![]()
European Parliament elections (June 11-13, 2009)
Ireland rejected the Lisbon Treaty (June 12, 2008)
Cyprus and Malta will join the Union (January 1, 2008)
the Reform Treaty (December 13, 2007) was signed at a summit in Lisbon
the Berlin Declaration (March 25, 2007)
Bulgaria and Romania joined the Union (January 1, 2007)

Switzerland (2005) agreed to join the Schengen zone in 2007

the European Council (December 13, 2004) adopted a regulation on standards
for security features and biometrics in passports and travel documents issued by Member States

the Treaty establishing a Constitution for Europe (October 29, 2004)
was signed but has yet to be ratified by all member states
Elections to the European Parliament (June 10-13, 2004)

the European Commission's Strategic Report (October 9, 2002) recommended 10 candidate
members for inclusion in the EU in 2004: Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, the Czech
Republic, Hungary, Slovakia, Slovenia, Malta and Cyprus

the Euro (January 1, 2002) was introduced as the new
'single currency' of the European Monetary Union,
the EU Copyright Directive (May 22, 2001)

the Charter of Fundamental Rights of the European Union (2000)

on the summit in Nice (December 2000) a treay that bears the same name was signed which amended
the two founding treaties of the European Union, namely the treaties of Rome and of Maastricht

the Lisbon Strategy (March 2000)
Elections to the European Parliament (1999)

the European Court of Human Rights (November 1, 1998) was created to systematise the hearing of human
rights complaints from Council of Europe member states. The court's mission is to enforce the Convention for
the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms, ratified in 1953

the European Central Bank (June 1, 1998)

the Treaty of Amsterdam (October 2, 1997) entered into force on May 1, 1999. It made
substantial changes to the Treaty on European Union, which had been signed at Maastricht in 1992
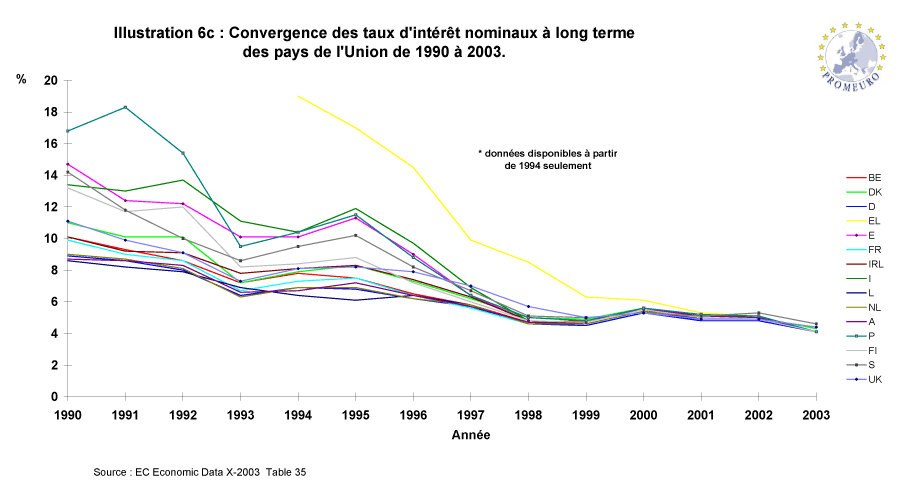
the Stability and Growth Pact (1997) is based on Articles 99 and 104 of the European Community Treaty (with the
amendments adopted in 1993 in Maastricht), and related decisions. It consists of enforcement policies of mutual surveillance
of fiscal positions and of an excessive deficit procedure defined in the treaty. The pact was adopted in 1997 so that fiscal
discipline would be maintained and enforced in the EMU. Member states adopting the euro have to meet the strict Maastricht
convergence criteria: The actual criteria that member states must respect: an annual budget deficit lower than 3% of GDP
and a public debt lower than 60% of GDP or approaching that value

OSCE (January 1, 1995)

Austria, Sweden and Finland (January 1, 1995) were admitted, but Norway, Iceland,
Switzerland and Liechtenstein remain the only members of the EFTA, because
referendums in these countries rejected the european idea
Elections to the European Parliament (1994)

the Maastricht Treaty (February 7, 1992) between the members of the European Community entered into
force on November 1, 1993, it was this treaty that established the European Union officially under that name
Elections to the European Parliament (1989)
the Single European Act (February 17, 1986)

Spain and Portugal (1986) joined

the Schengen treaty (June 14, 1985) is an agreement to end border checkpoints and controls within the
Schengen area. It was signed initially only by Belgium, France, Germany, Luxembourg, and the Netherlands
the European City of Culture (June 13, 1985)

Denmark's territory Greenland (1985) left the union following home rule and a referendum
the UK rebate (1984-200?)
Elections to the European Parliament (1984)
Butter mountains (80s)

Greece (January 1, 1981) joined under the presidency of Constantine Caramanlis
Elections to the European Parliament (1979)
European Monetary System (1979)

the Netherlands legalized the possession of soft drugs (1976) enabling so-called coffee shops to sell Cannabis openly
Lomé Convention (1975)
ECU (1975)

European Space Agency (1975)

CSCE (July 3, 1973)

Finally, Britain (January 1, 1973) joined successfully. In 1972,
Ireland and Denmark, Norway held referenda on whether to join
France withdrew its troops from the NATO (Febuary 1966) and French President Charles de
Gaulle advocated a ``Europeanized Europe'' free from American and Soviet intervention

the Merger Treaty (April 8, 1965) signed in Brussels and in force since July 1, 1967, gathered together the
organisational structures of the then three European Communities (European Coal and Steel Community, European
Economic Community and Euratom). It created the European Commission and the Council of the European
Communities to be the governing bodies for all three institutions, and it also had them share a single budget

the Elysée treaty (January 22, 1963) was signed by de Gaulle and Adenauer. It created the institutional
framework for a close coordination between both governments: their Heads of State and Government
were to meet at least twice annually, and their Foreign Ministers were to meet every three months.
Another major part of the treaty was the establishment of the Office franco-allemand pour la Jeunesse

Efta (1960) was established as an alternative for European states that
were not allowed or did not wish to join the European Community
Brussels World’s Fair (April 17 - October 19, 1958)
the European Parliament (1958) has its origin in the European Parliamentary Assembly,
a name adopted for the 'Common Assembly' of the ECSC which expanded in March
1958 to also cover the European Economic Community and Euratom

Euratom (1957)

the Treaty of Rome (March 25, 1957) established the European Economic Community (EEC)
and was signed by France, West Germany, Italy, Belgium, the Netherlands and Luxembourg

CERN (1954)

the European Coal and Steel Community (April 18, 1951) was established with the Treaty of Paris,
it was the earliest forerunner of the European Union and consisted of only six members: Belgium,
the Netherlands, Luxembourg (the Benelux countries), (West) Germany, France and Italy

the Schuman declaration (May 9, 1950)
the European Payments Union (1950-1958) was set up by the Organization for European Economic Co-operation. The
15 members were able to mutually offset deficits and surpluses up to the limits of their quotas which were set according to their
share of world trade. By 1958 most European currencies were sufficiently convertible for the payments union to be terminated
the Council of Europe (May 5, 1949) was founded by the Treaty of London taking up the European idea
that Winston Churchill first formulated in his speech three years earlier. However, this institution did not develop
into a legislative body with powers comparable to its younger counterpart the Council of the European Union.
Though in 1955 the Council of Europe did give Europe its own flag and in 1972 an anthem based on
the Ode to Joy in the final movement of Ludwig van Beethoven's ninth

the Organisation for European Economic Co-operation (OEEC) was set up in 1947 with support from the
United States and Canada to co-ordinate the Marshall Plan for the reconstruction of Europe after World War II.
In 1961 it was reneamed and is since known as the OECD
Winston Churchill (September 19, 1946) gave a speech at the University of Zürich
calling for a "United States of Europe", similar to the United States of America