![]()
![]()
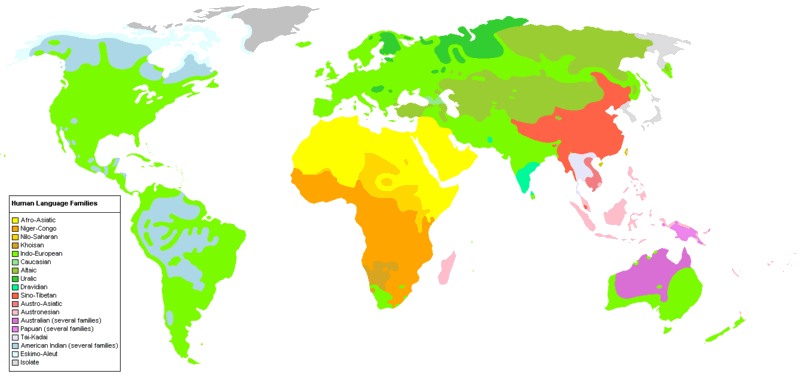
Current distribution of Human Language Families
the BNC (1994)
Lojban (1987)
Neuro-linguistic programming (1973)

Gestuno (1973)
the Brown corpus (1967)

Hindi (January 26, 1965) became the official language of India, although English and 21 other
languages are recognised as official languages by the Constitution of India. The language evolved
from the Middle Indo-Aryan prakrit languages of the Middle Ages, and indirectly, from Sanskrit

the People's Republic of China (1956) issued official character
simplifications in two phases, one in 1956 and the second in 1964
Interlingua (1951)
Naa Badda mi
Rastafarian (1930)
Novial (1928)

Turkish (1928) has been spoken at least since the 5th century. Kemal Atatürk
decreed that the Arabic script be replaced by a modified Latin alphabet in 1928
Zhuyin Zimu (1918)
Ro (1904)
Hiragana (1900)
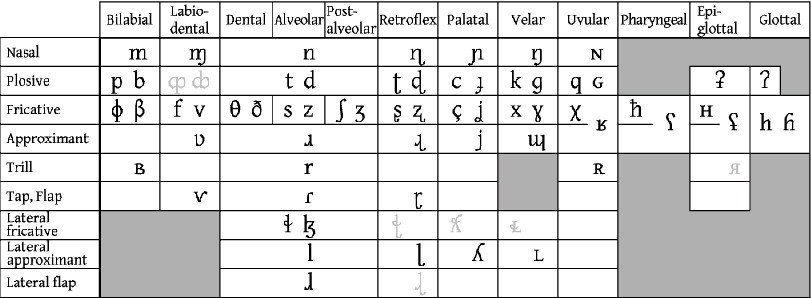
the International Phonetic Alphabet (1888)
Esperanto estas planlingvo proponita kiel internacia dua lingvo
Esperanto (1887) is the most widely spoken constructed international language
Grimm's law (1806)

Braille (1800)
Pennsylvania Dutch (1775)

the first written Bangla grammar (1734) Vocabolario em idioma Bengalla, e Portuguez dividido
em duas partes, was written by Manoel da Assumpcam, a Portugese missionary
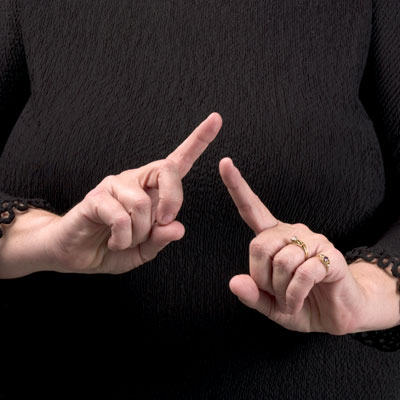
a standardized sign language (1600s) began to be used in Italy
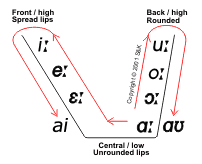
Modern English (1500-present)
Johann Gutenberg (re)invented the printing press (1455)
Hangul (1443)
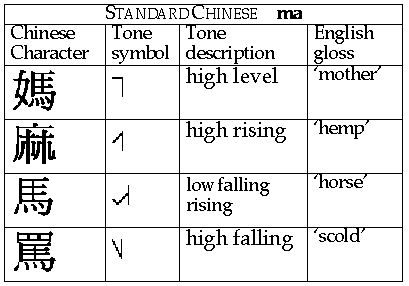
Mandarin (1100)
Middle English (1066-1500)
última flor do Lácio
Portuguese (900)

the Glagolitic alphabet (863) is the oldest known Slavic alphabet. It was created by Saint
Cyril around 862-863 in order to translate the Bible and other texts into the Slavic languages
Kana (9th century)

les Serments de Strasbourg (14 février 824) marquent la naissance de la langue française
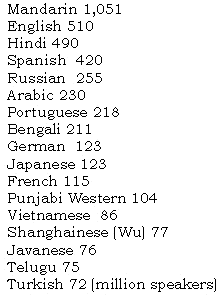
all figures according to: ethnologue
Spanish (800) is the fourth most widely spoken language in the world today
Yiddish (800)
L'italiano utilizza 21 lettere dell'alfabeto latino. In effetti k, j, w, x, y esistono
solo in parole d'origine straniera o come varianti grafiche di scrittura
Italian (800)
the Orkhon script (8th century) is the earliest known Turkic alphabet
Kanji (6th century)

Arabic (500)
God cwæð him þus tó
Old English (450-1150)
Ik gihorta dat seggen,
dat sih urhettun ænon muotin,
Hiltibrant enti Hadubrant untar heriun tuem.
German (400)
Langue d'oc ()
Langue d'oïl ()
Vulgar Latin (461-800) gave rise to the modern Romance languages
Telugu ()
Javanese ()

the Runic alphabets (200)
Cai Lun (105) invented paper
Vietnamese ()
Punjabi ()

the Rosetta stone (196 bc)
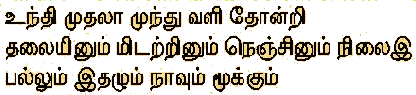
the Tolkaappiyam (200 bc)
Koine Greek (323 bc - 330 ad)
Japanese (400 bc)
the Duenos inscription (500 bc) shows the earliest known forms of the Old Latin alphabet
the Behistun Inscription (515 bc)
Pāli (600 bc)
the Cumae alphabet (7th century bc)
Proto-Celtic (800 bc)
Proto-Slavic (1000bc) is the parent language of East Slavic (including Russian, Ukrainian, Belarusian, and
Rusyn), West Slavic (Czech, Slovak and Sorbian) and South Slavic (Slovenian and Serbo-Croatian)
Non in legendo sed in intelligendo legis consistunt
Latin (1000 bc - 461 ad)

the earliest Aramaic alphabet (1100 bc) was based on the Phoenician script. In time, Aramaic developed
its distinctive 'square' style. The ancient Israelites and other peoples of Canaan adopted this alphabet for
writing their own languages. Thus, it is better known as the Hebrew alphabet today. This is the writing
system used in Biblical Aramaic and other Jewish writing in Aramaic

Old Chinese (1100 bc) refers to the Chinese spoken during the Zhou Dynasty. Since
Old Chinese was the language spoken by Chinese when classical works such as the Analects
of Confucius, the Mencius, and the Tao Te Ching were written, Old Chinese was preserved
for the next two millennia in the form of Classical Chinese, a style of written Chinese that
emulates the grammar and vocabulary of Old Chinese as presented in those works

Classical Hebrew (1200 bc) is further divided into the so called 'Golden Age'
Hebrew (1200 bc to 500 bc) and 'Silver Age' Hebrew (500 bc to 60 bc)
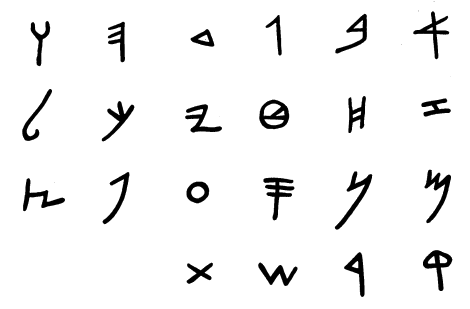
the Phoenician alphabet (1200 bc) is the predecessor of several other alphabets:
Hebrew, Arabic, Greek, Latin (via the Old Italic alphabet), and Cyrillic

Italic languages (1400 bc)
Proto-Dravidian (1500 bc)
Uralic languages (1??? bc) include Estonian, Finnish, and Hungarian

Vedic Sanskrit (1600 bc) is the language of the Vedas, the earliest sacred texts of India

Mycenaean (1600-1100 bc) is the most ancient known form of the Greek language, spoken on the Greek mainland and on Crete

Wadi el-Ħôl (1800 bc)
Altaic languages (? bc)
Proto-Greek (2600 bc) is the common ancestor of the Greek dialects, including the Mycenean language
Hieratic (around 2800 bc)
cuneiform script (late 4th millennium bc)
hieroglyphs (3200 bc)
Proto-Semitic (4th millennium bc)
Proto-Indo-European (4500 bc)

Australian Aboriginal languages (40,000 bc)

Cave paintings (40,000 bc)

Proto-World language (200,000 bc)