

Saddam Hussein (December 30, 2006) was hanged
Saddam Hussein was sentenced to death by hanging (November 5, 2006)
Khamis al-Obeidi (June 21, 2006) was a lawyer defending Saddam Hussein and Barzan Ibrahim al-Tikriti,
from the time the former leader's trial began in Baghdad on October 19, 2005 until his assassination
Abu Musab al-Zarqawi (June 7, 2006) was killed in a targeted attack by the US military
Nouri al-Maliki (April 22, 2006) was named prime minister-designate by President Jalal Talabani
the Al Askari Mosque bombing (February 22, 2006)
Iraq elected a permanent government (December 2005)
Al-Dujail trial (October 2005)
a majority of the Iraqi people voted in an election (January 30, 2005) conducted by their transitional government
which elected a 275-member Transitional National Assembly. The Assembly will: Draft Iraq's new constitution,
which will be presented to the Iraqi people for their approval in a national referendum in October 2005
Saddam Hussein (June 30, 2004) along with 11 senior Ba'athist officials,
was handed over legally to the interim Iraqi government to stand trial
the occupation was formally ended by the U.S.-led coalition (June 28, 2004)
which transferred power to an interim Iraqi government led by Prime Minister Iyad Allawi
Nick Berg (May 12, 2004)

Al Hurra (Febuary 14, 2004)

Saddām captured by U.S. forces (December 13, 2003) he will stand trial before
the Iraq Special Tribunal, established by the Iraq Interim Government
Chemical Ali (August 21, 2003) was captured

Saddam's two sons (July 22, 2003) were killed in an engagement with U.S. forces after a tip-off from an Iraqi informant
the initial US interim civil administrator, Jay Garner (May 2003) was replaced by
L. Paul Bremer, who was himself replaced by John Negroponte in April 19, 2004
the March 2003 invasion
Operation Desert Fox (December 16-18, 1998)
Al Jazeera (1996)
the Oil-for-Food Program (1996-2003)
the Persian Gulf war (January 17, 1991)

Nayirah (October 19, 1990)
the U.N. Security Council adopted Resolution 661 (August 6, 1990) which imposed stringent economic sanctions on Iraq,
providing for a full trade embargo, excluding medical supplies, food and other items of humanitarian necessity, these to be
determined by the Security Council sanctions committee
Iraq invaded Kuwait (August 2, 1990)
Iran-Iraq War (1980-1988)
Saddam Hussein (1979-2003)
the coup (1968) that brought the Baath party to long-term power
Iraq signed the Baghdad Pact (1956) it allied Iraq, Turkey, Iran, Pakistan, the United States and the United Kingdom.
Its headquarters were in Baghdad. The Pact constituted a direct challenge to Egyptian president Gamal Abdal Nasser.
In response, Nasser launched a media campaign that challenged the legitimacy of the Iraqi monarchy.
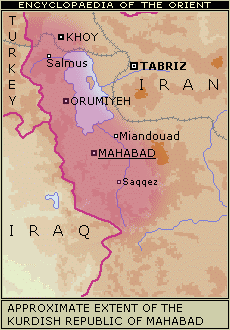
the republic of Mahabad (1946)
Iraq was carved out of the Ottoman Empire by the French and British as agreed in the Sykes-Picot Agreement.
On November 11, 1920 it became a League of Nations mandate under British control with the name "State of Iraq".
Iraq became a part of the Ottoman Empire (16th century)
the Black Sheep Turkmen (late 14th and early 15th centuries) ruled the area now known as Iraq.
In 1466, the White Sheep Turkmen defeated the Black Sheep and took control.
the Abbasid Caliphate established its capital at Baghdad (eighth century)
an army of 18,000 Arab Muslims (634) under the leadership of Khalid ibn al-Walid, reached and conquered the Euphrates
delta. Although the occupying Persian force was vastly superior in techniques and numbers, its soldiers were exhausted
from wars against the Byzantine Empire. The Sassanid troops fought ineffectually, lacking sufficient reinforcement
Nebuchadrezzar II (586 bc) conquered Judea, destroyed Jerusalem; Solomon's Temple was also destroyed;
Nebuchadrezzar carried away an estimated 15,000 captives, and sent most of its population into exile in Babylonia.
the great Akkadian leader Sargon (2340 bc) conquered Sumer and built the Akkadian Empire stretching over most of the
Sumerian city-states and extending as far away as Lebanon. Sargon based his empire in the city of Akkad, which became
the basis of the name of his people
Ur (25th century bc)
the Elamites (2700 bc)
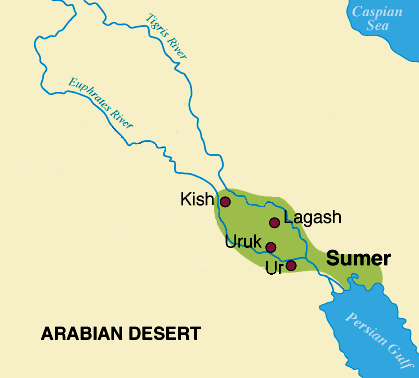
Uruk (3500 bc)
it was in Mesopotamia about 4000 BC where the Sumerian culture flourished
the Ubaid culture (5000 bc)