sinai |
|
| 1446 bc | ||
 |
||
| 1446 bc | ||
 |
the Exodus was the departure of the Hebrew slaves from Egypt under the leadership of Moses |
|
| around 1450 bc | ||
 |
the Battle of Megiddo was fought between Egyptian forces under the command of pharaoh Thutmose III and a large Canaanite coalition under the King of Kadesh. It is the first battle to have been recorded in what is accepted as relatively reliable detail |
|
| 1457 bc | ||
 |
||
| 1500-1100 bc | ||
 |
the Lapita Culture spread in Oceania from the Bismarck Archipelago near New Guinea to Samoa in Polynesia |
|
| 1500 bc | ||
 |
one of the first Southeast Asian civilizations to emerge were the Mon of Burma |
|
| 1500 bc | ||
 |
||
| 17th century bc | ||
 |
Mycenaean Greece is the Late Helladic Bronze Age civilization of Greece |
|
| 1600-1100 bc | ||
 |
the Code of Hammurabi included laws regulating the first banking operations in history, where the royal palaces and temples provided secure places for the safe-keeping of grain and other commodities. Receipts came to be used for transfers not only to the original depositors but also to third parties |
|
| 1780 bc | ||
 |
Abraham initiated Judaism by declaring his belief in the One God. He migrated with his clan to the land of Canaan, a province of the Egyptian empire, after receiving a calling from God while staying in Haran (in what is today southeastern Turkey). Abraham is considered father of the people of Israel through his son Isaac (Isaac's son Jacob's twelve sons comprise the twelve Tribes of Israel) and of the Ishmaelites, generally identified as the Arabs, through his son Ishmael |
|
| 1800 bc | ||
 |
Assyria (1900 - 605 bc) was named for its original capital, the city of Asshur. As a nation and Empire, it came to include roughly the northern half of Mesopotamia (the southern half being 'Babylonia') |
|
 |
the Hittites lived around what is now Cappadocia they mixed with the already-settled Hatti and were followed by the Lydians, Phrygians, Byzantines, Romans and Greeks. The name Cappadocia comes from the Hittite for "land of pretty horses" |
|
| 2000-700 bc | ||
 |
the Xia dynasty is the first dynasty to be described in Chinese historical records. Yu the Great, the legendary first Chinese monarch of the Xia Dynasty, is best remembered for teaching the people flood control techniques to tame China's rivers and lakes |
|
| 2033-1562 bc | ||
 |
the tower of Babel |
|
| 2200 bc | ||
.jpg) |
the Curse of Ham refers to the curse that Ham's father Noah placed upon Ham's son Canaan |
|
| 2300 bc | ||
 |
the Andronovo culture is a cover term for a group of Bronze Age cultures of southern Siberia and Central Asia, it was succeded by the Karasuk and the Srubna cultures |
|
| 2300-1000 bc | ||
 |
the Akkadian empire was established by Semitic princes who ruled over an area in and around the city of Kish. Sargon of Akkad made large additions to the empire by invading Syria |
|
| 2300-1600 bc | ||
 |
ancient Syria was a large empire around its capital city Ebla. Damascus, one of, if not the oldest continuously inhabited city in the world, was settled in 2500 bc |
|
| 2500 bc | ||
|
|
Stonehenge although used for worship by the Celts must have been built by an even older neolithic culture |
|
| 2500 bc | ||
 |
the Amorites conquered Sumer and founded Babylon, the city which became capital of the Babylonian Empire (1792-1595). Later the Hurrians, the Hittites as well as the Kassites managed to gain control of Babylon. The Kassites ruled for 400 years, and respected the Code of Hammurabi |
|
| 2500 - 1595 bc | ||
 |
the Great Sphinx of Giza is commonly accepted by Egyptologists to represent the likeness of King Khafra. the Great Pyramid of Giza was built a a few years earlier as the tomb of pharaoh Khufu |
|
| 2550 bc | ||
 |
Persian empire is the name used to refer to a number of historic dynasties that have ruled the country of Iran. Iran's earliest known kingdom was the Elamite Empire, followed by the Median Empire; but it is the Achaemenid Empire that emerged under Cyrus II the Great that is usually the earliest to be called "Persian" |
|
| 2700 - 330 bc | ||
 |
the Indus Valley Civilization is one of the two ancient Indian cultures, the second is the Vedic Civilization, a Caucasian race of nomadic warriors known as the Aryans which might have invaded northern India in 1800 bc. However, on a different account the Vedic culture is the Indus Valley Civilization itself |
|
| 2800 - 1800 bc | ||
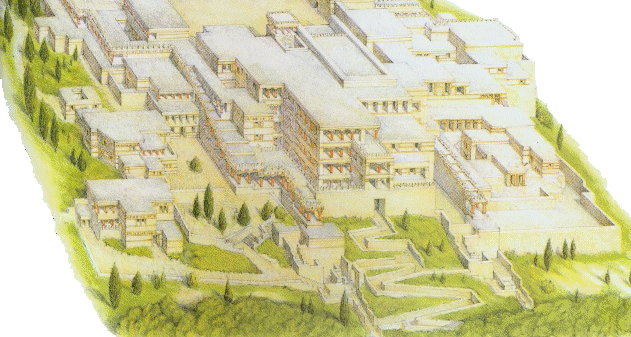 |
the Minoans were a pre-Hellenic Bronze Age civilization in Crete |
|
| 3000 - 1450 bc | ||
 |
the Mayan Empire was located in southern Mexico and northern Central America |
|
| 3000 bc - 1697 ad | ||
 |
King Menes, also known as Narmer unified the whole of the Nile Valley between the Delta and the First Cataract at Aswan, with the centre of power in Memphis |
|
| 3100 bc | ||
 |
the Corded Ware culture encompassed most of continental northern Europe from the Rhine River on the west, to the Volga River in the east |
|
| 3200 bc | ||
 |
the Sumerian pictographical cuneiform script is the earliest known form of written expression |
|
| 3200 bc | ||
 |
Egyptians invented the sail |
|
| 3500 bc | ||
 |
the Sumerians inhabited Mesopotamia where they built, among others, the cities of Ur and Uruk |
|
| 3500 - 1712 bc | ||
 |
Humans started using bronze tools |
|
| 3600 bc | ||
 |
||
| 4th millenium bc | ||
 |
Eridu according to the Sumerian kinglist was the first city in the world |
|
| 4th millenium bc | ||
 |
the wheel originated in ancient Sumer |
|
| 4000 bc | ||
 |
Thera showed signs of human settlement on the island that may be the source of Plato's story of Atlantis, a civilization which according to him existed around 9000 bc |
|
| 4000 bc | ||
 |
||
| 4000 bc | ||
 |
||
| 4300 bc | ||
 |
||
| 5000 bc | ||
 |
||
| 5050 bc | ||
 |
the Ubaid culture represents the earliest settlement on the alluvial plain of southern Mesopotamia |
|
| 5500 bc | ||
 |
the Black Sea deluge is a hypothesized prehistoric flood that occurred when the Black Sea rapidly filled, possibly forming the basis of Great Flood myths like that of Noah and his ark in the Old Testament |
|
| 5600 bc | ||
 |
people settled in Egypt and introduced the first solar calendar in the year 4236 bc. They began counting the 365 days of the year when the star Sirius rose at the same place as the sun |
|
| 6000 bc | ||
 |
Neolithic man started to domesticate animals in southeast Europe |
|
| 7000 bc | ||
 |
||
| 7500 bc | ||
 |
Ariha also known as Jericho is the oldest continuously inhabited settlement in the world |
|
| 7800 bc | ||
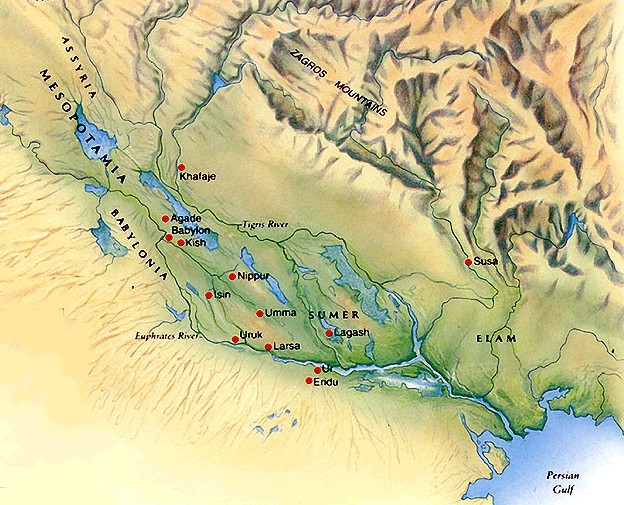 |
Mesopotamia was settled and conquered by numerous ancient civilizations, including the Sumerians, Amerites, Akkadians, Assyrians, the Persian Empire, the Hittites and the Elamites |
|
| 8000 bc | ||
 |
farming and agriculture began in the Fertile Crescent |
|
| 9000 bc | ||
|
|
the Capsian culture of North Africa is the origin of the Berber tribe |
|
| 9500 - 2700 bc | ||
 |
||
| 10,000 bc | ||
 |
||
| 12,000 bc | ||
 |
most Native Americans descend from people who migrated from Siberia across the Bering Strait |
|
| 15,000 - 9,000 bc | ||
 |
the invention of numbers |
|
| 30,000 bc | ||
 |
the last Neanderthal died out. MtDNA indicates a split between Homo sapiens and Neanderthals had occurred more than 500,000 years earlier |
|
| 30,000 bc | ||
|
|
||
| 40,000 bc | ||
|
|
the Australian Aborigines left earliest traces of their presence |
|
| 40,000 bc | ||
 |
Cro-Magnon man began to settle in Europe |
|
| 45,000 bc | ||
 |
||
|
|
the last Ice Age is also called the Wisconsin, Weichsel, Devensian or Würm glaciation corresponding to its location in North America, in Scandinavia, on the British Isles or in the Alps |
|
| 70,000 - 15,000 bc | ||
 |
Homo sapiens began to leave Africa and settle in the more fertile Near East |
|
| 80,000 bc | ||
 |
||
| 200,000 bc | ||
 |
||
 |
Homo sapiens began to hunt animals in a group instead of scavenging |
|
| 500,000 bc | ||
 |
Homo erectus/antecessor learned to control fire |
|
| 1,000,000 bc | ||
| 1,800,000 bc | ||
 |
first use of a tool |
|
| 10,000,000 bc | ||
 |
Aegyptopithecus zeuxis Dawn Ape |
|
| 33,000,000 bc | ||
 |
the beginning of the Tertiary period is marked by the extinction of dinosaurs |
|
| 65,000,000 bc | ||
 |
Eomaia scansoria Ancient Mother |
|
| 125,000,000 bc | ||
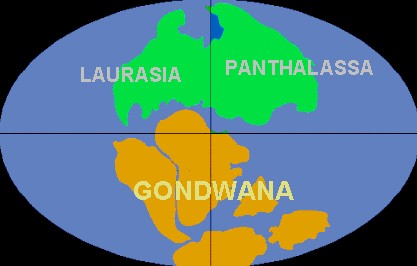 |
the supercontinent Pangea began to break up into several land masses. The largest was Gondwana, made up of the land masses which are now Antarctica, Australia, South America, Africa, and India |
|
| 180,000,000 bc | ||
 |
the Mesozoic era was the age of dinosaurs |
|
| 251,000,000 - 65,000,000 bc | ||
 |
Reptiles were the ancestors of mammals. Also three hundred million years before our time the continents on Earth fused into one - Pangaea |
|
| 300,000,000 bc | ||
 |
in the Paleozoic Era fish left the water (365,000,000 bc) |
|
| 542,000,000 - 251,000,000 bc | ||
 |
during the Cambrian explosion the first real animals, such as the Sponge, developed |
|
| 565,000,000 - 525,000,000 bc | ||
 |
the first Multicellular organisms were initially colonial algae and later, seaweeds |
|
| 1,000,000,000 bc | ||
| 1,200,000,000 bc |
evolution of early protists (3rd kingdom) from primitive eukaryotic cells |
|
 |
Sexual reproduction evolved and led to an explosion in the rate of evolution |
|
| 1,200,000,000 bc | ||
 |
the Oxygen level in the atmosphere reached its present day level and stabilized |
|
| 1,500,000,000 bc | ||
 |
the Milky Way started to swallow Canis Major Dwarf |
|
| 2,000,000,000 bc | ||
 |
more complex Cells appeared as Eukaryotes, which contain various organelles |
|
| 2,100,000,000 bc | ||
| 2,500,000,000 - 570,000,000 bc |
during the Proterozoic eon first multicellular life developed |
|
 |
the first Stromatolites (attached, lithified sedimentary growth structures) started to exist in the Mesoarchean era |
|
| 2,800,000,000 bc | ||
 |
Photosynthesizing cyanobacteria evolved, they used water as reductant, thereby producing oxygen as the waste product |
|
| 3,000,000,000 bc | ||
 |
Cells resembling prokaryotes appeared, they are chemoautotrophs, which use carbon dioxide as a carbon source and oxidize inorganic materials to extract energy. They are divided into Archaebacteria (1st kingdom) and Eubacteria (2nd kingdom) |
|
| 3,800,000,000 bc | ||
 |
Life appeared on earth for the first time possibly in the form of self-reproducing RNA molecules |
|
| 3,800,000,000 bc | ||
| 3,800,000,000 - 2,500,000,000 bc |
the Archean eon saw the evolution of the first unicellular life |
|
 |
the Primordial Soup was the Origin of Life. It consisted of the first simple molecules like, water (H2O), methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3) |
|
| 4,000,000,000 bc | ||
 |
the surface of the Earth cooled down enough for the crust to solidify. The oldest rocks that still exist today are 4,03 billion years old |
|
| 4,100,000,000 bc | ||
 |
the early Earth was bombarded by planetoids and other material left over from the formation of the solar system. The Moon originated after one of these collisions of the young Earth with another planet or large meteor 4,450,000,000 bc |
|
| 4,570,000,000 bc | ||
 |
||
| 4,570,000,000 bc | ||
 |
Planet Earth formed from the accretion disc revolving around the young Sun |
|
| 4,570,000,000 bc | ||
| 4,570,000,000 - 3,800,000,000 bc | ||
 |
our Sun and Solar System formed in the Milky Way galaxy |
|
| 4,600,000,000 bc | ||
 |
formation of quasars |
|
| 9,000,000,000 bc | ||
 |
Clustering of matter formed galaxies. The Milky Way formed 11,5 billion years ago |
|
| 13,688,800,000 bc | ||
 |
||
| 13,699,600,000 bc | ||
|
|
the Proportions marked on this timeline, starting from the Big Bang, are the origin of the Solar system 4,6 billion years before our time and the Cambrian explosion 500 million years before our time. On this scale an early ancestor of humans, homo habilis started to exist at 0,02 mm less than the tip of the arrow |
|
 |
||
| 13,700,002,000 bc |