![]()
![]()
Khabibullo Ismailovich Abdusamatov's contradiction (2007) of the prevailing scientific opinion on climate change

the modern panorama map (1930s) was developed by Heinrich C. Berann
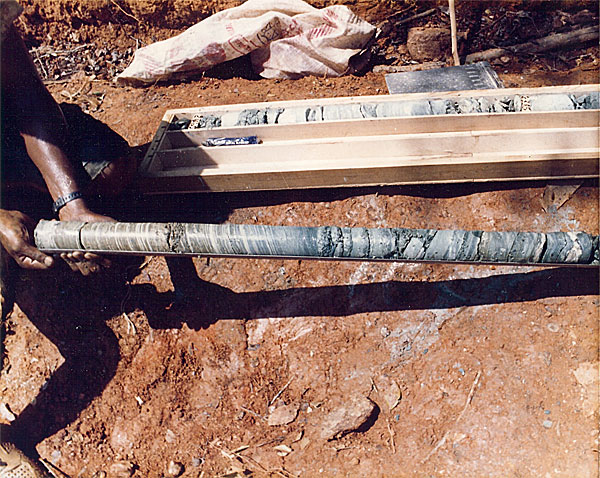
the Kola Superdeep Borehole (1970)
the butterfly effect (1963)
Seafloor Spreading (1960) was proposed by Harry Hess
Thermoluminescence dating (1950s)
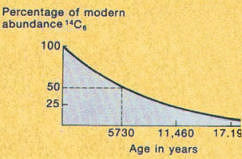
carbon-14 dating (1947) was introduced by Willard Libby

the Richter scale (1935)
Alfred Wegener's The Origin of Continents and Oceans (1915)
Echo sounding (1912)
the theory of continental drift (1912) was proposed by Alfred Wegener
the first uranium-lead radiometric dating (1910) was performed by Arthur Holmes
the Mohorovičić discontinuity (1909)
the troposphere and the stratosphere (1906) were named by Léon de Bort
the ionosphere (1902) was discovered by Oliver Heaviside and Arthur Edwin Kennelly
the idea that changes in the levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere (1896) could substantially
alter the surface temperature through the greenhouse effect was first formulated by Svante Arrhenius
El Niño (1892)
the National Geographic Society (January 27, 1888)

the International Meridian Conference (1884)
the International Meteorological Organization (1873)
the Challenger Expedition (1873-1876) discovered the Marianas Trench and confirmed the
presence of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge using marked rope and timed intervals for their ocean soundings

the first successful laying of a Transatlantic telegraph cable (August 1858)
revealed the presence of a mid-ocean ridge
the Temperature record (1850)
Alcide d'Orbigny's Prodrome de Paléontologie Stratigraphique (1849)

Roderick Murchison's Silurian System (1839)
Charles Lyell's Principles of Geology (1833)
Wiliam Smith's Strata Identified by Oragnised Fossils (1816)
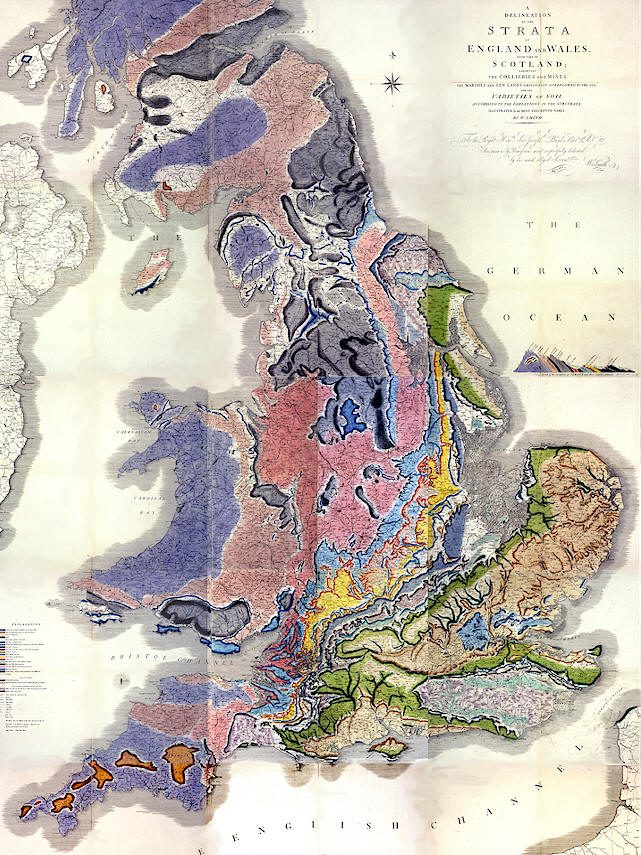
William Smith's geological map of England and Wales (and part of Scotland) (1815)
James Hutton's Theory of the Earth (1795)
the principle of faunal succession (early 1790s)
Buffon's Histoire naturelle, générale et particulière (1788)
Joseph Priestley (1772) showed that growing plants can restore air
that has been made 'lifeless' by animals breathing it or fire burning in it
Pierre Louis Maupertuis acted as chief of an expedition (1736) sent by
King Louis XV to Lapland to measure the length of a degree of the meridian
the sextant (1730)
John Harrison designed and built the world's first successful chronometer (1730) a maritime clock,
whose accuracy was great enough to allow the determination of longitude over long distances
the Longitude prize (1714)

Edmund Halley's hollow Earth theory (1692)
Nicolas Steno's De solido intra solidum (1669)
René Descartes published an explanation for rainbows and cloud formation (1637)
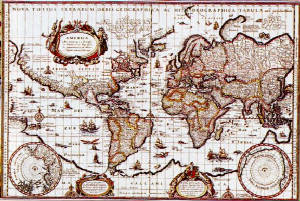
the Mercator projection (1569)

Agricola's De re metallica (1556)
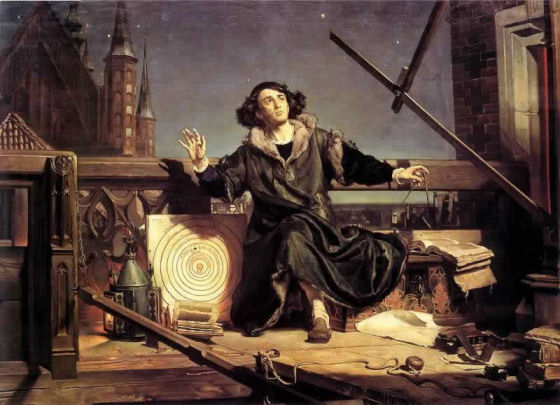

Nicolaus Copernicus (1543) was an astronomer who provided the first modern formulation of a heliocentric
(sun-centered) theory of the solar system in his epochal book On the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres

the first globe known as the "Nürnberg Terrestrial Globe" (1492) was finished by Martin Behaim

Toscanelli s world map (1474)
the Age of Discovery (early 15th century - early 17th century)

explanations for the rainbow phenomenon (1300)
Muhammad al-Idrisi's mappa mundi (1154)

the earliest record about the use of a compass in
navigation (1117) was Zhu Yu's
book "Pingzhou Ke Tan"
(Pingzhou Table Talks). Alexander Neckam has preserved to us the earliest
European notices of the magnet
as a guide to seamen in his work De naturis rerum, 1190
Shen Kuo's Dream Pool Essays (1088)
mappae mundi (Middle Ages)
the Venerable Bede On the Nature of Things (early 8th century)
Ptolemy's Geographia (150)

Chinese philosopher Chang Heng invented a seismoscope (132)

Hipparchus (150 bc) invented the astrolabe

Eratosthenes calculated the circumference of the Earth to be 39,690 km (240 bc) today it is measured at 40,008 km
Eratosthenes' map of the world

armillary spheres (255 bc)
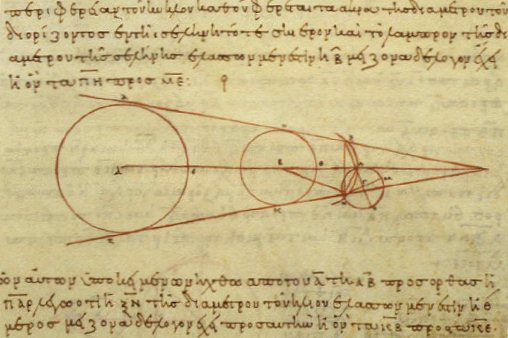
Aristarchus of Samos (around 250 bc) was the first to propose that
the sun is the center of the universe and that the earth moves around it
Strato of Lampsacus (310 bc) can be regarded as the first philosopher to formulate a worldview,
in which the universe is regarded as a mechanism and transcendent forces (i.e. deities) are nonexistent

Pytheas suggested (330 bc) that the tides were caused by the moon
and described the Midnight Sun, the aurora and Polar ice
Aristotle argued for a spherical Earth (ca 330 bc)
Eudoxus (around 380 bc) calculated the 23,6 degree tilt of the Earth
Hecataeus' map (ca 500 bc)

Xenophanes (540 bc) concluded from his examination of fossils
that water once must have covered all of the Earth's surface
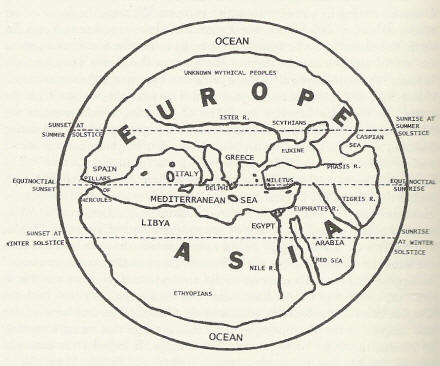
Anaximander created the first map of the world (580 bc)