![]()
the Cenozoic Era (65,000,000 bc)
Eomaia scansoria (125,000,000 bc) Ancient Mother
the formation of the Andes extends into the Paleozoic Era, when terrane accretion was the dominant process.
It was during the Cretaceous Period that the Andes began to take their present form, by the uplifting, faulting and
folding of sedimentary and metamorphic rocks of the ancient cratons to the east

the Cretaceous (146,000,000 - 65,500,000 bc) was the period when dinosaurs were at their most diverse
Pangaea (180,000,000 bc) began to break up

the Megazostrodon (180,000,000 bc) is one of the earliest mammals that we know of today

Hadrocodium wui (190,000,000 bc)
the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event (200,000,000 bc)
the Jurassic period (202,000,000 - 146,000,000 bc)
first dinosaurs (200,000,000 bc) evolved from reptiles called Archosaur

Cynognathus (210,000,000 bc) was among the first of the eucynodonts

Antetonitrus ingenipes (210,000,000 bc) was an early sauropod (first dinosaurs to walk on four short, equal-length legs)
the continents fused into one ie Pangaea (225,000,000 bc)
the Triassic period (245,000,000 - 202,000,000 bc)
Archosauromorpha (248,000,000 bc)
the Permian-Triassic extinction event (250,000,000 bc) wiped out about
95% of all animal species, it was the most severe mass extinction known
the Mesozoic era (251,000,000 - 65,000,000 bc) was the age of dinosaurs

Therapsids () previously known as the "mammal-like reptiles", are an order of synapsids

Eryops (299,000,000 bc) although it had no direct descendants, it is the best-known Permian amphibian
the Permian period (299,000,000 - 248,000,000 bc)

the Pelycosaurs (310,000,000 bc) were were the first Synapsids

Hylonomus lyelli (315,000,000 bc) was one of the first known reptiles
(and as such was the first creature to lay an egg, known as the 'amniote egg' on land

the cotylosaur (350,000,000 bc) is an evolutionary intermediate between amphibians and reptiles
the Carboniferous period (359,200,000 - 299,000,000 bc)

Ichthyostega (362,500,000 bc) is seen as a hybrid between a fish and an amphibian

Acanthostega (363,000,000 bc)
Amphibians (390,000,000 bc) are a taxon of animals that include all
tetrapods (four-legged vertebrates) that do not have amniotic eggs

fish left the water (365,000,000 bc)
the late Devonian extinction (365,000,000 bc)

fish (400,000,000 bc)
the Devonian period (416,000,000 - 359,200,000 bc)
first vascular land plants (420,000,000 bc)
the Silurian period (443,700,000 - 416,000,000 bc)
the Ordovician-Silurian extinction events (444,000,000 bc)

Ostracoderms (450,000,000 - 400,000,000 bc) are the ancestors of fish
first land plants (450,000,000 bc)

Molluscs ()

Conodonts () are the earliest known true chordates

Annelids ()

Pikaia () is the first known animal with a notocord

sea lilies (488,300,000 bc)
the Ordovician period (488,300,000 - 400,000,000 bc)
evolution of neurons (543,000,000 bc)
![]()
Euthycarcinoids (543,000,000 bc) relatives of modern centipedes ventured ashore

Arthropods (545,000,000 bc)
during the Cambrian explosion (565,000,000 - 525,000,000 bc) the first real animals, such as the Sponge, developed
the Paleozoic Era (565,000,000 - 251,000,000 bc)
evolution of the last 3 kingdoms (4th, 5th and 6th) (900,000,000 bc) from early protists:
fungi, from fungi like protists
first plants are algae-like , from plant-like protists
first animals which are sponges, from animal-like protists

the first Multicellular organisms (1,000,000,000 bc) were initially colonial algae and later, seaweeds
the Neoproterozoic era (1,000,000,000 - 565,000,000 bc)
evolution of early protists (3rd kingdom) (1,200,000,000 bc) from primitive eukaryotic cells

Sexual reproduction (1,200,000,000 bc) evolved and led to an explosion in the rate of evolution

the Oxygen level (1,500,000,000 bc) in the atmosphere reached its present day level and stabilized

the Milky Way (2,000,000,000 bc) started to swallow Canis Major Dwarf

more complex Cells (2,100,000,000 bc) appeared as Eukaryotes, which contain various organelles
during the Proterozoic eon (2,500,000,000 - 570,000,000 bc) first multicellular life developed

the first Stromatolites (2,800,000,000 bc) (attached, lithified
sedimentary growth structures) started to exist in the Mesoarchean era

Photosynthesizing cyanobacteria (3,000,000,000 bc) evolved, they used water
as reductant, thereby producing oxygen as the waste product
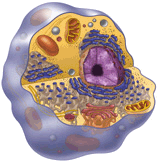
Cells (3,800,000,000 bc) resembling prokaryotes appeared, they are chemoautotrophs,
which use carbon dioxide as a carbon source and oxidize inorganic materials to extract energy.
They are divided into Archaebacteria (1st kingdom) and Eubacteria (2nd kingdom)

Life (3,800,000,000 bc) appeared on earth for the first time possibly in the form of self-reproducing RNA molecules
the Archean eon (3,800,000,000 - 2,500,000,000 bc) saw the evolution of the first unicellular life
the Primordial Soup (4,000,000,000 bc) was the Origin of Life. It consisted of
the first simple molecules like, water (H2O), methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3)