

the Nürnberg Trials (November 20, 1945-1949) were two sets of trials of Nazis involved
in World War II and the Holocaust. Out of 177 accused, 12 were sentenced to death
Nagasaki (August 9, 1945)
Operation August Storm (August 8-September 2, 1945) was the codename for the Soviet invasion
of Manchukuo, Mengjiang, Korea, the southern portion of Sakhalin, the Kuril Islands, and Hokkaido
Hiroshima (August 6, 1945)

the Potsdam Conference (July 17 - August 2, 1945)
two months after Germany surrendered (July 10 and August 17, 1945)
submarines U-530 and U-977 gave themselves up in Mar del Plata, Argentina

Germany surrendered officially (May 8, 1945) but the war continued in Asia. Hitler had
commited suicide on April 30, 1945 as Soviet troops battled their way toward his Reich
Chancellory. Joseph Goebbels commited suicide on May 1, Martin Bormann on May 2,
Heinrich Himmler on May 22, and Hermann Göring on October 15, 1946

Berlin fell to the Red Army on May 2. All military forces
in Germany surrendered to the Allies on May 4, 1945
Mussolini (April 28, 1945) was executed by Italian partisans

Elbe Day (April 25, 1945) was the date Soviet and American troops met at the River Elbe, near Torgau in Germany

Franklin D. Roosevelt (April 12, 1945) died of a stroke
the United States Army landed on Okinawa (April 1, 1945)
the Red Army entered Austria (March 29, 1945)
the Nerobefehl (March 19, 1945)
United States Army Air Force created a firestorm in Tokyo (March 9, 1945)

the miracle of Remagen (March 7, 1945)

Churchill, Roosevelt and Stalin (February 1945) made arrangements for post-war Europe at the Yalta Conference
start of Operation Ten-Go (February 2, 1945)

Wilhelm Gustloff (January 30, 1945) was attacked and sunk by the Soviet submarine S-13

the 322nd Infantry unit of the Red Army (January 27, 1945) liberated Auschwitz.
Dachau was freed by the 45th Infantry Division, Bergen-Belsen was captured by British troops
and Buchenwald as well as Kaufering/Landsberg by American and French troops in April 1945
the Red Army liberated Warsaw (January 17, 1945)
the Red Army established a new government in Hungary (December 21, 1944)

the battle of the Bulge (December 16, 1944) was the last major German offensive on the Western Front
Japanese kamikaze pilots (October 1944 - August 1945)
Bulgaria signed an armistice with the Allies (October 28, 1944)
the Battle of Leyte Gulf (October 24, 1944)
Erwin Rommel was forced to commit suicide by the Nazi government (October 14, 1944)
Morgenthau-Plan (October 9, 1944)
the Red Army entered Czechoslovakia (October 6, 1944)
the British Army landed in German-occupied Greece (October 4, 1944)
the German Army crushed the Warsaw Uprising killing 250,000 of the inhabitants of the city (October 2, 1944)
Canadian troops liberated the French port of Calais (September 28, 1944)
Volkssturm (September 25, 1944)
Finland signed an armistice with the Soviet Union (September 19, 1944)
start of Operation Market Garden (September 17, 1944)
Romania signed an armistice with the United States, Britain and the Soviet Union
(September 12, 1944)
Winston Churchill and Franklin D. Roosevelt met in Quebec to discuss post-war Germany (September 11, 1944)
Allied troops entered Nazi Germany (September 11, 1944)
the first V2 Rocket landed on Britain (September 8, 1944)

the Liberation of Paris (August 25, 1944)

the Dumbarton Oaks Conference (August 21 - October 7, 1944)
Allied troops landed on the French coast between the ports of Toulon and Cannes (August 14, 1944)
V1 Flying bomb brought down by a Gloster Meteor, Britain's first jet-fighter (August 4, 1944)
the Warsaw Uprising (August 1, 1944)
July Plot against Hitler failed (July 20, 1944)

the July 20 Plot (July 20, 1944) was a failed coup d'état which involved an attempt to assassinate Hitler.
It was initiated by officers of the Wehrmacht. The leader of the plot was Oberst Claus von Stauffenberg
Allied troops captured Caen in Normandy (July 9, 1944)

the Bretton Woods system (July 1944) of international economic management established the rules for
commercial and financial relations among the world's major industrial states. The meeting of 730 delegates from
all 44 Allied nations gathered at the Mount Washington Hotel, situated in the New Hampshire resort town
of Bretton Woods established the International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (later divided into
the World Bank and Bank for International Settlements) and the International Monetary Fund
the first V1 flying bomb landed on Britain (June 13, 1944)
the SS carried out a revenge attack on the Maquis at Oradour-sur-Glane (June 10, 1944)

on D-Day (June 6, 1944) the western Allies invaded German-held Normandy in a pre-dawn amphibious assault
spearheaded by American, British and Canadian paratroops, opening the "second front" against Germany
General Mark Clark and Allied troops captured Rome (June 4, 1944)
the German Army evacuated Sevastopol (May 9, 1944)
Allied bombing of Nürnberg Raid (March 30, 1944)
Paul von Kleist and Erich von
Manstein recalled to Germany and sacked by
Hitler (March 29, 1944)
Allied forces bombed the monastery at Monte Cassino (February 15, 1944)
General John Lucas and US 5th Army landed at Anzio (January 22, 1944)
the Scharnhorst was sunk by the Duke of York off the coast of Norway (December 26, 1943)
Eduard Benes and Joseph Stalin signed a Soviet-Czech peace treaty in Moscow (December 12, 1943)
the Tehran Conference (November 28 - December 1, 1943)
the Red Army recaptured the city of Kiev (November 6, 1943)
Evans Carlson and the 2nd Raider Battalion landed in Guadalcana (November 4, 1943)
the third Moscow Conference (October 18 - November 11, 1943)
General Mark Clark and 5th Army captured Naples (October 13, 1943)
Benito Mussolini established a new fascist government at Salo on Lake Garda, Italy (September 15, 1943)
Benito Mussolini was rescued from prison by a team led by Otto Skorzeny (September 12, 1943)
Italy (September 8, 1943) surrendered to the Allies shortly after the allied invasion
and declared war on Germany (October 13, 1943)
Bernard Montgomery and the 8th Army landed at Reggio in Italy (September 3, 1943)
the Red Army recaptured the city of Kharkov (August 23, 1943)
Victor Emmanuel III dismissed Benito Mussolini from office in Italy (July 25, 1943)
Allied troops landed on German-occupied Sicily (July 10, 1943)
Jean
Moulin, leader of the French Resistance, was murdered by the
Gestapo (July 8, 1943)
Jean Moulin held the first meeting of the Conseil National de la Resistance in
Paris (May 27, 1943)
the Royal Air Force carryout
the Dambuster Raid in the
Ruhr (May 16, 1943)
over 130,000 members of the German Army surrendered in Tunisia (May 13, 1943)
the Allies captured Tunis (May 7, 1943)
Yitzhak Zuckerman led the Warsaw Uprising (April 19, 1943)
British and US military aircraft began round-the-clock bombing of Nazi Germany (February
25, 1943)

in the Air war on Germany (1943) British and US military aircraft begin round-the-clock bombing of Nazi Germany on February 25.
The bombing of Hamburg began in July, the bombing of Berlin began in November and Dresden was attacked and destroyed in February, 1945
![]()
that the Sixth Army (early February 1943) would have to surrender became clear. Hitler made General Friedrich Paulus,
who was in charge of the German forces, a Field Marshal in the vain hope it would deter him from surrendering. It didn't, and
he surrendered completely on February 2. The results were the destruction of the city, millions of casualties, and the collapse
of Germany's Sixth Army as a viable fighting force. Nazi Propaganda Minister Joseph Goebbels responded with his Sportpalast
speech to the German people
Red Army recaptured the city of Kursk in the Soviet Union (February 8, 1943)
the Allies captured Tripoli (January 23, 1943)
the Luftwaffe renewed its air attacks on London (January 18, 1943)

the Casablanca Conference (January 14 - 24, 1943)
Admiral Jean Darlan was assassinated by a member of the French Resistance in Algiers (December 24, 1942)
Erich von Manstein and the 4th Panzer Army begin the attempt to relieve the 6th
Army (December 12, 1942)
British Admiral William Halsey
led successful naval campain at Guadalcana (November 13, 1942)
the British Army recaptured Tobruk (November 12, 1942)
Hitler ordered the occupation of Vichy France (November 11, 1942)
Admiral Jean Darlan surrendered French North Africa to Dwight D. Eisenhower (November 11, 1942)
General Dwight D. Eisenhower led the invasion of Tunisia (November 8, 1942)
the German Army was defeated at El Alamein (November 4, 1942)
Thomas Kinkaid faced Nobutake Kondo at
the Battle of Santa Cruz
Islands (October 26, 1942)
General Bernard Montgomery ordered counter-attack at El Alamein (October 23, 1942)
Erwin Rommel attacked the Eighth Army at Alam el Halfa (August 30, 1942)
the German Army entered
Stalingrad (August 24, 1942)
5,000 Canadian and 1,000 British troops raid the port of Dieppe in France (August
19, 1942)
the Flying Fortress
began making first daylight bombing raids on Europe (August 17, 1942)
the second Moscow Conference (August 12 - August 17, 1942)
Alexander Vandegrift and the US Marines landed on Guadalcanal (August 7, 1942)

an aborted German offensive (1942) was launched towards the Caucasus to secure oil fields and German armies reached
Stalingrad. The siege of Stalingrad continued for many months, with vicious urban warfare leading to high casualties on both sides
Japanese Army landed on Guadalcanal
(July 7, 1942)
General Erich von Manstein captured Sevastopol on the Black Sea (July 2, 1942)
Erwin Rommel and the German Army captured Tobruk (June 21, 1942)
Erwin Rommel defeated Neil Richie at Gazala (June 14, 1942)
the Gestapo destroyed the village of Lidice in Czechoslovakia (June 10, 1942)
Battle of Midway (June 3, 1942)

in the RAF´s 1000-bomber attack on Cologne (May 30, 1942) the city was
vitually destroyed; only 300 houses in the whole city escaped damage
Richard Heydrich was shot in Prague by Czech resistance fighters (May 27, 1942)
Battle of
the Coral Sea (May 6, 1942)
Japanese Army captured Mandalay in Burma (May 1, 1942)
the Luftwaffe started bombing Exeter, Bath and other historic cities in Britain
(April 23, 1942)
the United States Air Force bombed Tokyo (April 18, 1942)
Hermann Balck and the British 3rd Panzer Division captured Salonika (April 9, 1942)
Allied raid on St Nazaire
(March 27, 1942)
the Royal Air Force bombed Lübeck in Germany (March 23, 1942)
General Douglas MacArthur and the United States forces
left the Philippines (February 22, 1942)
Japanese Air Force bombed Darwin in Australia (February 19, 1942)
General Arthur Percival surrendered Singapore to Japanese (February 15, 1942)
the Scharnhorst and the Prinz Eugen started their
successfull break out of Brest (February 12, 1942)
Japanese troops landed on the northwest corner of Singapore (February 8, 1942)
USA government announced the establishment of relocation camps for Japanese Americans (January 29, 1942)
General Arthur Percival ordered retreat of British forces to Singapore (January 25, 1942)

the Wannsee conference (January 20, 1942) was a meeting
of german criminals discussing how to commit more mass murder
Japanese Army captured Kuala Lumpur, the capital of the Malaya (January 11, 1942)
Hong Kong surrendered with the loss of its 12,000 garrison
(December 25, 1941)
Japanese Army captured Manila, the capital of the Philippines (December 22, 1941)

the Arcadia Conference (December 22, 1941 - January 14, 1942)
Hitler sacked Walther von Brauchitsch as commander in chief of the German Army (December 19, 1941)
the National Service Act (December 18, 1941) which conscripted unmarried women, was passed by the British Parliament

Germany declared war on the United States (December 11, 1941) following the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor of December 7
America First Committee
was dissolved (December 11, 1941)
Japanese troops invaded Burma (December 11, 1941)
Japanese forces sunk the Prince of Wales and Repulse off the east coast of Malaya
(December 10, 1941)
Japanese troops invaded Malaya, Thailand and the Philippines (December 8, 1941)
Britain declared war on Finland, Hungary and Romania (December 5, 1941)
the Royal Air Force bombed the German city of Nürnberg (October 13, 1941)
the first Moscow Conference (September 29 - October 1, 1941)
the German Army captured Kiev, the Ukrainian capital in the Soviet Union (September 20, 1941)

the Yellow badge (September 1, 1941)
Military forces from Soviet Union and Britain invaded Iran (August 25, 1941)

Operation Typhoon (August 1941) was the German plan for the drive towards and invasion of Moscow
the German Army advanced on Leningrad (August 12, 1941)

the Atlantic Charter (August 14, 1941) was negotiated at the Atlantic Conference by British Prime Minister
Winston Churchill and U.S. President Franklin D. Roosevelt, aboard a warship anchored in a secure anchorage
at Argentia, Newfoundland (located on Placentia Bay) and was issued as a joint declaration. The Atlantic Charter
established a vision for a post-World War II world, despite the fact the United States had yet to enter the War. The
participants hoped in vain that the Soviet Union, since June invaded by her previous ally Nazi Germany, would adhere as well
Hungary declared war on the Soviet
Union (June 27, 1941)
Finland declared war on the Soviet Union (June 25, 1941)
Syria invaded by British Army and Free French forces (June 8, 1941)

Until attacked by it in June 1941, the Soviet Union was effectively allied with Nazi Germany through
the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact, invading and occupying parts or the whole of Poland, Finland, Estonia, Latvia,
Lithuania, and Romania. Operation Barbarossa, the German invasion of the Soviet Union, commenced on June 22, 1941
the Bismarck sunk the British battlecruiser Hood (May 24, 1941)
and was sunk in turn three days later by the Royal Navy
Rudolf Hess flew to Scotland and
was arrested by the authorities (May 10, 1941)
the Luftwaffe destroyed the House of Commons in Westminster (May 10, 1941)
General Erwin Rommel and his army entered Egypt (April 25, 1941)
Greece surrendered to the German
Army (April 21, 1941)
Marmaduke Pattle, RAF's leading war ace, was killed while fighting in Greece (April
20, 1941)
Yugoslavia surrendered to the German Army (April 17, 1941)
Yosuke Matsuoka of Japan
signed a non-aggression pact with Soviet Union (April 14, 1941)
Germany, Italy and Bulgaria invaded Yugoslavia
(April 10, 1941)
Italian Army in Ethiopia surrendered to Allied forces (April 6, 1941)
General Andrew Cunningham, commander of allied forces in East Africa, entered Addis Ababa
(April 6, 1941)
US Congress passed the Lend-Lease Act (March 11, 1941)
the British Army invaded Italian-controlled Ethiopia (March 7, 1941)
Bulgaria signed the Tripartite Pact and joined forces with Germany, Italy and Japan (March 1, 1941)

the Afrika Korps (February 19, 1941 - May 12, 1943) was sent to reinforce the Itlaian army, which had
been routed by an Allied counteroffensive, Operation Compass. The fighting was mostly for control of Libya and Egypt
British Army captured Tobruk (January 22, 1941)
the Royal Air Force bombed Hamburg
(November 16, 1940)
the Luftwaffe bombed Coventry (November 14, 1940)
the Royal Navy attacked the Italian Navy at Taranto (November 11, 1940)
Airbourbe radar was successfully used by the Royal Air Force for the first time (November 8, 1940)
Italy invaded Greece (October 28, 1940) from bases in Albania
Hitler met Francisco Franco in an attempt to persuade Spain to join the war (October 23, 1940)
Hitler postponed Operation Sealion (October 12, 1940)

the Tripartite Pact (September 27, 1940) was signed between Germany, Italy, and Japan formalizing
their alignment as the "Axis Powers." It was followed up by Yugoslavia's government succumbing
to the pressure of Italy and Germany and signing the Tripartite Treaty on March 25, 1941
Vidkun Quisling was installed by the Germans as prime minister of Norway
(September 25, 1940)
Winston Churchill decided to abandon the attempt to capture the port of Dakar (September
25, 1940)
City of Bernares sunk by a German torpedo killing 73 children on the way to Canada
(September 17, 1940)
Rodolfo Graziani and Italian Army made a rapid advance into Egypt (September 13, 1940)
the Royal Air Force bombed Berlin (August 25, 1940)
the Luftwaffe began attacking RAF Fighter Command's aircraft, airfields and installations (August 13, 1940)
the Italian Army
advanced into British Somaliland (August 3, 1940)
Winston Churchill invited Hugh Dalton to establish the Special Operations Executive
(July 16, 1940)
Henri-Philippe Petain became president of Vichy France (July 11, 1940)

the 3-month air war on Britain (July 10, 1940) was lost by October 30
the Royal Navy destroyed most of the French Navy at Mers-el-Kébir (July 3, 1940)
Winston Churchill recognized Charles De Gaulle as leader of the Free French (June 28, 1940)

France (June 24, 1940) officially surrendered to Germany,
after the Franco-German armistice was signed just two days
earlier and the country was divided into two zones

General De Gaulle formed (June 22, 1940) the Comité Français de la Libération Nationale, a French government in exile
the USA rejected France's renewed appeal for help against the German Army (June 15, 1940)
the German Army entered Paris (June 14, 1940)
Gotthard Heinrici and the 12th Corps broke through the Maginot Line (June 14, 1940)
Benito Mussolini declared war on the Allies (June 10, 1940)
Belgium surrendered to the German Army and Leopold III was arrested (May 28, 1940)

Operation Dynamo (27 May - 4 June 1940) was the name given to the
evacuation of 338,226 French and British soldiers from Dunkirk
General Gerd von Rundstedt and the German Army pierced the French defences at Sedan
(May 23, 1940)
Netherlands surrendered and Queen Wilhelmina fled to England (May 14, 1940)
Anthony Eden announced the formation of the Home Guard (May 14, 1940)
Neville Chamberlain resigned as prime minister and is replaced by Winston Churchill (May 10, 1940)
Hitler launched his Western Offensive (May 10, 1940)

Germany invaded Denmark and Norway (April 9, 1940) in Operation Weserübung,
ostensibly to counter the threat of an Allied invasion from the region
Britain and France agreed not to sign a separate peace with Nazi Germany (March 28, 1940)
Finland signed a peace treaty with the Soviet Union (March 12, 1940)
the Katyn massacre (March 5, 1940) was the mass execution of Polish citizens by the Soviet Union
Joseph Stalin formally annexed eastern Poland into the Soviet Union (November 2, 1939)
Germany formally annexed western Poland into the German Reich (November 1, 1939)
the Schutz Staffel (SS) established the first Jewish Ghetto in Piotrkow (October 28, 1939)
Franklin D. Roosevelt announced that the USA will remain neutral in the European war (October 3, 1939)

the Soviet Union invaded Finland (November 30, 1939) beginning the Winter War,
which lasted until March of 1940 with Finland ceding territory to the Soviet Union
the Polish Army surrenderd in Warsaw (September 27, 1939)
Reinhard Heydrich announced that all Jews in Poland were to be imprisoned in Ghettos (September 21, 1939)
the Soviet Red Army (September 17, 1939) invaded the eastern regions of Poland. The Soviets were
acting in co-operation with Nazi Germany, carrying out their part of the secret appendix of the Molotov-
Ribbentrop Pact (the division of Europe into Nazi and Soviet spheres of influence)

after the German invasion of Poland (September 1, 1939) France and the United Kingdom
honored their defensive alliance of March 1939 by declaring war two days later on 3 September

the Gleiwitz incident (August 31, 1939) was a staged attack against a German radio station in Gleiwitz.
There were other staged Polish-German border incidents (such as house torching in the Polish Corridor)
and spurious propaganda output. Together the Nazis claimed these incidents as the pretext for operation
Fall Weiss, the invasion of Poland the following day
Britain and Poland signed a treaty of mutal assistance (August 25, 1939)

the Molotov-Ribbentrop Pact (August 23, 1939) was signed in Moscow by the Soviet foreign
minister Vyacheslav Molotov and the German foreign minister Joachim von Ribbentrop
Sweden, Norway and Finland rejected Germany's offer of non-aggression pacts (May 17, 1939)
Soviet Union proposed a triple alliance with Britain and France (April 18, 1939)
Britain and France pledged to support Romania and Greece (April 13, 1939)
Italy invaded and occupied Albania (April 7, 1939)
Britain and France pledged to support Poland (March 29, 1939)
Hitler demanded the free city of Danzig in Poland (March 21, 1939)

Hitler arrived in Prague (March 15, 1939) and completed the occupation of
the German-speaking regions (Bohemia, Moravia) of Czechoslovakia

the Night of Broken Glass (November 9, 1938) was a massive nationwide pogrom in Germany
and Austria, directed at jewish citizens. The incident was a first step in the systematic persecution
and mass murder of Jews throughout Europe in what came to be known as the Holocaust

German troops marched into the Sudetenland (October 1, 1938)

the Munich Agreement (September 29, 1938) was an agreement regarding the Sudetenland
Crisis between the major powers of Europe after a conference held in Munich
Hitler ordered the mobilization of the German Army (August 12, 1938)
Francisco Franco, ruler of Spain, signed the anti-Comintern pact (April 7, 1938)

German troops crossed the border and occupied Austria (March 12, 1938)
Hitler created a new command (Febuary 4, 1938) for the German army, placing the old Wehrmacht
under it as the OKH department and made himself Supreme Commander of the all German armed forces

the Westwall (1938-1940)
Italy joined Germany and Japan in the Anti-Comintern Pact (November 6, 1937)

the Sino-Japanese war (1937-1945) began with the Japanese invasion of China on July 7, 1937
degenerate art (1937)
Guernica in Spain was bombed by the Luftwaffe (April 26, 1937)
Germany and Japan signed an anti-Comintern pact (November 25, 1936)
Hitler and Benito Mussolini agreed to form a military alliance (November 1, 1936)
der Vierjahresplan (October 1936)
Hitler introduced a compulsory two-year period of military conscription (August 24, 1936)

with the Propaganda Games (August 1936) for two weeks Hitler's Nazi dictatorship camouflaged its racist, militaristic
character while hosting the Summer Olympics. Softpedaling its antisemitic agenda and plans for territorial expansion, the regime
exploited the Games to bedazzle many foreign spectators and journalists with an image of a peaceful, tolerant Germany

the Spanish Civil war (July 1936 - April 1939) was a conflict in which incumbent Spanish Republicans
and left-wing groups fought against a nationalist rebellion led by General Francisco Franco, who
succeeded in overthrowing the Republican government and establishing a dictatorship which lasted
until his death in 1975

in violation of the Locarno Pact and the Treaty of Versailles (March 7, 1936) Nazi Germany reoccupied the Rhineland
Joseph Stalin began a ``great purge'' to liquidate his enemies (1936)
by 1939, over 8 million were dead and perhaps 10 million imprisoned
the Nürnberg laws (October 21, 1935)
Mussolini ordered the bombing of Adowa (October 2, 1935) by planes and the beginning of the invasion of Ethiopia
Adolf Hitler ordered Hermann Göring to reinstate the Luftwaffe (February 26, 1935) breaking the Treaty of Versailles
Paul von Hindenburg died (August 2, 1934) and Adolf Hitler became president as well as chancellor

the Night of the Long Knives (June 30, 1934) was a mass murder of
potential political rivals in the SA paramilitary wing of the Nazi Party

Reichskonkordat (July 20, 1933)
Book burning (May 10 - June 21 1933)
Hermann Göring formed the Gestapo from the former Prussian police (April 26, 1933)

Gleichschaltung (March 31, 1933-1937) was the process by which the Nazi regime successively established a
system of totalitarian control over the individual, and tight coordination over all aspects of society and commerce,
for example by eliminating all non-Nazi organizations, diminishing the influence of churches by instituting the
Ministry of Ecclesiastical Affairs, as well as setting up a Ministry for People’s Enlightenment and Propaganda

the Enabling Act (March 23, 1933) was the second major step after the Reichstag Fire Decree through
which the Nazis legally established Nazi Germany by providing the government with legislative powers,
effectively handing dictatorial powers to the chancellor Adolf Hitler
so called Concentration camps (March 20, 1933) were in fact extermination "factories", which the Nazi
regime had set up in order to commit the biggest genocide in history. Millions of jewish citizens were
deported to these camps to be tortured and killed

Responsibility (27 Februar, 1933) for the destruction by fire of Germany's parliament building the Reichstag,
according to the Nazis, was with the communists. Actually the fire had been laid by the Nazis themsleves
so that they were able to pinpont blame on their opposition. This method has been dubbed a "catch 23":
In order to solve a problem one has to create a larger problem

Hitler (January 30, 1933) was appointed Reichskanzler by Paul von Hindenburg

Unemployment (September 1932) reached more than thirty percent in Germany
Franz von Papen lifted the ban on the Sturm Abteilung (June 16, 1932)
the Sturm Abteilung was banned (April, 1932)
Paul von Hindenburg defeated Adolf Hitler in presidential elections (March 13, 1932)
Carl von Ossietzky was convicted of high treason and espionage (1931) after publishing details of Germany's
alleged violation of the Treaty of Versailles by rebuilding the Luftwaffe and training pilots in the Soviet Union

the Japanese invasion of Manchuria (1931)

the Maginot Line (1930-1936)
the Nazi party placed second in German elections (1930) but Adolf Hitler was kept from
his seat in the Reichstag because he did not have German citizenship. The former Austrian then
stateless citizen was awarded the German citizenship on February 26, 1932 by the city of Braunschweig
Standard Oil and IG Farben (November 9, 1929) signed a cartel agreement.

the Great Depression (1929-1939) was a massive global economic recession. It started on
Black Thursday, October 24, 1929 the day when the New York Stock Exchange crashed

the Kellogg-Briand Pact (August 27, 1928) was signed by Australia, Canada, Czechoslovakia, Germany,
India, the Irish Free State, Italy, New Zealand, South Africa, the United Kingdom, and the United States
the Nazi Party held its first Nürnberg Rally (July, 1927)

IG Farben (1926) was a German conglomerate of companies, that was the financial core of
the Hitler regime and the key supplier of poison gas to the Nazi racial extermination program

the Locarno Treaties (October 5-16, 1925) were formally signed in London on December 1, in which the World
War I Western European Allied powers and the new states of central and Eastern Europe sought to secure the
post-war territorial settlement, in return normalising relations with defeated Germany. The "spirit of Locarno" was
seen in Germany's September 1926 admission to the League of Nations, the international organisation established under
the Versailles treaty to promote world peace and co-operation, and in the subsequent withdrawal (completed in June
1930) of Allied troops from Germany's western Rhineland
the Schutz Staffel (June, 1925) was formed

for the crime of conspiracy to commit treason ( February 26, 1924 - December 20 1924) Hitler was sentenced to five years'
imprisonment at Landsberg prison where he received favoured treatment from the guards and had much fan mail from admirers.
While at Landsberg he dictated his political book Mein Kampf (My Struggle) to his deputy Rudolf Hess, which was published
in two volumes in July, 1925 and December, 1928

in the Beer Hall Putsch (November 8, 1923) the Kampfbund (a league of "patriotic" fighting societies and the German
National Socialist party in Bavaria) in league with Erich Ludendorff took over a meeting by the Bavarian Prime Minister,
Gustav von Kahr, at a beer hall in Munich. Ludendorff and Hitler declared a new government and planned to take
control of Munich the following day
Fritz Thyssen (1923) started to support the NSDAP

the Inflation (1923-1924) came about when by 1923 the Weimar Republic could no longer afford to maintain the reparation
payments for world war one as stated in the treaty of Versailles and the new government defaulted on payments. In response,
French and Belgian troops occupied the Ruhr region, Germany's most valuable industrial area at the time, taking control of the
mining and manufacturing companies in January of 1923. Strikes were called for, and passive resistance was encouraged. The
strikes had to last for eight months, which caused the German economy to suffer. Since striking workers also had to be paid
by the state, additional currency was printed, which fuelled a period of hyperinflation. The value of the Mark declined from 4.2
per US dollar to 1,000,000 per dollar by August 1923 and 4,200,000,000,000 per dollar on November 20. On December 1,
a new currency was established at the rate of 1,000,000,000,000 old marks for 1 new mark, the Rentenmark
der Stürmer (1923-1945)

the Ruhr Crisis (January 1923 - August 1925) occurred in 1923 when Germany stopped making their reparation
payments required by the Treaty of Versailles. In response, France, under Poincaré, occupied the Ruhr Area

Upper Silesia (October 10, 1921) was devided between Germany and Poland
after Upper Silesia voted to remain German in a plebiscite on March 20
Hitler became chairman of the NSDAP (July 29, 1921)
the Abwehr (1921-1944)
the Sturm Abteilung (October, 1920) was formed
der Völkische Beobachter (1920-1945)

the Weimar Republic (August 11, 1919 - January 30, 1933) was the first attempt at establishing a liberal democracy in Germany

the Treaty of Sèvres (August 10, 1920)

Dolchstosslegende (November 1919)

the Conservative Revolutionary movement (1919)

Prohibition (1919- 1933) in the U.S.
the Treaty of Saint-Germain (September 10, 1919) declared the Austro-Hungarian Monarchy dissolved. The new republic of Austria,
consisting of most of the German-speaking part of the former Austrian Empire, recognized the independence of Hungary, Czechoslovakia
Poland, and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes. Austria was reduced not only by the loss of crownlands incorporated into
Czechoslovakia, Poland, and Yugoslavia (the "successor states") but by the cession of Trentino, South Tyrol, Trieste, Istria, several
Dalmatian islands, and Friuli to Italy and the cession of Bukovina to Romania. In total, it lost land to Czechoslovakia, Yugoslavia,
Poland, Romania, and Italy. Burgenland, then a part of Hungary, was awarded to Austria. An important article of the treaty required
Austria to refrain from directly or indirectly compromising its independence, which meant that Austria could not enter into politica
or economic union with Germany without the agreement of the council of the League of Nations.
Mussolini launched his fascist movement (March 23, 1919)
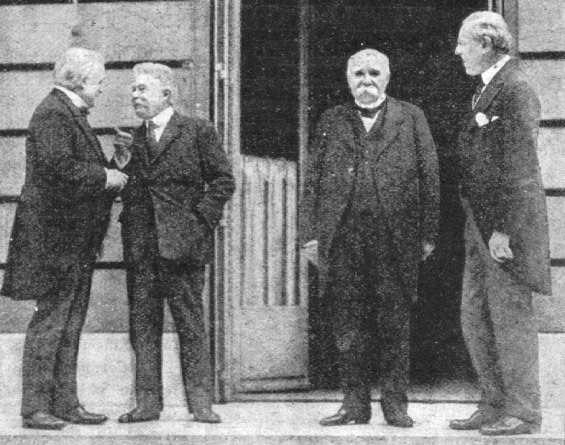
the Paris Peace Conference (January 18, 1919 - January 21, 1920) was dominated by the 'Big Three': David Lloyd
George of Britain, Georges Clemenceau of France and Woodrow Wilson of the United States of America. They
prepared treaties regarding Germany, Austria, Bulgaria, Hungary, Palestine and the Ottoman Empire. Among these
the Treaty of Versailles (June 28, 1919) put an official end to World War I between the Allies and Central Powers.
Also the decision to create the League of Nations and the approval of its Charter both took place during the conference.
The creation of the League was a centrepiece of Wilson's Fourteen Points for Peace
Kaiser Wilhelm II of Germany
abdicated (November 9, 1918)
Italian Vittorio Veneto Offensive (October 23, 1918)
Allied forces captured the Hindenburg Line
(October 5, 1918)
Canal du Nord Offensive (September 27, 1918)
Meuse-Argonne Offensive
(September 26, 1918)

Bulgaria (September 29, 1918) was the first of the Central Powers to sign an armistice in the first wold war. Germany
requested a cease-fire on October 3, 1918. When Wilhelm II ordered the German High Seas Fleet to sortie against the
Allied navies, they mutinied in Wilhelmshaven starting October 29, 1918. On October 30 the Ottoman Empire capitulated.
On November 3 Austria-Hungary sent a flag of truce to the Italian Commander to ask an Armistice and terms of peace.
The terms having been arranged by telegraph with the Allied Authorities in Paris, were communicated to the Austrian
Commander, and were accepted. The Armistice with Austria was granted to take effect at three o'clock on the afternoon
of November 4. Austria and Hungary had signed separate armistices following the overthrow of the Habsburg monarchy
United States St Mihiel Offensive
(September 12, 1918)
Allied breakthrough at Albert (August 21, 1918)
the Thule Society (August 17, 1918)
Amiens Offensive (August
8, 1918)
2nd Battle of the Marne
(July 15, 1918)
the last crowned Emperor of Russia (July 17, 1918) King of Poland and Grand Duke of Finland Czar
Nicholas II and his family was killed by the new Bolshevik government that had taken over control of
the country in the Russian Revolution of 1917
Battle of Le Hamel
(July 4, 1918)
3rd Battle of the Aisne
(May 27, 1918)
the Gulag (1918)
Foch appointed Allied Co-ordinator in France
(March 29, 1918)

Operation Michael (March 21, 1918) opened with an attack against the British towards the rail junction at Amiens.
It was Ludendorff's intention to split the British and French armies at this point. German forces achieved an
unprecedented advance of 60km. For the first time since 1914, manoeuvre had returned to the battlefield

treaty of Brest-Litovsk (March 3, 1918)
the forerunner of the NSDAP (January 1918) a party called the Freier
Ausschuss für einen deutschen Arbeiterfrieden was created in Bremen
Wilson announced 14 Points Peace Programme (January 8, 1918)
Massed tank attack at Cambrai
(November 20, 1917)
Sir Frederick Maude
died in Mesopotamia (November 18, 1917)

the battle of Caporetto (October 24 - November 9, 1917) took place near Kobarid (now Slovenia) on the Austro-Italian
front of World War I. Austro-Hungarian forces, reinforced by German units, were able to break into the Italian front
line and rout the Italian army, which had practically no mobile reserves. Austro-German forces advanced more than
100 km in the direction of Venice, but they were not able to cross the river Piave, where the Italians (with substantial
help from French, British and American allies) established a new defensive line, which they held for the rest of the war
British Offensive at
Passchendaele (October 12, 1917)
Greece declared war on the Central Powers (June 29, 1917)
United States troops arrived in France (June 25, 1917)
British attack at Messines (June 7, 1917)
Maria Bochkareva formed the Women's Battalion (May 16, 1917)
Petain became French Western Front C-in-C
(May 15, 1917)
French tanks used for the first time in battle (April 17, 1917)
2nd Battle of the Aisne (April 16, 1917)
Canadian Army captured Vimy Ridge (April 12, 1917)
Arras offensive
(April 9 - May 16, 1917)

President Woodrow Wilson (April 6, 1917) requested that the U.S. Congress declare war on Germany.
The Senate approved the war resolution. Wilson hoped a separate peace could be achieved with Austria-Hungary,
however when it kept its loyalty to Germany, the US declared war on Austria-Hungary in December 1917
the first Battle of Gaza (March 26, 1917)
Zimmermann Telegram intercepted by Britain (January 19, 1917)
Nivelle became French Western Front C-in-C (December 12, 1916)
Beatty replaced Jellicoe as C-in-C of Grand Fleet (November 29, 1916)
French recaptured Douaumont Fort at Verdun (October 24, 1916)
First use of British tanks at Flers-Courcelette (September 15, 1916)

Erich von Falkenhayn resigned as Chief of the General Staff (August 1916) Paul von Hindenburg took his place, with
Ludendorff as his First Generalquartiermeister (Deputy Chief of Staff), forming the so-called Third Supreme Command.
The "Third OHL", (Oberste Heeresleitung or "Supreme Army Command"), was effectively
a military-industrial dictatorship, which largely relegated Kaiser Wilhelm II to the periphery
Italian Gorizia Offensive (August 9, 1916)

the battle of the Somme (July 1, - November 18, 1916)
Lord Kitchener killed at sea
(June 5, 1916)
Russian Brusilov Offensive
(June 4, 1916)
Battle of Jutland (May 31, 1916)
the Sykes-Picot Agreement (May 16, 1916)
Germany declared war on Portugal (March 9, 1916)

the battle of Verdun (February 21 - 19 December 1916)
Britain introduced conscription (February 2, 1916)
Battle of Łódź
(November 11 - December 6, 1914)
Edith Cavell was executed
(October 12, 1915)
Allied troops landed at Salonika
(October 5, 1915)
Anglo-French Offensive at Artois-Loos (September 25, 1915)
First tank demonstrated to British military leaders
(September 11, 1915)
Grand Duke Nikolai sacked as Commander-in-Chief
(September 6, 1915)
Suvla Bay Offensive at Gallipoli
(August 6, 1915)
Isonzo Offensive (June
23, 1915)
First Zeppelin raid on London (May 31, 1915)
Italy joined the Allies after they declared war on Austria-Hungary (May 23, 1915)
Artois Offensive
(May 9, 1915)
Allied landings at Gallipoli
(April 25, 1915)

the Armenian Genocide (April 24, 1915)
German gas attack at Ypres (April 22, 1915)
Allied naval attack on the Dardanelles
(March 18, 1915)
BEF attacked at Neuve Chapelle
(March 10, 1915)
Battle of Dogger Bank
(January 24, 1915)
South African forces occupied Swakopmund (January 14, 1915)
Christmas Truce on the Western Front
(December 25, 1914)
Anglo-Indian invasion of Mesopotamia (November 21, 1914)
Turkey joined Central Powers (October 29, 1914)
Canadian troops arrived in Britain (October 16, 1914)
Battle of Ypres
(October 15, 1914)
the Battle of Albert (September 25, 1914) and the Battle of Arras ( October 1, 1914)
were encounter battles during
the Race to the Sea
French troops attacked German Army at the River Aisne (September 13, 1914)
Battle of the Marne
(September 6, 1914)
War Propaganda Bureau Writers Conference (September 2, 1914)
Battle of Helgoland (August
28, 1914)
Battle of Tannenberg
(August 26, 1914)
French Army abandoned Plan 17
(August 24, 1914)
Battle of Mons (August
23, 1914)
British Expeditionary Force
arrived in France (August 22, 1914)
French troops entered Lorraine
(August 14, 1914)
Austro-Hungarian troops invaded Serbia (August 12, 1914)
Big Bertha used against Liege Forts
(August, 12 1914)
Moltke (August 4, 1914) ordered the Schlieffen Plan to proceed

Austria-Hungary declared war on Serbia through a telegram (July 28, 1914) after Serbia failed to meet
the conditions of an ultimatum set on July 23 and refused to hand over the leaders of the Black Hand
group. Germany declared war against Russia on August 1 and, two days later, against the latter's ally
France. Britain declared war against Germany on August 4. This was not officially the result of
understandings with France and Russia (Britain was technically allied to neither power),
but of Germany's invasion of Belgium on August 4, 1914
Austra-Hungary demanded that Serbia arrest the leaders of the Black Hand (July 23, 1914)

Franz Ferdinand, Archduke of Austria (June 28, 1914) and heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne,
was assassinated in Sarajevo by Gavrilo Princip, a Bosnian Serb student. After the assassination
of Franz Ferdinand, after nearly a month of debate, the government of Austria-Hungary sent a
10-point ultimatum to Serbia (July 23, 1914), to be accepted within 48 hours
the Bosnian Crisis (1908)

the Triple Entente (1907) was the alliance between the United Kingdom,
France and Russia after the signing of the Anglo-Russian Entente

the Entente cordiale (8 April, 1904) is a series of agreements between the United Kingdom and France.
Beyond the immediate concerns of colonial expansion addressed by the agreement, the signing of the Entente
Cordiale marked the end of centuries of intermittent conflict between the two nations, and the start of the
peaceful
co-existence that continues to the present day
the Russo-Japanese war (February 8, 1904-1905)
Basil Zaharoff (1900s)
Krüger Depesche (January 3, 1896)
alldeutscher Verband (1891-1939)

the Triple Alliance (May 20, 1882) was the treaty by which Germany, Austria-Hungary and Italy pledged
to support each other militarily in the event of an attack against any of them by two or more great powers