
the United States presidential election (November 4, 2008)
the Violent Radicalization and Homegrown Terrorism Prevention Act (October 23, 2007) was passed
the United States general elections of 2006 (November 7, 2006)
the Military Commissions Act of 2006 (October 17, 2006)

the U.S. Population hit 300 Million (October 17, 2006)
the Mark Foley scandal (September 2006)

America: From Freedom to Fascism (2006) by Aaron Russo
the United States' Supreme Court ruled in Hamdan v. Rumsfeld (June 29, 2006) that the military
commissions to be used to try some detainees in Guantanamo Bay's Camp Delta are illegal
the 9/11 + The Neo-Con Agenda Symposium (June 24-25, 2006) was held in Los Angeles
the NSA call database scandal (May 2006)
Stephen Colbert (April 30, 2006) at the White House Correspondents' Association Dinner
constuction (April 27, 2006) on the Freedom Tower began
the Baker Commission (March 15, 2006)
the Dick Cheney hunting incident (Febuary 11, 2006)
Jack Abramoff (January 3, 2006) pled guilty to three felony counts, conspiracy, fraud, and tax evasion
the Sago Mine disaster (January 2, 2006)
Stanley "Tookie" Williams (December 13, 2005) was executed via lethal injection amidst debate
over the death penalty and whether his anti-gang advocacy in prison made for genuine atonement

Black sites (November 2, 2005)

Fema (August, September 2005) deliberately
sabotaged Hurricane Katrina relief efforts in New Orleans
Tom DeLay (September 28, 2005) was indicted for conspiring to violate Texas state election law

Cindy Sheehan (August, 2005)
W. Mark Felt (May 31, 2005) revealed his identity as the Watergate
source known as Deep Throat in a Vanity Fair magazine article
REAL ID Act (May 11, 2005) was signed. It will take effect on May 11, 2008
C reported on his recent talks in Washington. There was a perceptible shift in attitude.
Military action was now seen as inevitable. Bush wanted to remove Saddam, through
military action, justified by the conjunction of terrorism and WMD. But the intelligence and
facts were being fixed around the policy. The NSC had no patience with the UN route, and
no enthusiasm for publishing material on the Iraqi regime's record. There was little
discussion in Washington of the aftermath after military action.
the Downing Street memo (May 1, 2005)
the Security and Prosperity Partnership of North America (March 23, 2005)
Red Lake High School massacre (March 21, 2005)
Loose Change 911 (March 2005)
Terri Schiavo (March 2005)

VeriChip (2005) is a Radio Frequency IDentification device
(January 27, 2005)
the Resistance Manifesto (2005) John Conner
the Director of National Intelligence (December 17, 2004)
Gary Webb (December 10, 2004)
newscorp (November 12, 2004)

W (November 2, 2004) was "reelected"
Memogate (September 8, 2004)
Pier 57 (August 31, 2004)
the National Security Whistleblowers Coalition (August 2004)

Fahrenheit 9/11 (June 25, 2004) by Michael Moore

Abu Ghraib torture and prisoner abuse (April 2004)

Martha Stewart (March 5, 2004) was found guilty by a jury of eight women and four men on all four
remaining counts against her: conspiracy, obstruction of justice, and two counts of making false statements
Khalid Sheikh Mohammed (March 1, 2003) was captured
the U.S. Forest Service (2003) announced that it will exempt the Tongass National Forest in southeastern Alaska from a national
rule prohibiting timber cutting in roadless areas. The decision means about 300,000 acres of dense, old-growth rain forest will be
available for logging. Until 2003 the Bush administration had initiated more than 200 major rollbacks of America's environmental laws

Schwarzenegger (November 17, 2003) was elected on October 7, 2003 in a
special recall election which removed sitting Governor Gray Davis from office

Huge power cut (August 14, 2003) hit the east coast of the United States and Canada
the proposed Victory Act (August 2003)
Plamegate (July 2003)
Jayson Blair (May 2003) of the New York Times was caught committing repeated journalistic fraud
PROTECT Act (April 30, 2003)
Michael Moore (March 23, 2003)

invasion of Iraq (March 20, 2003)

Representatives Robert W. Ney (Ohio) (March 11, 2003) and Walter B. Jones, Jr. (North Carolina) declared that all
references to French fries and French toast on the menus of the restaurants and snack bars run by the House of
Representatives would be removed. House cafeterias were ordered to re-name French fries as "freedom fries"
the proposed Patriot Act II (February 7, 2003)

Powell (February 5, 2003) at the UN

Space Shuttle Columbia (February 1, 2003) disintegrated during re-entry on its 28th mission, STS-107
![]()
(January 22, 2003)

Penn & Teller: Bullshit! (2003)
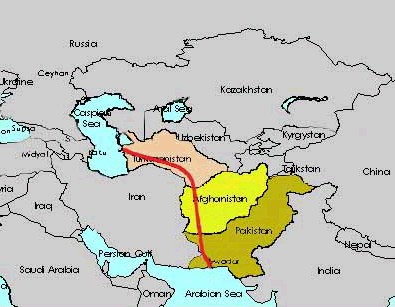
the Trans-Afghanistan Pipeline (December 27, 2002)

the United States Department of Homeland Security (November 25, 2002)
the best democracy money can buy (2002) by Greg Palast

Help America Vote Act (October 29, 2002)

United States Northern Command (October 1, 2002)
America, Awake! : We Must Take Back Our Country (2002) by Norman D. Livergood
the Proactive and Preemptive Operations Group (2002)

WorldCom (July 21, 2002) went bankrupt
the Bush Doctrine (June 1, 2002)

National Commission on Terrorist Attacks Upon the United States (2002)

"friendly fire" (April 18, 2002) an American F-16 fighter jet dropped a laser-guided 225-kilogram
bomb near Kandahar, accidentally killing four Canadian soldiers and injuring eight others

the Bush Administration (March 1, 2002) officially admitted the implementation of the Continuity of Operations Plan
Margie Schoedinger (2002) filed a pro se lawsuit against George W. Bush alleging that Bush had raped her in October 2000

Guantanamo Bay (2002)

the Information Awareness Office (January 2002)
the 9/11 Truth Movement (January 8, 2002)

Charles Bishop (January 5, 2002) a 15 year-old student pilot,
crashed a light aircraft into a Tampa, Florida building
Federal District Court judge William Yohn (December 2001) overturned Mumia Abu-Jamal`s death sentence

Enron went bankrupt (December 2, 2001) and became the largest corporate failure in history

24 (November 6, 2001)
Executive Order 13233 (November 1, 2001)

USA PATRIOT Act (October 26, 2001)
USA Act (October 12, 2001)

the United States invaded Afghanistan (October 7, 2001)
as part of the Operation Enduring Freedom

anthrax attacks (September 18, 2001)
7 World Trade Center (September 11, 2001) "was pulled"

(9-11, 2001)

John Patrick O'Neill (August 23, 2001) started his new
job as the head of security at the World Trade Center
Jim Jeffords (June 5, 2001) abruptly left the Republican Party to become an Independent,
shifting the balance of power in the U.S. Senate to the Democrats for the first time since 1994

the U.S.-China spy plane incident (April 1, 2001)

the Dark Side of the All-American Meal (2001) by Eric Schlosser
the wide by side (2001)
the very first act of the new Bush administration (January 20, 2001) was to have
a Protestant Evangelist minister officially dedicate the inauguration to Jesus Christ

AOL purchased Time Warner (January 11, 2001) Time Warner was
created in 1990 by the merger of Time Inc. and Warner Communications

Presidential Directive W199i (January 2001) ordered the FBI to stop the investigation of Islamic Terrorists

the supreme court (December 12, 2000) stopped the florida recount
Delmart Vreeland (December 6, 2000) was arrested
Bushwatch (2000)

Gore won the popular vote (November 7, 2000)

the USS Cole bombing (October 12, 2000)

the California electricity crisis (2000-2001)
compassionate conservatism (2000)

Elián González (April 22, 2000)

Jackass (2000-2002)

Pardongate (1999)

Big Brother (September 1999) is a popular reality television format, where, over 10
weeks or so, a number of contestants (typically 10 or 12) try to avoid periodic
publicly-voted evictions from a communal house and hence win a cash prize
John F. Kennedy, Jr. (July 16, 1999) died in a plane crash

Columbine High School massacre (April 20, 1999)
Chinagate (1999)

the Biggest Secret: The Book That Will Change the World (1999) David Icke
Steve Kangas (February 8, 1999) was found dead
Clinton was impeached by the House of Representatives (December 1998) on
charges of perjury and obstruction of justice, and tried by the Senate in January
1999. Clinton was acquitted by the Senate on both counts

Jesse Ventura (November 3, 1998) was elected Governor of Minnesota after a
career as Navy SEAL, professional wrestler, actor, mayor, and radio talk show host
the United States Congress passed the "Iraq Liberation Act" (October 31, 1998)

the Digital Millennium Copyright Act (October 28, 1998)

Viagra (1998)

Bill Clinton (August 20, 1998) "Today, I ordered our Armed Forces to strike at terrorist-related facilities in
Afghanistan and Sudan because of the threat they present to our national security," Clinton told reporters. two
bombs exploded August 7 at the U.S. embassies in Nairobi and Dar es Salaam, killing 247 people in Kenya
and 10 in Tanzania. More than 5,500 people were injured, mostly Kenyans

U.S. embassy bombings (August 7, 1998) in Dar es Salaam, Tanzania, and Nairobi, Kenya
playboating (late 90s)
Jonesboro massacre (March 1998)

News (January 17, 1998) of the Lewinsky scandal first broke on the Drudge Report website, which reported
that Newsweek editors were sitting on a story by investigative reporter Michael Isikoff exposing the affair
dot-com frenzy (1998)
the Smoking Gun (1997)
maxim (1997)
Monsanto pressured Fox News to suppress an investigative report (1997) on the
health risks associated with Monsanto's bovine growth hormone product, Posilac

Kenny G (1997) greatest hits
America Destroyed By Design (1997) was Alex Jones' first documentary film

Project for the New American Century (1997)
39 followers of the cult Heaven's Gate (March 26, 1997) committed suicide

South Park (1997)
Clinton (November 5, 1996) was reelcted
A Clean Break: A New Strategy for Securing the Realm (1996)

the Khobar Towers bombing (June 25, 1996)
Filegate (June 1996)
the Antiterrorism and Effective Death Penalty Act (April 24, 1996)

Project Lucid (1996) by Texe Marrs
the Centennial Olympics (1996)

the Unabomber (April 3, 1996) was arrested
Telecommunications Act (February 8, 1996)

the million man march (October 16, 1995)
Trance Formation of America (1995) by Cathy O'Brien with Mark Phillip
Lockheed Martin (1995)

Oklahoma City bombing (April 19, 1995)
the History Channel (1995)
FTAA (1994)

Kevin Mitnick (February 15, 1995) was arrested by the FBI
the Republican revolution (1994)
the Whitewater scandal (1994)
the x games (1994)
Paula Jones (May 1994) filed a sexual harassment suit against President Clinton

Friends (1994-2004)

OJ Simpson (June 17, 1994)
Northrop Grumman (1994)

Kurt Cobain (April 8, 1994) was found dead in his garage

Nancy Kerrigan (January 6, 1994)

the southern California fires (November 1993)
River Phoenix (October 31, 1993) died of a drug overdose
the battle of Mogadishu (October 3 and 4, 1993)
x files (1993-2002)
Marvin Bush (1993) became director of Securacom
Vince Foster (July 20, 1993)

Jordy Chandler (1993) claimed that he and Michael Jackson often had sex

Lorena Bobbitt (June 23, 1993) cut off her husband's sex organ with a kitchen knife
Heidi Fleiss (1993) was arrested

the High Frequency Active Auroral Research Program (1993)

siege of waco (February 28, 1993)

wtc bombing (February 26, 1993)

Clinton (November 3, 1992) was elected president

the book "the End of History and the Last Man" (1992) by Francis Fukuyama argues that the end of the
Cold war signals the end point of mankind's ideological evolution and the universalization of Western
liberal democracy as the final form of human government

the Federal Siege At Ruby Ridge (August 1992)
the Twenty-seventh Amendment (1992)
NAFTA (1992)

the Los Angeles riots (April 29, 1992)
Revolution in Military Affairs (1991)

(9-11 1991)

the Jerry Springer Show (September 30, 1991)

"Rodney" Glen King (March 3, 1991)

the Persian Gulf war (August 2, 1990 - February 27, 1991)

the Intelligent Design movement (1990s)

the Simpsons (December 17, 1989)

Baywatch (1989-2001)
the national Debt clock (1989)
Vice president Bush (November 8, 1988) was elected president
the Indian Gaming Regulatory Act (1988)

"Read my lips: no new taxes" (1988)
Yo! MTV Raps (1988-1995)
the christian colaition (1988)

Black Monday (October 19, 1987)
the Canada-U.S. Free Trade Agreement (1987)
the Carlyle Group (1987)
Z Communications (1987)

Long Island's wandering garbage barge (1987)
![]()
Fox (October 9, 1986)

Iran-Contra Affair (November 3, 1986)

Burning Man (1986)
the Challenger (January 28, 1986) exploded shortly after take off

the Oprah Winfrey Show (1986)

Luz (1985-1992) in the Mojave desert
the Gramm-Hollings Deficit Reduction Act (1985)
Reagan (1984) was reelected
the Green Party (1984)
the Rush Limbaugh Show (1984)
Culture wars (1980s)

Rex 84 (1984)
the Summer Olympics (1984) were held in Los Angeles.
They were boycotted by fourteen countries of the Soviet bloc
Crack (1980s)
Centcom (1983)
Frontline (1983)

Hooters (1983)
former U.S. Secretary of State Henry A. Kissinger (January 1983) succeeded in persuading his cronies
on the President's Foreign Intelligence Advisory Board (PFIAB) to issue a recommendation for a covert
national-security operation against LaRouche et al., according to the provisions of Executive Order 12333.
This recommendation was promptly put into effect by the FBI that same month. This operation, which grew into
one of most far-reaching intelligence operations ever directed against a U.S. citizen, resulted in the fraudulent
conviction of LaRouche and six of his associates on Dec. 16, 1988

solar one (1982)
USA Today (1982)

the Betty Ford center (1982)
Executive Order 12333 (December 4, 1981) extended
the powers and responsibilities of US intelligence agencies

Masters of the Universe (1981)
John Lennon (December 8, 1980) was shot
Reagan (November 4, 1980) was elected president
October surprise (1980)
aerobics (1980s)
the Cable News Network (1980) is a cable television network
that was founded by Ted Turner & Reese Schonfeld
A People's History of the United States (1980) by Howard Zinn

the Carter Doctrine (1980)
the Guardian Angels (1979)

Three Mile Island nuclear accident (March 28, 1979)
C-SPAN (1979)

Fema (1979) the Federal Emergency Management Agency was created
through Executive Order 12148, by President Jimmy Carter. The Rex 84
Program was established on the reasoning that if a "mass exodus" of
illegal aliens crossed the Mexican/US border, they would be quickly
rounded up and detained in detention centers by FEMA
the Lufthansa heist (December 11, 1978)

the Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Act (1978)
the Presidential Records Act (1978)
the Camp David Accrods (1978)
Delta Force (1978)
Spotlight magazine (1978) published an article saying that Howard Hunt
was in Dallas the day JFK died and had murdered Kennedy
William Sullivan, one of six top FBI officials who died in a six month period in 1977 (November 9, 1977)
was shot dead. He was scheduled to testify before the House Select Committee on Assassinations

Arbusto Energy (1977)

Departement of Energy (August 4, 1977)
the Rock Steady Crew (1977)

Star Wars (1977)

Studio 54 (1977-1986)
George de Mohrenschildt (March 29, 1977) was found dead
Carter (November 2, 1976) was elected president
James R. Bath (1976) purchased the Houston Gulf Airport on behalf of Salem bin Laden
the Center for the American Idea (1976)
US Bicentennial (1976)
Wall street and the rise of Hitler (1976) Antony C. Sutton

Saturday Night Live (October 11, 1975)

Thrilla in Manila (October 1, 1975)

President Ford faced two assassination attempts (September 1975) over a three-week period
negative income tax (1975)
Jimmy Hoffa ( July 30, 1975) disappeared from the parking lot
of the Machus Red Fox Restaurant in Bloomfield Hills, Michigan

the Rockefeller Commission (1975) was created by President Ford to whitewash CIA history
See you at the top (1975) by Zig Ziglar
the Church Committee (1975)
Operation Frequent Wind (April 1975) was the emergency evacuation of Americans
by helicopter from Saigon, South Vietnam during the last days of the Vietnam War
people magazine (1974)
Nixon (August 9, 1974) resigned. Vp Ford became president
the nation-wide 55-mph speed limit (1974) became permanent in America
Project Jennifer (1974)
mountain biking (1974)
the Trans-Alaska Pipeline Authorization Act (November 16, 1973)
Vp Spiro Agnew (October 10, 1973) was forced to resign and Nixon appointed Ford
the Endangered Species Act (1973)
the World Trade Center (1973)
DEA (1973)
the Heritage Foundation (1973)

the Trilateral Commission (1973)
Abortion law (1973)
war on drugs (1972)
Nixon (November 7, 1972) was reelected
the first Rainbow Gathering (July 4, 1972) was held in Colorado

the Watergate scandal (June 17, 1972-1974) was an American political scandal
and constitutional crisis that led to the resignation of President Richard Nixon
the Anti-Ballistic Missile Treaty (May 26, 1972 - June 13, 2002)

HBO (1972)
the Pentagon Papers (1971)
Captain Crunch (October 1971)

the Nixon Shock (August 15, 1971)
Jim Morrison (July 3, 1971) died
the Twenty-sixth Amendment (July 1, 1971)

Viacom (1971)
NASDAQ (February 8, 1971) was the world's first electronic stock market
Janis Joplin (October 4, 1970) died of a drug overdose
Jimi Hendrix (September 18, 1970) was found dead
the New Age movement (1970s)
Stagflation (1970s)

the interstate 80 (1970s)
Cosmetic surgery (70s)
Controlled Substances Act (1970)
the Strawberry Statement (1970)

snowboarding (1970)
PBS (1969)

Accuracy in Media (1969)

the Altamont festival (December 1969)

Sesame Street (1969)
SALT I (November 1969 - May 1972)

the Chicago Seven (September 24, 1969 - November 21, 1972) on trail

the Woodstock Music and Art Festival (August 15-17, 1969)

Charles Manson (August 9, 1969)
the Nixon Doctrine (July 25, 1969)

the U.S. Apollo program (July 20, 1969)
the Gap (1969)
Nixon (November 5, 1968) was elected president
under operation cable splicer (1968) all local government agencies
would be confiscated and placed under the shadow government's control
operation garden plot (1968) is a general U.S. Army and National Guard plan
to respond to major domestic civil disturbances within the United States
Operation CHAOS (1968)

Civil rights leader Rev. Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. (April 4, 1968) was assassinated in Memphis, Tennessee

the Club of Rome (1968)

the Democratic National Convention (August 26-29, 1968)
Jim Garrison charged Kerry Thornley with perjury (1968) after Thornley
denied that he had been in contact with Oswald in any manner since 1959

Bobby Kennedy (1968) was killed

National Missile Defense (1967)
the Phil Donahue Show (1967-1996)
Owsley Stanley's lab (1967) was raided by police
the U.S. population officially hit 200 million (1967)

during the Exorcism of the Pentagon (October 21-22, 1967) Abbie Hoffmann led 50,000 of the more than
250,000 people organized by the National Mobilization to End the War in Vietnam to gather around the
Pentagon in Washington D.C. in an effort to levitate the building by their combined psychic energy
Abbie Hoffman (August 24, 1967) and several friends threw dollar bills from the visitors' gallery
onto the floor of the New York Stock Exchange, resulting in a near-riot as traders scrambled for the cash
the "Rockefeller Amendment" (1967) also known as the 25th Amendment to the US Constitution,
allows any person to become Vice president of the US, by simple appointment, not by election

the Monterey Pop Festival (June 16-18, 1967)
the Summer of Love (1967)

the USS Liberty incident (June 8, 1967)
The Alternative: An American Spectator (1967)

the Super Bowl (1967)
the Phoenix Program (1967) was a program aimed at "neutralizing"
the civilian infrastructure that supported the Viet Cong insurgency in South Vietnam
Apollo One (January 27, 1967) was destroyed by fire during a training exercise

Menwith Hill (1966)

Star Trek (September 8, 1966)

the Black Panther Party (1966)
Condon Committee (1966) was the informal name of the University of Colorado UFO Project
Interrupted Journey (1966)
the National Endowment for the Humanities (1965)
the Voting Rights Act (August 6, 1965)

the Selma to Montgomery marches (March 7, 1965) marked the political and emotional peak of the American
civil rights movement. They were the culmination of the movement in Selma for voting rights, launched by
Amelia Boynton Robinson and her husband, who brought many prominent leaders of the American Civil Rights
Movement to Selma, including Martin Luther King Jr., Jim Bevel, and Hosea Williams

the Merry Pranksters (1964)
Johnson (November 3, 1964) was elected president
electronic voting machines (1964)

Mary Pinchot Meyer (October 12, 1964) was shot

the Gulf of Tonkin Incident (August 1964)

the Civil Rights Act (July 2, 1964) prohibited discrimination in public facilities, in government, and in employment

the Great Society (1964) was a set of domestic programs enacted in
the United States on the initiative of President Lyndon B. Johnson
the Consciousness Revolution (1964-1984)
the Twenty-fourth Amendment (January 23, 1964)
the war on poverty (1964)

the Warren Commission (November 29, 1963)
the George Bush memo (November 29, 1963)

Lee Harvey Oswald (November 24, 1963) was shot by Jack Ruby


John F. Kennedy (November 22, 1963) was assassinated by Lee Harvey Oswald
according to the conclusions of two government investigations into the assassination.
He was replaced in office by vp Johnson
the 16th Street Baptist Church Bombing (September 15, 1963)

march on Washington (August 28, 1963)

Executive Order 11110 (June 4, 1963)
Clean Air Act (1963)

the Cuban Missile Crisis (October 14 - November 20, 1962)

Wal-Mart Stores (1962) is the largest retailer
and the largest company in the world based on revenue
Marilyn Monroe (August 5, 1962) was found dead in the bedroom of
her Brentwood, California, home at age 36 from an overdose of barbiturates
the first World Factbook was published in (August 1962) and was "classified." An
unclassified version was published in 1971 and first made available to the public in 1975

Mary Pinchot Meyer (1962) turned JFK on to psychedelics
Kennedy fired Dulles (1961)

Operation Northwoods (1961) was the code name for various false flag actions, including domestic terror
attacks (such as involving the use of "hijacked" planes as missiles) on U.S. soil, proposed in 1962 by senior
U.S. Department of Defense leaders to generate U.S. public support for military action against Cuba
the Cuban Project (November 1961)

the Bay of Pigs Invasion (April 17, 1961)
the Twenty-third Amendment (1961)
the Military-industrial complex (1961)
Alpha 66 (1960s)
Kennedy (November 8, 1960) was elected president

the Harvard Psilocybin Project (1960-1962)
Institute for Scientific Information (1960)
the Brookings Report (1960) was formally called Proposed Studies
on the Implications of Peaceful Space Activities for Human Affairs
the Student Nonviolent Coordinating Committee (April 1960)
DomiNick's (1960) was renamed "Domino's Pizza" in 1965
windsurfing (1960s)
Operation 40 (1959)

NASA (1958)
John Kenneth Galbraith (1958) published "the Affluent Society"
the John Birch Society (1958)
North American Air Defense Command (May 12, 1958)
ARPA (February 1958)

the Vietnam war (1957-1975)
the Counter Intelligence Program (1956-1971) is a program of the United States Federal Bureau of
Investigation aimed at investigating and disrupting dissident political organizations within the United States

peak oil (1956) concerns the long-term rate of conventional oil (and other fossil fuel) extraction and depletion
Eisenhower (1956) was reelected
the President's Foreign Intelligence Advisory Board (1956)
the Montgomery Bus Boycott (December 5, 1955 - December 21, 1956) was a political protest campaign in started
in 1955 in Montgomery, Alabama intended to oppose the city's policy of racial segregation on its public transit system.
The ensuing struggle led to a United States Supreme Court decision that declared illegal the Alabama and Montgomery
laws requiring segregated buses
the Fortune 500 (1955)

Disneyland (July 17, 1955)

the Chase Manhattan Bank (1955)

Area 51 (1955)
the National Review (1955)
skateboarding (1950s)

antidepressants (1950s)
the Tonight Show (September 27, 1954)
the Bilderberg Group (1954)

Operation pbsuccess (1954) was a CIA-organized covert operation that overthrew
the democratically-elected President of Guatemala, Jacobo Arbenz Guzmán
Frank Olson (November 28, 1953) committed suicide after having been given a
secret dose of LSD by the CIA, under the direction of the mysterious Dr. Sidney Gottlieb
World Wrestling Entertainment (1953)

Playboy magazine (1953)

Operation Ajax (1953)
Project Mkdelta (1953) was later renamed Project Mknaomi
Project Mkultra (April 1953-1970s) was the code name for a CIA mind-control research program

the McDonald brothers begin to franchise their restaurant (1953) with Neil Fox as the first franchisee.
The second McDonald's opens in Phoenix, Arizona. It is the first to feature the Golden Arches design;
Eisenhower (November 4, 1952) was elected president
Secrets of the Federal Reserve - Eustace Mullins (1952)
the Twenty-second Amendment (1951) of the United States Constitution sets a two-term limit for the President of the United States

NSA (December 10, 1951)
Project Monarch (1951) is reputedly a subsection of the Central
Intelligence Agency's mind control research projects Artichoke and MKULTRA
Project Artichoke (1951) was a CIA project that researched interrogation methods

rock 'n' roll (1951)
Bluebird (1951-1953) was the cryptonym for a CIA mind control program
the Rosenbergs (1951) were convicted and sentenced to death under section 2 of the Espionage Act
Project Blue Book (1950) was one of a series of systematic studies of
Unidentified flying objects (UFOs) conducted by the United States Air Force

McCarthyism (1950-1954)

Diners Club (1950) invented the charge card, a forerunner of the credit card

the Northgate Mall (1950) in north Seattle has been referred
to as the first regional, covered mall in the United States
National Council of Churches (1950)
surfing (1950s)

suburbia (1950s)

Joint Chiefs of Staff (1949)
Department of War became Department of Defense (1949)

the novel Nineteen Eighty-Four (June 8, 1949) coined vocabulary such as "memory hole,"
"Big Brother," "Room 101," "doublethink," "thought police," "unperson", and "newspeak"
Basketball Association of America (June 6, 1949)
the fair deal (1949)

under Project Silverbug (1940s) the US military was testing and flying UFO design aircraft
the Office of Policy Coordination (1940s) was a U.S. spy organization separate from the CIA
James Forrestal (May 22, 1949) was found dead
Truman (November 2, 1948) was elected president
Operation Ohio (1948)
Operation Mockingbird (1948) is an alleged Central Intelligence Agency operation to influence domestic and foreign media
RAND Corporation (1948)
Project Sign (December 30, 1947) was an official U.S. government study
of unidentified flying objects undertaken by the United States Air Force

the Cold war (1947-1991)
Mary Kay and Johnny (November 18, 1947) was the first sitcom
under the UKUSA Agreement (1947) the five main English-speaking countries
took responsibility for overseeing surveillance in different parts of the globe

Majestic-12 (1947) is the code name of a secret committee of high-level scientists, military leaders,
and government officials, supposedly to have been formed at the direction of U.S. President Harry S.
Truman. The purpose was to investigate UFO activity in the aftermath of the Roswell UFO incident
Roswell UFO incident (1947)

the CIA (1947) was created by Harry S. Truman
the National Security Act (1947) established the National Security Council,
the United States Air Force and the CIA
National Training Laboratories (1947)
Project Chatter (1947)
the Truman Doctrine (March 1947)
Red's Giant Hamburgs (1947) opened as the world's first drive-thru restaurant

Operation Highjump (January 29, 1947) was the invasion of Antarctica
Truman fired Henry A. Wallace (1946) as secretary of commerce
the Fulbright Program (1946)
Murder of wire service king James Ragen (August 15, 1946)
Stanford Research Institute (1946)
.jpeg)
National Air Museum (1946)
Gehlen Org (April 1, 1946)

Official beginning of the Bermuda Triangle mystery (December 5, 1945) when
Flight 19, made up of five naval bombers, disappeared off the coast of Florida
HUAC (1945-1975)

Hiroshima (August 6, 1945)

the Trinity test (July 16, 1945)
Roosevelt died (April 12, 1945) vp Truman became his immediate successor
Glenn Miller (December 15, 1944) disappeared on a flight over the English Channel

Operation Paperclip (1944) was the codename under which the US intelligence
and military services extracted scientists from Germany
Roosevelt (November 7, 1944) was reelected
"An American Dilemma: The Negro Problem and Modern Democracy" (1944)
the Bretton Woods Agreements (1944)
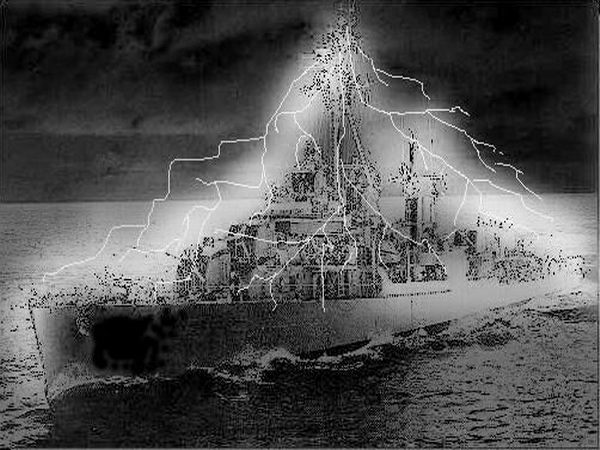
the philadelphia experiment (October 28, 1943)
Los Alamos National Laboratory (1943)

ABC (1943)

the Office of Strategic Services (June 1942) was the wartime (but not direct) precursor to the Central Intelligence Agency
the GED (1942) is a test that certifies the taker has attained American or Canadian high school-level academic skills
NTSC (July 1, 1941)

Grand Coulee (1941)
Captain America (March 1941)
Sandia National Laboratories (January 1941)
Fantasia (November 13, 1940)
Alien Registration Act (1940)
Franklin D.Roosevelt (November 5, 1940) was reelected

NBC (1940)

CBS (1939)

the Manhattan Project (1939)
2nd world war (1939-1945)

Einstein (August 2, 1939) wrote a letter to Roosevelt
about his concerns regarding nuclear weapons

Mount Rushmore (1939)

the War of the Worlds (October 30, 1938) radio adaptation of H. G. Wells' classic novel famously
frightened many in the audience into believing that an actual Martian invasion was in progress

Route 66 (1938-1985) became the first U.S. highway completely paved

Straussianism (1930s) criticised modern liberalism for giving primacy to individual liberty
the Marihuana Tax Act (1937)

Mount Weather (1936) started to be transformed into a secret underground city
Franklin D.Roosevelt (November 3, 1936) was reelected

the Lincoln Brigades (1936) went to Spain to help fight Franco's fascism
Reefer Madness (1936)

the Fort Knox Bullion Depository (1936)

20th Century Fox (1935)

the Social Security Act (August 14, 1935)

FCC (June 19, 1934)
the National Archives Establishment (1934)
the Indian Reorganization Act (1934)

Alcatraz (January 1, 1934) became a federal prison

News-Week (1933)
the Business Plot (1933) was a conspiracy of moneyed interests which tried to overthrow
President Franklin D. Roosevelt during the early years of the Great Depression

Radio City Music Hall (1932-1955)
the New Deal (1932)
Franklin D.Roosevelt (November 8, 1932) was elected president
the Summer Olympics (1932) were held in Los Angeles

the novel a Brave New World (1932) anticipates developments in reproductive
technology, eugenics and mind control that combine to change society

Santa Claus (1931) is dressed in red since coca cola adopted the theme in one of their ad campaigns
Northrop Corporation (1931)

the Scottsboro Boys (1931)
Legalization of gambling in Nevada (March 19, 1931)
the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act (June 1930)
the Nation of Islam (1930)
Fortune magazine (1930)
![]()
the Castellammarese war (1930-31)

the Dust Bowl (1930-1941

the Great Depression (1929-1939)
the Wall Street Crash (October 24-October 29, 1929)

Academy Awards (May 16, 1929)
Hoover (November 6, 1928) was elected president

Steamboat Willie (November 18, 1928)

the Law of Success (1928) by Napoleon Hill
the Harlem Globetrotters (1927)
Buck v. Bell (1927) was the United States Supreme Court ruling that upheld a statute instituting
compulsory sterilization of the mentally retarded "for the protection and health of the state."
Hill & Knowlton (1927)
the New Yorker (1925)
Coolidge (1924) was elected president
Union Banking Corporation (1924-1942)
Howard Hughes Jr. (1924) inherited the Hughes Tool Company
the Indian Citizenship Act (June 2, 1924)
John Edgar Hoover (1924-1972) served as the director of the FBI
MCA (1924)
the U.S. Senate (October 25, 1923) began investigation into the Teapot Dome Scandal
involving leases for naval oil reserves at Teapot Dome in Wyoming and Elk Hills in California
Coolidge (August 3, 1923) became president upon the death of President Harding

the Hollywood sign (July 13, 1923)
President Harding set out on a cross-country "Voyage of Understanding" (June 1923) planning to meet ordinary people and explain
his policies. During this trip, he became the first president to visit Alaska. Rumors of corruption in his administration were beginning to
circulate in Washington by this time, and Harding was profoundly shocked by a long message he received while in Alaska,
apparently detailing illegal activities previously unknown to him. At the end of July, while traveling south from Alaska through British
Columbia, he developed what was thought to be a severe case of food poisoning. Arriving at the Palace Hotel in San Francisco,
he developed pneumonia. Harding died of either a heart attack or a stroke at 7:35 p.m. on August 2, 1923, at the age of 57
Time magazine (March 3, 1923)
Reader's Digest (1922)

Tuxedo Park (1922)
Muzak (1922)
the Council on Foreign Relations (1921)
the Curb Exchange (1921) was moved inside
Bechtel Corporation (1920)

Wall Street bombing (September 16, 1920)
Harding (1920) was elected president
the Nineteenth Amendment (August 1920)

the Harlem Renaissance (1920-1940)
the United States Senate (January 19, 1920) voted against joining the League of Nations

Prohibition (January 15, 1920) was established by the Eighteenth Amendment

the Royal Institute of International Affairs (1920) think tank offshoot of the Round Table, was founded in London
the American Professional Football Association (1920)
Halliburton Energy Services (1919)

U.S. authorities deported anarchists Emma Goldman and Alexander Berkman (1919)

the House of Representatives refused to seat socialist Victor Berger (1919)
Raymond Loewy (1919) emigrated to the US

Eugene Victor Debs (June 16, 1918) was arrested for making an anti war speech
the Sedition Act (1918) along with the Trading with the Enemy Act was repealed in 1921
the Warner Brothers studio (1918)
the National Civil Liberties Bureau (1917)
Trading with the Enemy Act (1917)
Brookings Institution (1916)
Wilson (1916) was reelected
the Pancho Villa Expedition (March 14, 1916 and February 7, 1917) was an abortive punitive expedition
conducted by the United States against the military forces of Mexican Revolutionary General Pancho Villa
in retaliation for Villa's invasion of the United States and attack on the village of Columbus, New Mexico
the U.S. population officially hit 100 million (1915)
1st world war (1914-1919)
FTC (1914)

the Federal Reserve Act (December 24, 1913) created the Federal Reserve System

Henry Ford installed the World's first moving assembly line (December 1, 1913)

Harry Houdini (1913)
Rockefeller foundation (May 14, 1913)
the Seventeenth Amendment (April 8, 1913)
the Sixteenth Amendment (February 3, 1913) authorized income taxes
Wilson (1912) became president
the progressive party (1912)
Lockheed Corporation (1912)

Arizona (February 14, 1912) was admitted as the 48th U.S.
state, completing the continental United States' territory
American banana shipper Samuel Zemurray (1911) sponsored a coup in
Honduras to establish a government more favorable to banana growers
F.W. Woolworth Company (1911)
the Supreme Court broke up Standard Oil (1911)

Hollywood (1911)
the National Association for the Advancement of Colored People (February 12, 1909)
the round table (1909)

the Federal Bureau of Investigation (1908)
Taft (1908) was elected president

Model T (1908)

the Panic of (1907) prompted the United States Congress to form the Federal Reserve System
the American Messenger Company (1907) was renamed United Parcel Service in 1919
the United States Meat Inspection Act (1906)
the San Francisco earthquake (1906)
the National Audubon Society (1905)

the Roosevelt Corollary (December 4, 1904)
Theodore Roosevelt (1904) was elected president

the Louisiana Purchase Exposition (1904)
The History of the Standard Oil Company (1904) by Ida Tarbell

the Protocols of the learned Elders of Zion (1903) were published in a Russian newspaper
the General Education Board (1902)
Rhodes Scholarship (1902)

the Quaker Oats Company (1901) was founded in by the merger of three oat mills
President William McKinley (September 6, 1901) was shot
the United States Steel Corporation (1901) was the world's first billion-dollar corporation
Edgar Cayce (1901)
the Platt Amendment (1901)
McKinley (November 6, 1900) was reelected
the Hamburger (1900)
the Gold Standard Act (1900)

the Wonderful Wizard of Oz (1900)
Reform in Our Street Traffic Urgently Needed (1900) by William Phelps Eno

Spain was forced to cede Puerto Rico, along with Cuba and the Phillippines, to the United States under the Treaty of Paris (1898)
New York City (1898)

the Spanish-American war (1898)
USS Maine (ACR-1) was sunk by explosion (February 15, 1898)
the United States Copyright Office (1897)

the United States annexed the Hawaiian Islands (1897)
McKinley (1896) was elected president
the Dow Jones Industrial Average (May 26, 1896)
the Atlanta Compromise (September 18, 1895) was a speech given by
Booker T. Washington at the Cotton States and International Exposition in Atlanta
one of the first uses of home refrigeration (1895) was
at Biltmore Estate in Asheville, North Carolina
J.P. Morgan & Co (1895) was forced in the 1930s by the Glass-Steagall Act to split into two companies:
J. P. Morgan (a commercial bank) and Morgan Stanley (an investment bank). After a 1959 merger J. P.
Morgan became Morgan Guaranty Trust, but ten years later it established a bank holding company called
J.P. Morgan & Company as its parent. By the late 1990s, when it was acquired by Chase Manhattan, J.P.
Morgan had turned itself into an investment bank too
Cleveland (November 8, 1892) was elected to a second term as president

the Carnegie Steel Company (1892)
Sierra Club (1892)

the Homestead Strike (1892)
the Coca-Cola Company (1892)

Ellis Island (1892)

the Wounded Knee Massacre (1890)

the Sherman Anti-Trust Act (1890)

Jim Crow laws (1890s)

"Bosses of the Senate" by Joseph Keppler (1889)
the Wall Street Journal (July 8, 1889)
Harrison (November 6, 1888) won the electoral vote, while incumbent
president Grover Cleveland received the greatest number of popular votes
Edward Bellamy (1888) published "Looking Backward"

the Statue of Liberty (October 28, 1886)

Geronimo surrendered (September 4, 1886) to United States Army
General Nelson A. Miles at Skeleton Canyon, Arizona
the American Federation of Labor (1886)

Haymarket Riot (May 4, 1886)
AT&T (March 3, 1885)
Cleveland (November 4, 1884) became the first Democrat elected to the Presidency since the Civil War

Life Magazine (1883)

the Buffalo Bill Wild West Show (1883)
the Chinese exclusion act (May 6, 1882)
President Garfield (July 2, 1881) was shot

Liberty (1881-1908)
the third great Awakening (1880s - 1900s)
Garfield (1880) was elected president

General Electric (1879)
the Washington Post (1877)
an electoral commision (January 29 - March 2, 1877) decided that Hayes won the election for president
at the Massasoit Convention (November 23, 1876) the first rules for American football were laid down
Samuel J. Tilden and Rutherford B. Hayes (1876)

the Centennial Exposition (1876)

the battle of the Little Bighorn (1876)
the Chautauqua Institution (1874)

the New York Society for the Suppression of Vice (1873)

the Bohemian Grove (1872)

Yellowstone National Park (1872)
Grant (1872) was reelected
Barnum's Monster Classical and Geological Hippodrome (1871)
American Rifle Association (1871)
the National Association (1871) is regarded as baseball's first professional league
hotdogs (1870)
the first dollar store (1870) was operated by Ben Marks

a western movie is typically set to take place in the year (1870)
the Fifteenth Amendment (February 3, 1870) grants voting rights regardless of race

the Standard Oil Company (1870-1911) was founded by John D. Rockefeller

American Museum of Natural History (1869)

the Black Friday crisis of (September 24, 1869)

First Transcontinental Railroad (May 10, 1869)
Grant (1868) was elected president
the Fourteenth Amendment (July 9, 1868) provides a broad definition of national citizenship, overturning a central
holding of the Dred Scott case. It requires the states to provide equal protection under the law to all persons (not
only to citizens) within their jurisdictions

the United States purchased Alaska (9 April, 1867)
from Russia for $7,200,000 ($90,000,000 approx in 2003)
the first Reconstruction Act (March 2, 1867)
Ku Klux Klan (1866)

Indian reservations (1860s)
the Secret Service (July 5, 1865)
Jacob H. Schiff (1865) moved to the United States

Abraham Lincoln (April 14, 1865) was assassinated
the Thirteenth Amendment (January 31, 1865) abolished slavery

Arlington National Cemetery (1864)
Lincoln (1864) was reelected

the Statue of Freedom (December 2, 1863)

the battle of Chattanooga (November 23-25, 1863)
Lincoln's Gettysburg Address (November 19, 1863)
the National Bank Act (1863)

the Emancipation Proclamation (September 22, 1862) announced
that all slaves in Confederate territory still in rebellion were freed.
Units made up of ex-slaves started to fight in the Union Army

the battle of Antietam (September 17, 1862)

the Homesteads Act (May 20, 1862) gave one quarter of a section of a township (160 acres, or about 65
hectares) of undeveloped land in the American West to any family head provided he lived on it for five years
the Commissioner of Internal Revenue (1862)

the Legal Tender Act (1862)

the Trent affair (December 1861)

the first battle of Bull Run (July 21, 1861)

the American Civil war (April 12, 1861-1865)

the Confederate States of America (February 4, 1861-1865)
South Carolina (December 20, 1860) seceded from the United States
Lincoln (1860) was elected president

the Pony Express (April 3, 1860 - August 1861)

Militant abolitionist leader John Brown (December 2, 1859) was hanged for his October 16th raid on Harper's Ferry
Joshua A. Norton (September 18, 1859) proclaimed himself "Emperor of These United States"

Edwin Drake (August 27, 1859) drilled the first oil well in the United States, near Titusville, Pennsylvania

the National Association of Base Ball Players (1857) was the first
organization to govern the sport and the first to establish a championship

Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857)
Buchanan (1856) was elected president

Henry David Thoreau´s Walden (1854)

the Kansas-Nebraska Act (1854)

the Republican party (February 28, 1854) is seen by some as the successor
to the Federalist Party of John Adams and Alexander Hamilton
Pierce (1852) was elected president
the New York Daily Times (September 18, 1851)
Harper's Magazine (1850)

the Fugitive Slave Law (1850) made any federal marshal or other official
who did not arrest an alleged runaway slave liable to a fine of $1,000
President Taylor (July 9, 1850) died of indigestion, thought to be brought on by too
many iced cherries and milk consumed at the opening of the Washington Monument
the Oneida Society (1848)

Chicago Board of Trade (1848) is the world's oldest futures and options exchange
Taylor (1848) was elected president
the Smithsonian Institution (1846)

the Oregon treaty (1846) permanently established the 49th parallel
as the boundary between the United States and Canada

the Mexican-American War (1846-1848)
Polk (1844) was elected president
B'nai Brith (1843)
manifest destiny (1840s) is a phrase that expressed the belief that the United States
had a divinely inspired mission to expand, spreading its form of democracy and freedom

the Oregon trail (1842)
Commonwealth v. Hunt (1842)
President Harrison (April 4, 1841) died
Harrison (1840) was elected president
John C. Frémont assisted Joseph Nicollet in exploring the lands
between the Mississippi and Missouri Rivers (1838-1839)

the trail of tears (1838)
the Gold rushes (1838-1898)

August Belmont immigrated to New York City (1837) after becoming the
American representative of the Rothschild family's banking house in Frankfurt
the Panic of (1837)
former vice president Van Buren (1836) was elected president
the Specie Circular (1836)

the great fire of New York (December 16, 1835)

the billboard (1835)
an unsuccessful assassination attempt (January 30, 1835)
against president Jackson occurred in the United States Capitol
George Bancroft (1934) published "the History of the United States"
the bank war (1833)
the force bill (1833)
Jackson (1832) was reelected

Skull and Bones (1832)

Jedediah Smith (1831) died on the Santa Fe Trail
the Indian Removal Act (1830)
Jackson (1828) was elected president
the Nullification crisis (1828)
the Tariff of Abominations (1828)
the Anti-Masonic Party (1828)

the Democratic party (1828)
the Cincinnati Time Store (1827-1830)
Thomas Jefferson and John Adams died (July 4, 1826)

the Erie Canal (October 26, 1825) was opened
John Quincy Adams (1824) was elected president by the House of Representatives

the Monroe Doctrine (1823)

the Santa Fe Trail (1821)
the Genius of Universal Emancipation (1821)
Monroe (1820) was reelected

the Missouri Compromise (1820)

the American Colonization Society (1820) founded Liberia and transported free
black Americans there, in an effort to remove them from the United States
the second great Awakening (1820s-1830s)

the Arcade in Providence, Rhode Island (1819) introduced the concept of indoor shopping to the United States
the Anglo-American Convention (1818)
the Tariff of (1816)
Monroe (1816) was elected president
the American bible society (1816)
the North American Review (1815)

the treaty of Ghent (December 24, 1814) ended the War of 1812. Yet the battle of New
Orleans is fought two weeks later (in January 1815) because word of the peace has not yet arrived
British troops (1814) burned the White House in Washington, D.C., gutting it completely

the Star-Spangled Banner (1814)
Madison (1812) was reelected

Uncle Sam (1812)

the British-American war (1812-1815)

the underground railroad (1810)
Madison (1808) was elected president

the American Fur Company (1808)

the Chesapeake-Leopard affair (1807)

the Lewis and Clark expedition (1804-1806)
Jefferson (1804) was reelected

the Aaron Burr vs. Alexander Hamilton duel (July 11, 1804)
the Twelfth Amendment (June 15, 1804)
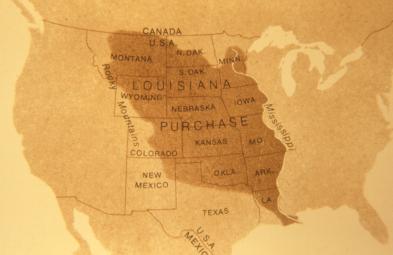
the Louisiana Purchase (1803)

West Point (1802)

the United States Congress passed the first federal bankruptcy law (1801)
by virtue of which Founding Father Robert Morris gained release from debtors' prison

John Chapman (1800) better known as Johnny Appleseed, began scattering religious
tracts and apple seeds in pioneer communities throughout the American Midwest

Parson Weems (1800) published "the life of Washington"

the Tripolitan war (1800-1815)
Jefferson (1800) won the election against the incumbent president John Adams

the Capitol building (November 17, 1800) held its first session of U.S. Congress

Construction of the White House was completed on (November 1, 1800)

John Robison (1798) Proofs of a Conspiracy
the U.S. House Committee on Standards of Official Conduct (1798)
John Adams (1796) won the election against Thomas Jefferson
the Eleventh Amendment (1795)
the Democratic-Republican Party (1794) was the precursor of the Democratic Party

the issue of the Muhlenberg Vote (January 13, 1795) was wether
to print the federal laws in German as well as English or not
Samuel Slater (1793) began the American Industrial Revolution
with the construction of the first successful textile mill
Washington (1792) was reelected

outside of 68 Wall Street (May 17, 1792) the Buttonwood Agreement,
which established the NYSE, was signed by twenty-four stock brokers

the Whiskey Rebellion (1791-1794)

the Bill of Rights (1791) was ratified by Virginia,
making the first 10 amendments to the U.S. Constitution
Washington, D.C. ( July 16, 1790) was established as the
seat of government of the United States by the Residence Bill,
yet Philadelphia remained the de facto capital of the US until 1800
the federalist party (1790)

the House of Representatives (April 1, 1789)

the United States Judiciary Act (1789) established the U.S. Supreme Court

George Washington (1789) was elected the first President of the United States
the U.S. Government under the Constitution began in New York City (March 4, 1789) in 1790 it came
to Philadelphia, the result of a compromise whereby Southern congressmen agreed to support Secretary
of the Treasury Alexander Hamilton's financial proposals in return for locating a permanent capital
somewhere on the banks of the Potomac River. Philadelphia was named temporary capital while the
new federal city was being prepared
New Hampshire became the ninth state to ratify the U.S. Constitution, rendering it operative on (June 21, 1788)

the Federalist Papers (October 27, 1787)

the US constitution (September 17, 1787) was completed and the new government it prescribed
came into existence on March 4, 1789, after fierce fights over ratification in many of the states

the Constitutional Convention (May 25 - September 17, 1787)
Brook Farm (1841-1847)
the Tammany Society (1786)

the Land Ordinance (1785)

the United States Army (June 3, 1784)
the American Spelling Book (1783) was published by Noah Webster

the Treaty of Paris (1783) formally ended the American Revolutionary War between
the Kingdom of Great Britain and the Thirteen Colonies in North America who had
rebelled against British rule in 1776

the Barton/Thomson seal (1782) was adopted
the Bank of North America (January 7, 1782)
General Cornwallis (October 19, 1781) surrendered at the battle of Yorktown

the battle of the Chesapeake (September 5, 1781)

the Congress of the Confederation (March 1, 1781 - March 4, 1789) met in the
Independence Hall, officially known as the Pennsylvania State House

John André (September 23, 1780) was arrested

the winter at Valley Forge (December 19, 1777)

the Articles of Confederation (November 15, 1777)

stars and stripes (June 14, 1777)
Brother Jonathan (1776)
the Battle of Trenton (December 26, 1776) took place after Washington's crossing of the Delaware River
the Phi Beta Kappa Society (December 5, 1776)

the Declaration of Independence (July 4, 1776) was ratified by the Continental Congress
the Virginia Declaration of Rights (May 20 to 26, 1776)
the Grand Union Flag (December 3, 1775)

the Continental Marines (November 10, 1775)
George Washington (June 15, 1775) was selected commander in chief by the Continental Congress

the Shot heard 'round the world (April 19, 1775) is a phrase that comes from the opening stanza
of Ralph Waldo Emerson's Concord Hymn (1837), and describes the impact of the battle at Old
North Bridge in Concord, Massachusetts

the American war of Independence (1775-1783)

Patrick Henry (March 23, 1775) made his famous speech in the House of Burgesses

the Continental Congress (1774-1789) was the federal legislature
of the Thirteen Colonies and later of the United States

the Boston Tea Party (1773)

the Boston Massacre (1770)
the Townshend Acts (1767) were passed by the British Parliament, having been proposed by
Charles Townshend as Chancellor of the Exchequer just before his death. These laws placed a
tax on common products, such as lead, paper, paint, glass, and tea. In contrast to the Stamp Act
1765, the laws were not a direct tax but a tax on imports

the Stamp Act Congress (1765)

Pontiac's Rebellion (1763-1764)

the Albany Congress (1754)

Fort Necessity (1754)
the French and Indian War (1754-1763)
the first great Awakening (1730s-1740s)

George Washington (1732-1799)