![]()
![]()
 |
Steven Pinker |
| 1954 | |
 |
James Redfield author of "the Celestine Prophecy" |
| 1950 | |
 |
Robert Plutchik |
| 19?? | |
 |
Raymond Moody is most famous as an author of books about life after death and near-death experiences (a term which he coined in 1975) |
| 1944 | |
 |
Julia Kristeva linguist and psychoanalyst |
| 1941 | |
 |
|
| 1934 | |
 |
Paul Ekman developed the Facial Action Coding System (FACS) to taxonomize every conceivable human facial expression |
| 1934 | |
 |
Philip Zimbardo |
| 1933 | |
 |
Robert Rosenthal author of "On the Social Psychology of the Self-Fulfilling Prophecy: Further Evidence for Pygmalion Effects and their Mediating Mechanisms" |
| 1933 | |
 |
Stanley Milgram |
| 1933-1984 | |
 |
Luce Irigaray feminist and psychoanalyst |
| 1930 | |
 |
Félix Guattari |
| 1930-1992 | |
 |
Aura Augustinavičiute is the founder of Socionics which is based on Carl Jung's work on Psychological Types, Freud's theory of the conscious and subconscious, and Antoni Kepinski's theory of information metabolism |
| 1927 | |
 |
Ernest Becker created the science of evil |
| 1925-1975 | |
 |
Julian Jaynes is best known for his book "The Origin of Consciousness in the Breakdown of the Bicameral Mind", in which he argues that ancient peoples were not conscious as we consider the term today, and that the change of human thinking occurred within the last few thousand years, possibly even within recorded historical times |
| 1920-1997 | |
 |
|
| 1920-1996 | |
 |
Hans Eysenck |
| 1916-1997 | |
|
○
|
John C. Lilly |
| 1915-2001 | |
 |
Jerome Bruner his ideas are based on categorization. "To perceive is to categorize, to conceptualize is to categorize, to learn is to form categories, to make decisions is to categorize" |
| 1915 | |
| |
Clare W. Graves originator of the Level Theory of Personality |
| 1914-1986 | |
 |
Paul D. MacLean defined the triune concept of the brain |
| 1913 | |
 |
Albert Ellis is a psychologist who originated Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy (REBT), a theory which holds that one's personal beliefs and evaluations control one's feelings |
| 1913 | |
 |
Abraham Maslow |
| 1908-1970 | |
 |
Gerda Alexander |
| 1908-1994 | |
 |
Viktor Frankl was the founder of logotherapy and Existential Analysis, the "Third Viennese School" of psychotherapy |
| 1905-1997 | |
 |
B. F. Skinner |
| 1904-1990 | |
 |
Erik Erikson was a developmental psychologist and psychoanalyst known for his theory on social development of human beings, and for coining the phrase 'identity crisis' |
| 1902-1994 | |
 |
Carl Ransom Rogers 'Rogerian psychotherapy' became widely influential, embraced for its humanistic approach |
| 1902-1987 | |
 |
Jacques Lacan theorist of psychoanalysis |
| 1901-1981 | |
 |
Milton Hyland Erickson developed a type of hypnotherapy |
| 1901-1980 | |
 |
Erich Fromm psychologist and humanistic philosopher |
| 1900-1980 | |
 |
Wilhelm Reich |
| 1897-1957 | |
 |
Anna Freud was the daughter of Sigmund Freud and the pioneer of child psychoanalysis |
| 1895-1982 | |
 |
Alfred Charles Kinsey his research on human sexuality profoundly influenced social and cultural values in the United States especially in the 1960s and was an important influence on the sexual revolution |
| 1894-1956 | |
 |
Frederick Perls coined the term 'Gestalt Therapy' for the approach to therapy he developed with his wife Laura Perls |
| 1893-1970 | |
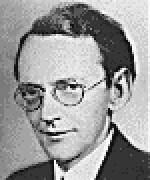 |
Karl Lashley his failure to find a single biological locus of memory (or "engram", as he called it) suggested to him that memories were not localized to one part of the brain, but were widely distributed throughout the cortex |
| 1890-1958 | |
 |
Kurt Lewin was the most influential of the gestalt psychologists |
| 1890-1947 | |
 |
Roberto Assagioli was the founder of the transpersonal psychology movement known as Psychosynthesis |
| 1888-1974 | |
 |
Charlie Dunbar Broad was the president of the society for psychical research |
| 1887-1971 | |
| Wolfgang Koehler gestalt psychologist | |
| 1887-1967 | |
 |
Louis Leon Thurstone was responsible for the standardized mean and standard deviation of IQ scores used today, as opposed to the mental age system originally used by Binet, as well he is known for the development of the Thurstone scale, the first formal technique for measuring an attitude |
| 1887-1955 | |
 |
Karen Horney challenged many of Freud's ideas as being misogynist, particularly his concept of penis envy, she countered with the claim of "womb envy", that males perceived females as being inferior largely due to males' inability to give birth |
| 1885-1952 | |
 |
Johannes H. Schultz invented autogenic training |
| 1884-1970 | |
 |
Otto Rank was one of Sigmund Freud's closest aides and later colleagues and finally critic |
| 1884-1939 | |
 |
Hermann Rorschach developed the projective test known as the Rorschach Inkblot Test |
| 1884-1922 | |
 |
Max Wertheimer was one of the founders of Gestalt psychology |
| 1880-1943 | |
 |
John Watson established the psychological school of behaviorism |
| 1878-1958 | |
 |
Lewis Terman was best known for inventing the Stanford-Binet IQ test, which popularized IQ tests in America |
| 1877-1956 | |
 |
Robert Mearns Yerkes studied the intelligence and social behavior of gorillas and chimpanzees |
| 1876-1956 | |
 |
Carl Jung founder of analytical psychology |
| 1875-1961 | |
 |
William McDougall invented hormic psychology |
| 1871-1938 | |
 |
Alfred Adler founder of the school of individual psychology |
| 1870-1937 | |
 |
Charles Edward Spearman was an English psychologist known for work in statistics, as a pioneer of factor analysis, and for Spearman's rank correlation coefficient, he also did seminal work on human intelligence, including the discovery of the g factor |
| 1863-1945 | |
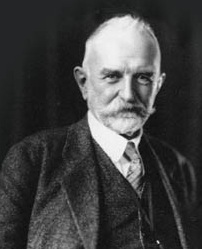 |
George Herbert Mead |
| 1863-1931 | |
 |
Vladimir Bekhterev noted the role of the hippocampus in memory and founded the field of psycho reflexology, transferring Pavlov's work on dogs to humans, and discovered Bekhterev's disease |
| 1857-1927 | |
 |
Alfred Binet was the inventor of the first usable intelligence test, the basis of today's IQ test |
| 1857-1911 | |
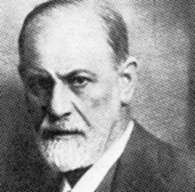 |
Sigmund Freud founder of psychoanalysis, |
| 1856-1939 | |
 |
Emil Kraepelin his laboratory discovered the pathologic basis of Alzheimers disease, as well as what we now know as schizophrenia, dementia praecox |
| 1856-1926 | |
 |
Alexius Meinong founder of Gegenstandstheorie |
| 1853-1920 | |
 |
Santiago Ramón y Cajal is considered the father of modern neuroscience |
| 1852-1934 | |
 |
Hermann Ebbinghaus pioneered experimental study of memory, and discovered the forgetting curve |
| 1850-1909 | |
 |
Ivan Petrovich Pavlov was a Russian physiologist who made important contributions to psychology such as describing the phenomenon now known as "conditioning" in experiments with dogs |
| 1849-1936 | |
 |
Edmund Gurney |
| 1847-1888 | |
 |
William James |
| 1842-1910 | |
 |
Gustave le Bon |
| 1841-1931 | |
 |
Wilhelm Max Wundt was the founder of experimental psychology |
| 1832-1920 | |
 |
Roberto Ardigo Psychology as a Positive Science |
| 1828-1920 | |
 |
Jean-Martin Charcot was the teacher of Sigmund Freud |
| 1825-1893 | |
 |
Alexander Bain |
| 1818-1903 | |
 |
John Stuart Mill developed utilitarianism |
| 1806-1873 | |
 |
James Braid coined the term and invented the procedure known as hypnotism |
| 1795-1860 | |
 |
Arthur Schopenhauer |
| 1788-1860 | |
 |
Jeremy Bentham was the founder of utilitarianism |
| 1748-1832 | |
 |
Franz Anton Mesmer |
| 1734-1815 | |
 |
Rudolphus Goclenius |
| 1547-1628 | |
 |
Juan Huarte de San Juan |
| 1530-1592 |