![]()
![]()
computability logic (2003)
Jon Barwise & John Etchemendy's Language, Proof and Logic (2000)
Rod Girle's Modal Logics and Philosophy (2000)
George Boolos' Logic, Logic, and Logic (1998)
Newton da Costa's Is there a Zande Logic? (1998)
George Boolos' The Logic of Provability (1993)
Michael A. E. Dummett's Origins of Analytical Philosophy (1993)
Kleine Einführung in die Aussagenlogik (1992) von Marion Soreth
David K Lewis' Parts of Classes (1991)
Michael A. E. Dummett's The Logical Basis of Metaphysics (1991)
Newton da Costa's Paraconsistent logic (1989)
Jon Barwise's The Situation in Logic (1988)
linear logic (1987)
Trudy Govier's Practical Study of Argument (1985)
Susan Haack's Philosophy of Logics (1978)
Newton da Costa's On Jaskowski's Discussive Logic (1977)
Ruth Barcan Marcus' The Logical Enterprise (1975)
Susan Haack's Deviant Logic (1974)
George Boolos' Computability and Logic (1974)
Newton da Costa's On the theory of inconsistent formal systems (1974)
dynamic logic (1970s)
Evert Willem Beth (1970) Formal Methods: An introduction to
symbolic logic and to the study of effective operations in arithmetic and logic
Relational algebra (1970)
Stephen Cole Kleene's Mathematical Logic (1967)
fuzzy logic (1965)
Kazimierz Ajdukiewicz' Pragmatic Logic (1965)
Haskell Curry's Foundations of Mathematical Logic (1963)
Saul Aaron Kripke's Semantical Considerations on Modal Logic (1963)
Fitch's paradox of knowability (1963)
Transistor-transistor logic (1962)
Ernest Nagel's The Structure of Science: Problems in the Logic of Scientific Explanation (1961)
computational complexity theory (1960)
Saul Aaron Kripke's A Completeness Theorem in Modal Logic (1959)
Gotthard Günther's Die philosophische Idee einer nicht-Aristotelischen Logik (1959)
Haskell Curry's Combinatory Logic (1958)
Tadeusz Kotarbinski's Leçons sur l'histoire de la logique (1957)
Alfred Tarski's Logic, Semantics, Metamathematics (1956)
Arthur Prior's Formal Logic (1955)
abstract algebraic logic (1950s)
Frederic Fitch's Symbolic Logic (1952)
P. F. Strawson's Introduction to Logical Theory (1952)
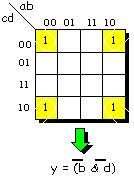
Karnaugh maps (1952)
G. H. von Wright's An Essay in Modal Logic (1951)
G. H. von Wright's Deontic Logic (1951)

Logistics (1950s)
Willard van Orman Quine's Methods of Logic (1950)
the Nash equilibrium (1950)
Hans Reichenbach's Elements of symbolic logic (1947)
![]()
the Barcan Formula (1946)
G. H. von Wright's The Logical Problem of Induction (1941)
Willard van Orman Quine's Elementary Logic (1941)
Willard van Orman Quine's Mathematical Logic (1940)
higher-order logic (1940)
topological logic (1937)
Susanne Langer's An Introduction to Symbolic Logic (1937)
Turing machines (1936)
the Journal of Symbolic Logic (1936)
Karl Popper's Logik der Forschung (1934)
Ernest Nagel's An Introduction to Logic and Scientific Method, Logic without Metaphysics (1934)
metalogic (1930s)
Lambda calculus (1930s)
model theory (1930s)
Tarski's the concept of truth in the languages of the deductive sciences (1933)
Clarence Irving Lewis' Symbolic Logic (1932)
Clarence Irving Lewis's Symbolic Logic (1932)
infinitary logic (1931)
Gödel's incompleteness theorems (1931)
Kurt Gödel's Über formal unentscheidbare Sätze der Principia Mathematica und verwandter Systeme (1931)
Frank Plumpton Ramsey's On a problem of formal logic (1930)
Heyting (1930) Die formalen Regelen der Intuitionistischen Logik
Gödel's completeness theorem (1929)
Rudolf Carnap's Abriss der Logistik (1929)
Jaakko Hintikka's The Logic of Epistemology and the Epistemology of Logic (1929)
Edmund Husserl's Formale und transzendentale Logik. Versuch einer Kritik der logischen Vernunft (1929)
relevance logic (1928)
David Hilbert's Grundzüge der theoretischen Logik (1928)
Wilhelm Ackermann's Grundzüge der theoretischen Logik (1928)
Mereology (1927)
deontic logic (1926)
intuitionistic logic (1925)
Moses Schönfinkel's Über die Bausteine der mathematischen Logik (1924)
William Ernest Johnson's Logic (1924)
Ludwig Wittgenstein's Tractatus Logico-Philosophicus (1922)
proof theory (1922)
combinatory logic (1920)
ternary logic (1920)
multi-valued logic (1920)
Polish notation (1920)
Bertrand Russell's Introduction to mathematical philosophy (1919)
p -⊰ q
the strict conditional (1918)
Clarence Irving Lewis Survey of Symbolic Logic (1918)
Jean Nicod's Reduction in the Number of Primitive Propositions of Logic (1917)
Leopold Löwenheim's Über Möglichkeiten im Relativkalkül (1915)
![]()
the Sheffer stroke (1913)
Russell and Whitehead's Principia Mathematica (1913)
Josiah Royce's Principles of Logic (1913)
Luitzgen Egbertus Jan Brouwer's Beweis des Jordanschen Satzes für N Dimensionen (1912)
Wilhelm Windelband's Theories in Logic (1912)
intuitionistic logic (1912)
modal logic (1910)
Louis Couturat (1904) proposed the name "La logistique" for modern logic
type theory (1903)
Louis Couturat's La Logique de Leibniz (1901)
Russell's paradox (1901)
Husserl's Logische Untersuchungen zur Phänomenologie und Theorie der Erkenntnis (1901)
Edmund Husserl's Logische Untersuchungen. Erster Teil: Prolegomena zur reinen Logik (1900)
Nikola Tesla (1899) invented the electronic AND logic gate circuit
Lewis Carroll's Symbolic Logic (1896)
the Lwow-Warsaw School of Logic (1895)
Lewis Carroll's What the Tortoise Said to Achilles (1895)
Gottlob Frege's Grundgesetze der Arithmetik (1893)
Ernst Schröder's Vorlesungen über die Algebra der Logik (1890-1905) prepared the way for the
emergence of mathematical logic as a separate discipline in the twentieth century by systematizing the
various systems of formal logic of the day
Peano axioms (1889)
mathematical logic (1887)
Giuseppe Peano's Applicazioni Geometriche del Calcolo Infinitesimale (1887)
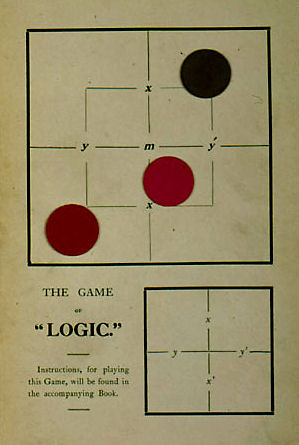
Lewis Carroll's Game of Logic (1886)
Friedrich Harms' Logik (1886)
Second-order logic (1885)
Peirce's law (1885)
Charles S. Peirce's Studies in Logic (1883)

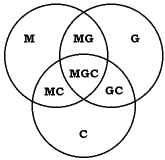
Charles Sanders Peirce's graphical logic (1882)
Venn diagrams (1881)
Friedrich Harms' Geschichte der Logik (1881)
the amphecks (1880) were discovered by Charles S. Peirce
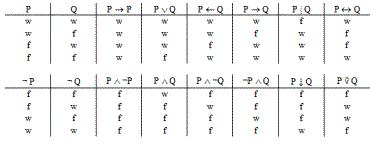
truth tables (1880)
![]()
Frege's Begriffsschrift (1879)
first-order logic (1879)
Hugh MacColl (1879) published a four-part article setting out the first known variant of the
propositional calculus, calling it the "calculus of equivalent statements", anteceding Frege's Begriffschrifft
Rudolf Hermann Lotze's Logik (1874)
set theory (1874)
Christoph von Sigwart's Logik (1873)
Charles S. Peirce's Logic of Relatives (1870)

Jevons' Logic Piano (1869)
William Stanley Jevons's Pure Logic (1864)
boolean algebra (1860s)
William Hamilton's Lectures on Logic (1856)
Karl von Prantl's Geschichte der Logik im Abendland (1855)
algebraic logic (1850s)
boolean logic (1854)
George Boole's An Investigation of the Laws of Thought (1854) on
which are founded the Mathematical Theories of Logic and Probabilities
Hermann Ulrici's System der Logik (1852)
Henry Longueville Mansel (1851) Prolegomena logica: an
Inquiry into the Psychological Character of Logical Processes
Bernard Bolzano's The Paradoxes of the Infinite (1851)
symbolic logic (1847)
George Boole's Mathematical Analysis of Logic (1847)
Augustus De Morgan's Formal Logic (1847)
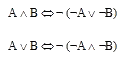
De Morgan's laws (1847)
Hermann Ulrici's Grundprincip der Philosophie (1846)
John Stuart Mill's System of Logic (1843)
Hermann Ulrici 's Über Princip u. Methode der Hegelschen Philosophie (1841)
Friedrich Adolf Trendelenburg's Logische Untersuchungen (1840)
Jules Barthélemy-Saint-Hilaire's De la Logique d’Aristote (1838)
game theory (1838)
digital logic (1837)
logic gates (1837) were first used by Charles Babbage in constructing his Analytical Engine
William Whewell's (1837) History of the Inductive Sciences, from the Earliest to the Present Time
Friedrich Adolf Trendelenburg's Elementa inices Aristoteticae (1836)
Richard Whately's Elements of Logic (1826)
Schopenhauer On the Fourfold Root of the Principle of Sufficient Reason (1813)
Hegelian dialectic (19th century)
Hegel's Science of Logic (1811-1816)
Jakob Friedrich Fries' System der Logik (1811)
Christoph Gottfried Bardili's Grundriss der ersten Logik (1800)
Logik: vom Schüler Jäsche nach Kants Vorlesungen erstellt (1800)
Gottfried Ploucquet (1782) developed a symbolic calculus
Kant's Transcendental Logic (1781)
Etienne Bonnot de Condillac's Logique (1781)
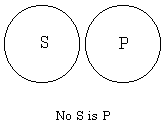
Euler diagrams (1768)
Johann Heinrich Lambert's De universaliori Calculi idea (1765)
Kant's the false subtlety of the four syllogistic figures proved (1762)
Francis Hutcheson's Compendium of Logic (1756)
Hermann Samuel Reimarus' Vernunftlehre als Anweisung zum richtigen Gebrauche der Vernunft (1756)
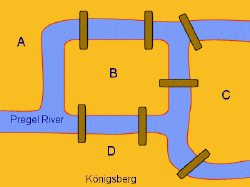
the Seven Bridges of Königsberg (1734)
Christian Wolff's Philosophia rationalis, sive logica (1734)
Giambattista Vico's New Science (1725)
Isaac Watts' Logick: Or, the Right Use of Reason (1724)
Gershom Carmichael's Breviuscula Introductio ad Logicam (1720)
the identity of indiscernibles (1714)
the principle of sufficient reason (1714)
the Port-Royal Logic (1662)
Pierre Gassendi's Syntagma philosophicum (1658)
Johannes Clauberg's Logica vetus et nova (1654)
Francisco Suarez' Metaphysical Disputations (early seventeenth century)
Joachim Jungius' Logica hamburgensis (1638)
Francis Bacon's Novum Organum (1620)
Jacopo Zabarella's Opera Logica (1578)
Petrus Ramus' Quecumque ab Aristotele dicat essent, commentita esse (1536)
Cajetan distinguished between the extension and intension of terms (1530)
John Mair's Quaestiones logicales (1528)
Rodolphus Agricola (1479) De inventione dialectica
Paul of Venice (15th century) Logica parva et logica magna
Occam's razor (14th-century)
Albert of Saxony (14th century) Perutilis logica, Quaestiones logicales, Quaestiones on the Ars Vetus
Jean Buridan (14th century) Compendium Logicae, Summa de Dialecticâ
William of Ockham (14th century) Summa logicae
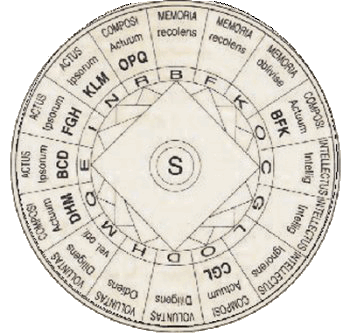
Ramon Lull's Ars Magna (1275) contained one of the earliest attempts to construct a universal language
John Duns Scotus' parva logicalia (1295)
Roger Bacon's Opus majus (1267)

Tractatus, Summule logicales magistri Petri Hispani (13th century)
William of Sherwood's Introductiones in logicam and Syncategoremata (13th century)
Adam Parvipontanus (12th century) Ars disserendi
John of Salisbury (12th century) Metalogicon
Gilbert de la Porrée (12th century) De sex principiis
Abu Hamid al Ghazali (12th century) composed three works on Aristotelian logic,
Mi'yar al-'ilm (The Standard Measure of Knowledge), Mihakk al-nazar f'l-mantiq
(The Touchstone of Proof in Logic) and al-Qistas al-mustaqim (The Just Balance)

Averroës (12th century) was one of the first philosophers to propose the omnipotence paradox
Scholasticism (1100-1500)
the fourth syllogistic figure (Middle Ages) was derived from
the indirect modi of the first figure by Islamic philosophers
Dharmakirti (circa 7th century) Seven Treatises on Valid Cognition
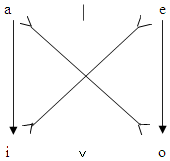
Boethius's square of opposition
Boethius' logical commentaries (516)
Dignaga (5th century) Treatise on the Correct Principles of Logic
Sextus Empiricus' Adversus Mathematicos (3rd century)
Porphyry's Introduction to Categories (late 3rd century)
Diogenes Laërtius' Lives and Opinions of Eminent Philosophers (ca. 220)
Galen's Institutio logica (2nd century)
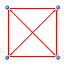
the square of opposition was introduced by Apuleius (2nd century)
to illustrate the relations between Aristotle's four basic propositions
the surviving logical works of Aristotle were arranged by Andronicus of Rhodos (40 bc)
into six books, this body was later on called Organon (instrument) by the Byzantine logicians
the five undemonstrated modes of Chrysippus (mid 3rd century bc)
propositional calculus was developed by the Stoics,
ordinal numerals were used as variables
Stoic logic (early 3rd century bc)
Zeno of Citium introduced the term "logic" to replace Aristotle`s term "analytic"
Philo of Megara defined material implication with a truth table (late 4th century)
Diodorus' master argument (late 4th century)
Diodorus Chronos invented propositional calculus (late 4th century)
Theophrastus improved Aristotle's logic (323 bc)
the duality of disjunction and conjunction
the law of the excluded middle
Aristotelian logic (330 bc)
Eubulides of Miletus (4th century bc) is credited with the invention of several logical paradoxes
Plato's Euthydemus (380 bc)
the Megarian school of philosophy (400 bc) was founded by Euclid of Megara

![]()
Zeno's paradoxes (450 bc)
Sophistry (fifth century bc)
chinese logic (fifth century bc)
indian logic (sixth century bc)

legal logic (21st century bc)