

the Human Genome Project (2000) announced having completed its task
Louise Brown (July 25, 1978)
in the first instance of genetic engineering (1978) Stanley Cohen and Herbert Boyer splice together fragments
of bacterial DNA and introduce this "recombinant" DNA into a strain of Escherichia coli bacteria
restriction enzymes (1978) were discovered by Werner Arber
Ebola (1976)
positron emission tomography (1974)
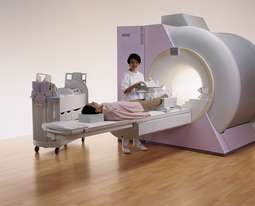
Magnetic resonance imaging (1973)
computed axial tomography (1972)
Cosmetic surgery (70s)

the first documented case of HIV (1966) in Europe dates to 1966 when a 20-year-old Norwegian sailor,
who had traveled to Africa, checked himself into a hospital. The official date for the beginning of the AIDS
epidemic is marked as June 5, 1981

the first working laser was made (1960) by Theodore H. Maiman.
The term was laser itself was coined in 1959 by Gordon Gould
the health care system (1950s)

the WHO (April 7, 1948)
the citric acid cycle (1937)
the Rh Factor (1937)
Arthroscopy (1921)
Casimir Funk (1912) coined the term Vitamin
three types of human blood (1900) were discovered Karl Landsteiner, which were
later named A, B, and O. In 1902 he discovers a fourth type, to be named AB
Chiropractic (1895)
Christiaan Eijkman (1893-1897) found that fowl fed only polished rice develop a condition resembling beriberi (a disease caused
by lack of vitamin B1). He concludes that disease can be caused by depriving the body of certain substances, later known as vitamins
health insurance (late 19th century)
Louis Pasteur successfully used his vaccine against rabies (July 6, 1885) on 9-year old Joseph Meister
pasteurization (1862)
Gray's Anatomy (1858)
the orthopedic cast (1851)
the two-part telescoping gelatin capsule (1848)

in the first public demonstration of diethyl ether as an anesthetic agent (October 16, 1846)
William Thomas Green Morton removed a vascular tumour from the neck of his patient
operating rooms (1822)
the spectroscope (1814) was invented by Joseph von Fraunhofer
Homeopathy (1796)
the first successful vaccine (1796) was developed by Edward Jenner from cowpox to cure smallpox

on the recommendation of Scottish physician James Lind (1795) sailors in the British navy are given lime juice to prevent scurvy
Julien Offray de La Mettrie's L'homme machine (1747)
Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit invented the first mercury thermometer (1714)

microorganisms (1676) were discovered by Anton van Leeuwenhoek
Francesco Redi disproved the theory of spontaneous generation (1668) with experiments on flies
Jan Swammerdam (1668) observed and described red blood cells with his microscope
Thomas Willis' Cerebri Anatome (1664) was the first monograph on brain anatomy and physiology
Capillaries (1661) were discovered by Marcello Malpighi
William Harvey announced his discovery of the circulatory system (1616) and in
1628 published his work Exercitatio Anatomica de Motu Cordis et Sanguinis in Animalibus
Sanctorius' studies of insensible perspiration originated the study of metabolism (1614)
Michael Servetus' Christianismi Restitutio (1553)
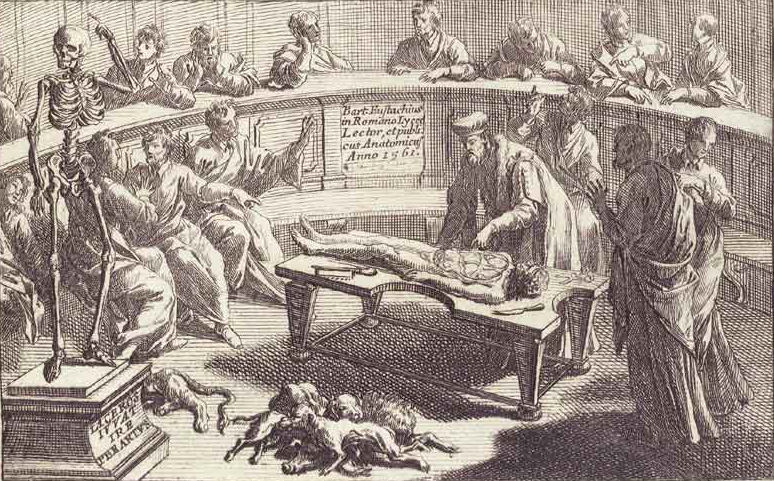

Bartolomeo Eustachi's Anatomical Engravings (1552)
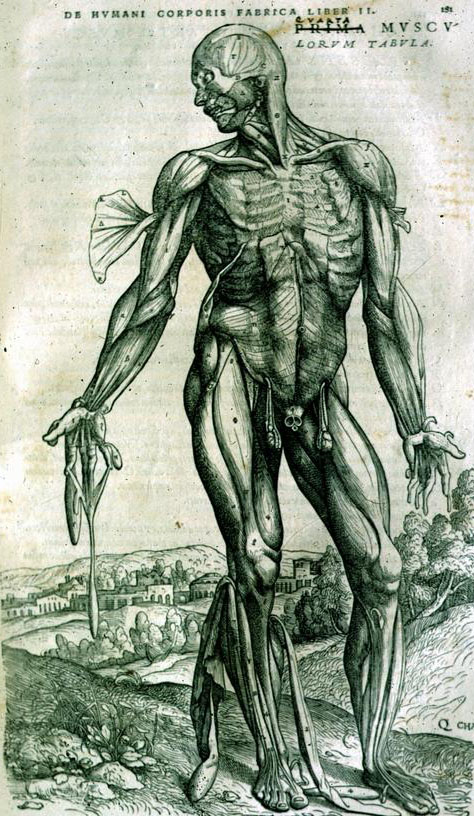
Andreas Vesalius' De Humanis Corporis Fabrica (1550)
Paracelsus (1520) pioneered the use of chemicals and minerals in medicine
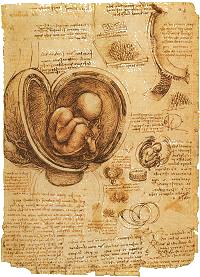
Leonardo da Vinci's studies in science and engineering (1500)

the Wound Man (1492)
Lazarettos (1403)

the Black Plague (1347-1679) was a devastating pandemic that is
estimated to have killed about a third of Europe's population
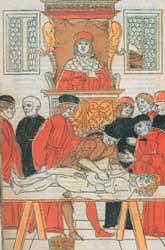
the first public, systematic dissection of a corpse (1315) was conducted by Mondino de Liuzzi
pharmacies (1241)
Al-Razi's books on medicine and chemistry (925)
Galen's On the Elements According to Hippocrates (160)
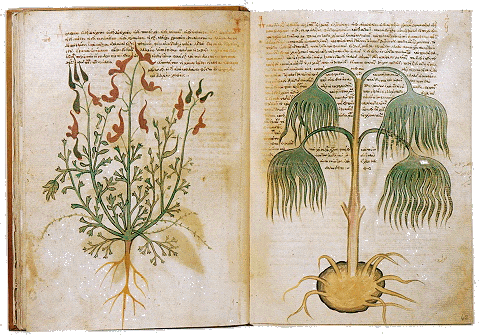
Pedanius Dioscorides' De Materia Medica (70)
hospitals (100 bc)
Erasistratus' and Herophilus' school of anatomy in Alexandria (280 bc)
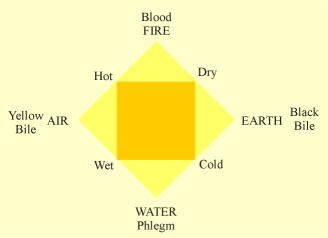
the Hippocratic Corpus (450 bc)
inoculation (1000 bc)

Acupuncture (1000 bc)

Ayurveda (1400 bc)