![]()

James Redfield's The Celestine Prophecy (1993)
Robert Plutchik's theory of emotion (1980)
Multiple Personality Disorder (1980) was included in the DSM

Timothy Leary's Exo-Psychology (1977)

the Facial Action Coding System (1976) was developed by Paul Ekman
and Wallace Friesen to taxonomize every conceivable human facial expression
Julian Jaynes' The Origin of Consciousness in the Breakdown of the Bicameral Mind (1976)
Mihaly Csikszentmihalyi's Flow (1975)
Raymond Moody coined the term near-death experiences (1975)
Sybil by Flora Rheta Schreiber (1974)
Robert Rosenthal's On the Social Psychology of the Self-Fulfilling Prophecy (1974)
Neuro-linguistic programming (1973)
Socionics (1970s)
the Stanford prison experiment (1971)
Clare W. Graves's Levels of Existence: An Open System Theory of Values (1970)
the Kübler-Ross model (1969)
The Third Wave (1967)
Jacques Lacan's Écrits (1966)
Man and His Symbols (1964)
Eric Berne's Games People Play (1964)
the Milgram experiment (1963)
Joseph Murphy's the Power of your Subconscious Mind (1962)
the Bobo doll experiment (1961)
the Beck Depression Inventory (1961)

the Harvard Psilocybin Project (1960-1962)
the Cognitive revolution (late 1950s)
Kohlberg's stages of moral development (1958)
the Myers-Briggs Type Indicator (1958)
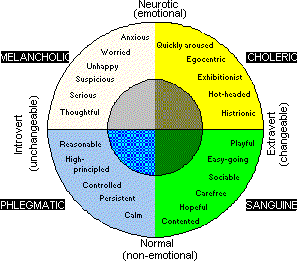
Hans Eysenck's Dimensions of Personality (1957)

John C. Lilly's experiments with isolation tanks (1954)

antidepressants (1950s)
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (1953) was developed by Albert Ellis
Project Mkultra (April 1953-1970s)
Synchronicity (1952)
the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (1952) was published by The
American Psychiatric Association marking the beginning of modern mental illness classification
scientology (1952)
the Asch conformity experiments (1951)
Project Bluebird (1951)
Erikson put forth his stages of psychosocial development (1950) in his book Childhood and Society
the Kinsey Reports (1948, 1953)
Walden Two (1948)
Viktor Frankl's Man's Search for Meaning (1946)
The Journal of Clinical Psychology (1945)
Music therapy (1944)
Maslow's hierarchy of needs (1943)

Lysergic acid diethylamide (April 16, 1943)
Rogerian psychotherapy (1940s)
Carl Rogers' Counseling and Psychotherapy (1942)
B.F. Skinner's The Behavior of Organisms: An Experimental Analysis (1938)
Anna Freud's The Ego and the Mechanisms of Defense (1936)
the Montreal Neurological Institute and Hospital (1934)
Lev Vygotsky's Thought and Language (1934)
Johannes Schultz' autogenic training (1932)

Freud's The Ego and the Id (1923)
Karen Horney's Feminine Psychology (1922)
Psychodrama (1921)
Jung's Psychological Types (1921)
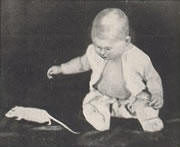
the Little Albert experiment (1920)
the lie detector (1913)
Behaviorism (1913)
Carl Jung departed from Freudian views and developed his own theories citing Freud's inability to
acknowledge religion and spirituality. His new school of thought became known as Analytical Psychology (1913)
MDMA (December 24,1912)
Alfred Adler left Freud's Psychoanalytic Group to form his own school of thought,
accusing Freud of overemphasizing sexuality and basing his theory on his own childhood (1911)
the term Depth psychology (1910) was introduced by Eugen Bleuler, who also
named schizophrenia in 1911, a disorder which was previously known as dementia praecox
Robert Yerkes' The Dancing Mouse, A Study in Animal Behavior (1907)
Vladimir Bekhterev founded the field of psycho reflexology (1900s) transferring Pavlov's work on dogs to humans
the Oedipus complex (1905)
the g factor (1904)
the Psychological Wednesday Society (1902)
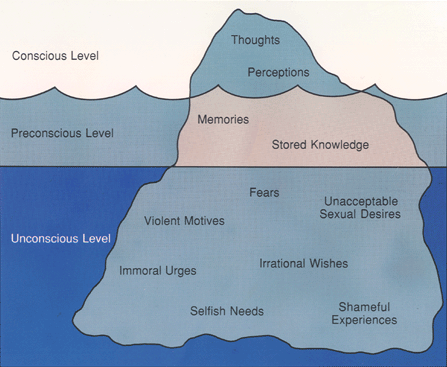
Sigmund Freud's The Interpretation of Dreams (1900)
Edward Thorndike described the law of effect (1898)
neuroscience (late 19th century)
Edward B. Titchener's Outline of Psychology (1896)

Gustave Le Bon's La psychologie des foules (1895)
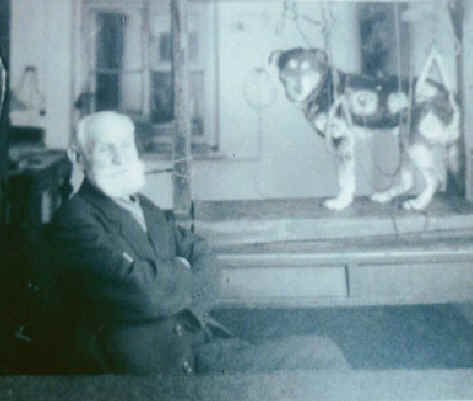

conditional reflexes (1890s) were investigated by Ivan Pavlov in his experiments with dogs
Psychoanalysis (1890s)
Gabriel Tarde's Les lois de l'imitation (1890)
William James' Principles of Psychology (1890)
the term parapsychology (1889) was coined by psychologist Max Dessoir
Sigmund Freud opened a private practice in Vienna (1886)
Jean-Martin Charcot established a neurology clinic at Salpêtrière (1882) which was the first of its kind in Europe
the first two psychological laboratories in the world (1875) were founded by William James and by Wilhelm Wundt
Wilhelm Wundt published his Principles of Psychiological Psychology (1874)
the first textbook of experimental psychology
Charles Darwin's The Expression of Emotion in Man and Animals (1872)

Vin Mariani (1863)
John Stuart Mill's book Utilitarianism (1863)
in "Neurypnology: or the Rationale of Nervous Sleep" James Braid (1843)
coined the words hypnotism, hypnotize, and hypnotist, which remain in use
mental wards (early 19th century)

mesmerism (1774)
the term neurosis (1769) was coined by the Scottish doctor William Cullen to refer
to "disorders of sense and motion" caused by a "general affection of the nervous system"
Jeremy Bentham's Introduction to Principles of Morals and Legislation (1789)
Witelo's Perspectiva (1270)
