![]()
wikipedia (January 15, 2001)
PISA (2000)
the Bologna process (1999)
babylon translator (1997)
JSTOR (1995)
John Taylor Gatto's I Quit, I Think (1991)
Thomson Wadsworth (1978)
Hackett Publishing Company (1972)
the Introducing series (1970s)
instructional theory (1970s)
the Hidden Curriculum (1970)

Sudbury school (1968)
Logo (1968)

the set square (1964)
the leadership continuum model of Robert Tannenbaum and Warren Schmidt (1958)
Bloom's Taxonomy (1956)
Ruth Cohn (1955)
Robert Hutchins' University of Utopia (1953)

Piaget's theory of cognitive development (1951)
Didacta (1951)
Outdoor Preschool (1948)
Edgar Dale's cone of experience (1946)
the General Educational Development Test (1942)

the Overhead Projector (1940s)
Penguin Books (1935)

Kurt Hahn's Salemer Gesetze (1930)

the second Goetheanum (1928)

Summerhill (1924)
Freinet's pedagogy (1920)
Janusz Korczak's How to Love a Child (1919)
Waldorf education (1919)
John Dewey's Democracy and Education (1916)
the first youth hostel (1912) was founded by Richard Schirrmann

Maria Montessori's "Il metodo della pedagogia scientifica" (1909)
Maria Montessori founded the Casa dei Bambini (1907)

Ovide Decroly founded the École pour la vie, par la vie (1907)
Paul Geheeb and Gustav Wyneken's Wickersdorf Free School Community (1906)
Sigmund Freud's stages of psychosexual development (1905)
the General Education Board (1903)
Ellen Key's Century of the Child (1900)

Alexander Technique (1900)

Learning by Doing (1896)
Stanford University (1881)
Corrado Ricci's L'arte dei bambini (1887)
Carnegie libraries (1883)
nature versus nurture (1874)
Educational progressivism (end of the 19th, beginning of the 20th century)

Summer camp (1861)
Special education (1861)
Social Darwinism (1851)
Allotment gardens (19th century)

Fidgety Philip (1845)
the term social pedagogy has been first used (1844)
in an article by Karl Mager in "Pädagogische Revue"

Folk high schools (1844)

the first Kindergarten (1840) was opened by
Friedrich Wilhelm August Fröbel in Bad Blankenburg

Friedrich Daniel Ernst Schleiermacher's Pädagogische Schriften (1834)

Turnvater Jahn (1811) opened the first open-air gymnasium
the School Cone (1810)
Jean Paul's Levana, or, doctrine of education (1807)
Johann Friedrich Herbart's Allgemeine Pädagogik (1806)

Kant On Pedagogy (1803) edited by his student Rink

Johann Heinrich Pestalozzi (1801) How Gertrude teaches her Children

Friedrich Schiller On the Aesthetic Education of Man (1795)


Schnepfenthal institution (1784)
Gotthold Ephraim Lessing's Education of Humankind (1780)
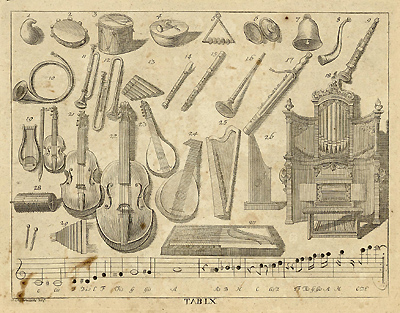
Johann Bernhard Basedow's Elementarwerk (1774)

the Philanthropinum in Dessau (1771-1793) was founded
by Johann Bernhard Basedow and Christian Heinrich Wolke
Charles Michel de l'Epée founded the "Institution Nationale des Sourds-Muets de Paris" (1771)
Jean Frédéric Oberlin's salle d'asile (1766)
Philanthropism
Jean-Jacques Rousseau's Émile (1762)
the Age of Enlightenment (mid 18th century - beginning of the 19th century)
August Hermann Francke's Kurzer und einfältiger Unterricht (1702) wie die
Kinder zur wahren Gottseligkeit uund christlicher Klugheit anzuführen sind
John Locke (1693) Some Thoughts Concerning Education
John Locke's Tabula rasa (1690)
Pietism (1675)

Comenius' Orbis sensualium pictus (1658)
Comenius' Didactica magna (1657)

the Nuremberg funnel (1647)
Milton's Of Education (1644)
Harvard University (September 8, 1636)
Wolfgang Ratke (1619) introduced the term didactics

Compulsory education (1616)
Ratio atque institutio studiorum Societatis Jesu (1599)
the term education was first recorded (1588) in Shakespeare's Love's Labour's Lost
Cambridge University Press (1584)
Michel de Montaigne's Essays (1572)
Petrus Ramus' Scholae in liberales artes (1569)
Philipp Melanchthon's Philosophiae moralis epitmois (1546)
the Schulpforta (1543)
Pier Paolo Vergerio's Libellus über Primärerziehung
Johannes Sturm's Gymnasium in Strasbourg (1538)
François Rabelais (1535) Pantagruel
Johannes Bugenhagen (1529) founded the Johanneum
Valentin Trotzendorf (1523) was called to be a master in the school at Goldberg in Silesia
Joan Lluís Vives' De ratione studii puerilis epistolae duae (1523)

Erasmus of Rotterdam's Handbook of a Christian Knight (1516)
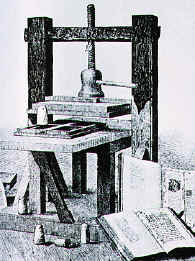
Printing (1440s)
Vittorino da Feltre's Giocosa (1425)
Jean Gerson (1410)
sapiens atque eloquens pietas
University of Cologne (1388)
University of Heidelberg (1386)
Humanism (14th century)
Aegidius Romanus (late 13th century) De Regimine Principum
Thomas Aquinas (late 13th century) De Magistro
the Renaissance (13th century)
University of Cambridge (1209)
Alexander de Villa-Dei's Doctrinale (1200)
Peter Lombard's Book of Sentences (1142)
Hugh of St Victor (ca 1130) Didascalicon de studio legendi
University of Paris (1150)
University of Oxford (1117)

Vocational training (12th centuy)

Scholasticism (1100)

Universities (9th century)
Hrabanus Maurus (801) received a deacons order at Fulda
Alcuin became principal at the Palace School of Charlemagne (782)
Rattan canes (-1950)
praecepta, exempla, imitatio
Cassiodorus' Institutiones divinarum et saecularium litterarum (555)
the Synod of Vaison (529)

monastic schools
the Dark Age (476-1000)
John Chrysostom (late 4th century)
Augustine's De Magistro (389)
Donatus' Ars grammatica (4th century)
Clement of Alexandria (200) Paidagogos
Plutarch (100) de liberis educandis
Quintilianus (95) Institutio Oratoria

Minerva (207 bc)

the Bibliotheca Alexandrina (284 bc)

wax tablets (3rd century bc)

the classical rules for definitions by Aristotle
Aristotle's Lyceum (335 bc)
Plato's Republic (370 bc)
Plato founded the Academy (385 bc)
Isocrates' eu legein, eu prattein, eu phronein (392 bc)
the Socraic method (440 bc)
Paideia (450 bc)
the memory palace (477 bc) of Simonides of Coes
the homeric Aien Aristeuein (730 bc)
schools in Mesopotamia (3000 bc)
schools in ancient Egypt (3000 bc)