

the annexation of Greece by Rome (146 bc)
Macedonian wars (215-168 bc)
the Chremonidean war (267-261 bc) was fought by a number of Greek states against Macedon domination
the Ptolemaic dynasty (305-30 bc)
the Lamian war (323-322 bc) was a war in Greece between Athens and her allied city-states in
mainland Greece and Macedonia. It was the last war in which the Athenians played a central part
the Diadochi wars (322-315 bc)
in the Battle of Issus (333 bc) Alexander the Great of Macedonia defeated
Darius III of Persia. Alexander´s campaign had started one year earlier and
reached its eastern most part at the Beas River in 336 bc
Aristotle started the Lyceum (335 bc)
the Battle of Chaeronea (338 bc)
Plato founded the Academy (387 bc)
the trial of Socrates (399 bc)
Sparta captured the Athenian silver mines at Laurion (407 bc) and released around 20,000 slaves
the Thirty Tyrants were a pro-Spartan oligarchy (April 404 bc) installed in Athens after its defeat in the
Peloponnesian war. They were overthrown by the exiled general Thrasybulus and his allies from Thebes in 403 bc
the Peloponnesian war (431-404 bc) between the Athenian empire and
the Peloponnesian league which included Sparta and Corinth lasted 27
years, with a 6-year truce in the middle, and ended with Athens' surrender
the Age of Pericles (439-338 bc)
the Histories of Herodotus (440 bc)
the battle of Coronea (447 bc)
the Peace of Callias (449 bc)
the magnificent temple of Zeus (450 bc) was designed by the architect Libon
Sparta (457) needing a counterpoise against Athens in central Greece, reversed her policy and reinstated Thebes as the dominant power in Boeotia
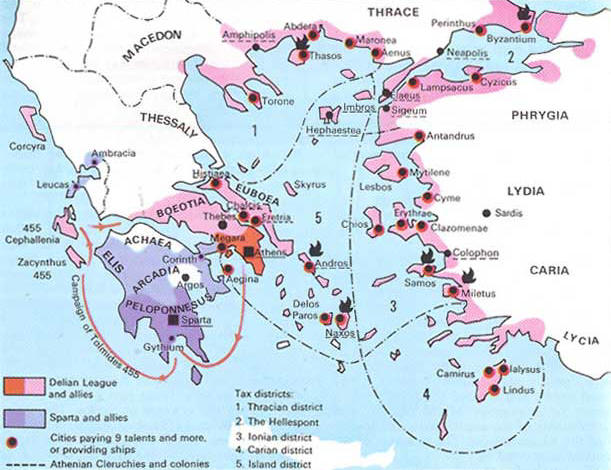
the Delian League (478 bc)
the battle of Mycale (479 bc)

the battle of Plataea (479 bc)
the battle of Salamis (September 480 bc)
the battle of Thermopylae (August 480 bc)
a Rich Seam of Silver was discovered in the Laurion Mines (490 bc) Themistocles
subsequently persuaded the Athenians to use some of the proceeds to build a fleet of warships
the battle of Marathon (490 bc)
the Ionian Revolt (499 bc)
the Greco-Persian wars (500-448 bc)
the Crotoniats (510 bc) razed Sybaris to the ground and turned the waters of Crathis to flow over its ruins
Pythagoras founded a school in Croton (523 bc) which can be said to have been the first
university in history. He was also the first to coin the terms philosophy and mathematics
Hippias (527 bc)

the Acropolis (550 bc)
Peisistratos (561 bc)
the Council of the Four Hundred (594 bc)
Solon (594 bc) was appointed archon of Attica in the world's first democratic system of government
the Seven Sages of Greece (620-550 bc)
Draco's code of law (621 bc)
Megacles (632 bc)
Annual archons (682-614 bc)
the Illiad (8th century bc)
the Odyssey (8th century bc)
Decennial archons (753-683 bc)
Alcmaeon (755-753 bc)
the Olympic games (776 bc - 393 ad)
Ancient Greece (776 - 146 bc) was also called the Delian League which was formed after a coalition of
Greek states thwarted an attempted invasion of the Greek peninsula by the Persian empire in
.
Under Alexander the Great Greece was able to extent its boundaries as far as India and included Persia,
Egypt and Mesopotamia. However, the Greek era known as the Hellenistic Age came to end with
.
Messenian wars (800 bc)
the Dorian invasion (1150 bc) of Greece led to the end of the Bronze Age Mycenaean civilization
the Trojan war (1193-1183 bc)

the oracle of Delphi (1??? bc)

the Eleusinian Mysteries (1500 bc)
Mycenaean Greece (1600-1100 bc) is the Late Helladic Bronze Age civilization of Greece
the Aegean civilization (2??? bc)
the Minoans (3000 - 1450 bc) were a pre-Hellenic Bronze Age civilization in Crete