

invasion of Iraq (March 20, 2003)

the Persian Gulf war (August 2, 1990 - February 27, 1991)
the Carter Doctrine (1980)

with the Soviet invasion of Afghanistan (1979-1989) the Great "Game" between the
British
and the Russian Empire for supremacy in Central Asia was continued, now with
involvement form
the United States who supported Mujahideen forces like the Taliban to create an
anti-Soviet resistance
the Organisation internationale de la Francophonie (1970)
the Vietnam war (1965-1973)
the Commonwealth of Nations (1949)
World War II (1939-1945)
the Salt Satyagraha (March 12 - April 6, 1930)
the Balfour Declaration of 1926
the Rif War (1920)
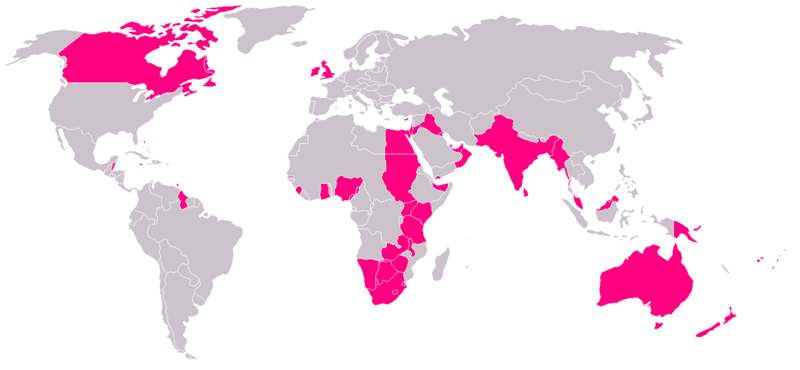
the British Empire at its zenith in 1919
the Balfour Declaration of 1917
the Sykes-Picot Agreement (May 16, 1916)
World War I (1914-1918)
the Tangier Crisis (1905)
The White Man's Burden (1899)
the Spanish-American
war (1898) resulted in the United States gaining
control over the former colonies of Spain in the Caribbean and Pacific
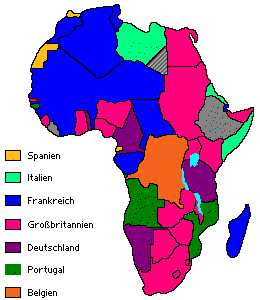
die deutsche Kolonialgesellschaft (19. Dezember 1887)
the Berlin Conference (1884-1885)
the Franco-Chinese war (September 1884 to June 1885)
the Boer wars (1880-1881,
1899-1902) were fought between the british and the settlers of dutch
origin in South Africa that put an end to the two independent republics that
they had founded
the second Anglo Afghan war (1878-1879)
New Imperialism (1871-1914))
the Indian Rebellion of 1857
William Walker (1855) a private adventurer, invaded Nicaragua and conquered the country
the Crimean War (1854-1856)
the second Anglo-Sikh war (1848-1849)
the first Anglo-Sikh war (1845-1846)

the Opium wars (1839-1842, 1856-1860) were conflicts between Britain and
its East India company fighting to gain easier access to ports in China for
trading Opium
the first Anglo Afghan war (1839-1842)
the French Foreign Legion (1831)
the French conquest of Algeria (1830)
the American Colonization Society (1817) founded Liberia, a colony on the coast of West
Africa and transported free blacks there, in an effort to remove them from the United States

Pax Britannica (1815-1870)
the British-American
war (1812-1815) was caused mostly due to the interference of the Royal Navy
in American
shipping. More than half of the British forces were made up of Canadian militia,
because Britain was at the same
time engaged in Europe with the Napoleonic wars. This war in North America ended
in a stalemate
the South American Wars of Independence (1810s -1820s)
the Mexican war of Independence (1810-1821) was Mexico's struggle for independence against Spanish colonial rule
the Tripolitan war
(1800-1815) also known as the Barbary Coast war was one of two wars
fought between the United States of America and the semiautonomous North African
city-
states of Morocco, Algiers, Tunis, and Tripoli, known collectively as the
Barbary States
the Russian-American Company (1799)

the Cape Frontier wars (1779-1879) were nine different wars between the Cape
colonists and
the Xhosa agricultural and pastoral peoples of the Eastern Cape, in South
Africa. It ended in
the annexation of Xhosa territories by the Cape Colony and the incorporation of
its peoples
Association for Promoting the Discovery of the Interior Parts of Africa (1788)

Captain Arthur Phillip (January 26, 1788) founded the first permanent European settlement in Australia
the First Anglo-Maratha war (1775-1782)

the American war of Independence (1775-1783) was a war fought primarily between
Great Britain
and revolutionaries within the thirteen North American colonies. The war, which
eventually widened
far beyond British North America, resulted in the overthrow of British rule in
the thirteen colonies and
the establishment of the United States of America on July 4, 1776 with the
Declaration of Independence.
The Battle of Yorktown (1781) was a victory by a combined American and French
force led by General
George Washington and the Comte de Rochambeau over a British army commanded by
General Lord Charles
Cornwallis. The surrender of Cornwallis' army caused the British government to
negotiate an end to the war
Quebec Act (1774)
the Treaty of Paris (1763)
French governor Marquis de Vaudreuil instructed François Gaston de Lévis to surrender Montreal to the British (1760)
the Battle of the Plains of Abraham gave Quebec City to the British (1759)
the French and Indian war (1755-1763)
le Grand Dérangement
(1755) was when some 6,000-7,000 Acadians were expelled from Nova Scotia
to France or the American colonies by the British government, after the Acadians
refused to take an oath
of allegiance to the Crown at the outbreak of the French and Indian war. Earlier
the Acadians became British
subjects when France ceded Acadia by the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713, and Acadia
became known as Nova Scotia

the Anglo-French war in India (1748-1757) were battles fought by the British
East India Company
against the French Compagnie des Indes Orientales and Indian forces in order to
establish the supremacy
of Britain over Bengal and India. The East India Company was founded in 1600 and
abolished in 1858
with the India act, when its powers were transferred to the Crown, represented
by the Viceroy
King George's war (1740-1748)

Queen Anne's war (1702–1713)
King William's war (1689-1697)

Rupert's Land (1670) was originally owned by the Hudson's Bay Company
the Second Anglo-Dutch war (March 4, 1665 - July 31, 1667) was fought between England and the United Provinces
the French East India Company (1664)
in the Anglo-Dutch wars (1652-1678) Dutch admiral Michiel de Ruyter destroyed most of the English fleet
in 1667, but England, who became the world’s greatest maritime power, won the final round of conflict

Jan van Riebeck conquered Africa’s Cape of Good Hope from the Portugese (1652)
the Navigation Acts (1651-1750) were passed in an effort to undermine Dutch trade and build commerce within the
British Empire. The Acts restrict colonial trade to English ships and channel the flow of goods through England
the turbulence of the fur trade, and poor relations with other Native American groups (1650) forced many Native
American nations to move west around the late 17th century. The Cheyenne, established as village-based farmers
and fishers in central Minnesota, migrated to the Great Plains where they take up a nomadic life based on buffalo hunting

Buccaneers (1650-1750) were pirates who attacked French and Spanish shipping
Dutch merchant Gerrit Van Wuysthoff journeyd to the Kingdom of Lan (1641) Xang in pursuit of resins for wood dye
and incense. The account of his journey up the Mekong River provides a rare record of Southeast Asian society
Anton van Diemen's capture of Malacca (1641) from the Portuguese assured Dutch control
over the international spice trade. Other dutch captures of trading ports of the East Indies included:
Achem, the native kingdom in Sumatra, 1667; Macassar, 1669 and finally Bantam itself, 1682
New Sweden (1638-1655)
the court of Mughal emperor Shah Jahan permited British merchants to set up a trading post (1632)
at Surat on the west coast of India and to trade along the southeastern Coromandel Coast
France gave a monopoly in its North American region to the Company of One Hundred Associates (1627)
in exchange for the promotion and management of French settlement. The Company promised to bring in
200 to 300 immigrants each year
New England (1620-1788)
the first Africans in England's North American Colonies arrived in Jamestown (August 1619) in the hold of a Dutch privateer ship.
Because of rough seas, 80 of the 100-person cargo perished, and the 20 remaining were sold into the servitude of English Colonists
New Netherland (1614-1674)
Dutch theologian and lawyer Hugo Grotius argued in Mare Liberum (1609) that by natural law
the seas belong to no one country. Therefore, the seas are free to all nations and subject to none
Samuel de Champlain (July 3, 1608) landed at the "point of Quebec" and set about fortifying
the area, establishing the first permanent European settlement in what today is Canada
Captain John Smith (May 13, 1607) established the first permanent English
settlement in North America the Virginia Colony at Jamestown
the Virginia Company (1606)
a group of Separatists led by William Brewster broke away from the Church of England (1606) the group escaped religious
persecution in England by moving to the Netherlands. In 1620, they traveled to America on the Mayflower and founded
the Plymouth colony near present-day Provincetown, Massachusetts. The group was later known as the Pilgrims
Runaway slaves established Maroon communities (1605-1695) known as quilombos, in the interior of northeastern Brazil.
The most important of these was Palmares, which was organized similarly to African societies and was ruled by its own king.
Dutch colonists were the first to try to destroy the Palmares quilombo, followed by the Portuguese, who signed a peace
treaty with King Ganga-Zumba in 1678. Ganga-Zumba’s general, Zumbi, continued to fight against the Portuguese until he was
imprisoned and hanged in 1694. Palmares fell to the Portuguese the following year
the Acadians (1604) were farmers of western France who started to settle in what today is Nova Soctia
the Dutch East India Company (March 20, 1602)
the British East India Company (1600)
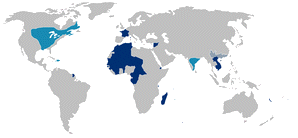
the French colonial empire (17th century -1960)
the Dutch Empire (1588)
Thomas Harriot's Brief and True Report of the New Found Land of Virginia (1588)
the Anglo-Spanish war (1585-1604)
Queen Nzinga of the Mbundu people in the Ndongo Kingdom (in present-day Angola) (1582-1663)
struggled unsuccessfully to defend her homeland against Portuguese colonialism in the region
Francis Drake (1577) was commissioned by Queen Elizabeth to undertake
an expedition against the Spanish along the Pacific coast of the Americas
a Spanish force in South America, under Hurtado de Arbieto (June 24, 1572 - September 24, 1572) captured the last Inca capital
of Vilcabamba after a short campaign. The last Inca ruler, Tupac Amarú, was publicly executed in the former Inca capital of Cuzco
after the assassination of two Franciscan missionaries (April 14, 1572) and an emissary, Francisco de Toledo,
the Spanish viceroy of Peru, declares war on the Vilcabamba Inca state of the newly enthroned emperor Tupac Amarú
Saint Augustine (August 28, 1565) the oldest permanent European settlement
in the United States was founded by Spanish explorer Pedro Menéndez de Avilés
Short Account of the Destruction of the Indies (1552) Bartolomé de Las Casas
Spanish colonists establishrf the University of San Marcos, in Lima, Peru (1551)
It was the first institution of higher education in the western hemisphere
Iroquois nations formed a league of 12,000 tribal members (1550) in reaction to the growing European presence.
At its height, the confederacy controled land from the St. Lawrence River to Tennessee, and as far east as Michigan
Silver was discovered in the mountains of southern Charcas (present-day Bolivia) (1546) and the mining town of
Potosí was founded within a year. By the early 17th century, the Potosí mines became the largest source of silver in the world
Leyes Nuevas (1542)
attracted by the fur trade with Europe, Algonkins (1542 - 1650) from the north and west crowd the Iroquois along the Saint
Lawrence River, pushing them toward the Great Lakes. The competition leads to skirmishes and the ultimate victory of the Iroquois

Pedro de Valdivia founded Santiago de la Nueva Extremadura (1540-1541)
and began the struggle to conquer Chile. The native Araucanian people resisted
fiercely in the south, killing Valdivia in 1553
the Viceroy of Mexico Antonio de Mendoza (1540) compiled surviving Aztec documents by order of King Charles V of Spain. Aztec
scribes assemble the Codex Mendoza and mix Spanish with indigenous painting and writing styles to record their history and way of life

the legend of El Dorado (1537)
A Spanish expedition led by Diego de Almagro (April 18, 1537) relieved Cuzco from its siege by the Inca leader
Manco Capac II. Almagro then seized the city from Hernando Pizarro, starting the civil wars between the conquistadors
New Spain (1535-1821)
Francisco Pizarro signed an agreement with Diego de Almagro (June 12, 1535) to divide the territories of the Inca Empire
between them. Almagro gave up his claim to the Inca capital of Cuzco in return for full rights to the area of modern Chile
New France (1534-1763)
Sebastián de Belalcázar (May 3, 1534) set out toward Quito, the northern
capital of the Inca Empire, aiming to complete the Empire's conquest
Pizarro’s army marched south toward Cuzco (November 8, 1533) the vanguard of the tiny army, under Hernando de Soto,
was badly bloodied at the battle of Vilcaconga, Peru. However Quisquis, the general of the Inca forces, fails to press his advantage,
and the Spanish continue to advance on the Inca capital of Cuzco
Pizarro executed Atahualpa (July 26, 1533) despite having accepted a large ransom for his release
the forces of Pizarro (November 1532) seized the Inca emperor Atahualpa by ambush in the city of Cajamarca
the Spanish conquistador Francisco Pizarro entered the Inca Empire with horses and fewer than 200 men (May 16, 1532)
Atahualpa became Emperor (April 1532) after his forces decisively defeated those of Huáscar, his rival as Inca emperor
Portuguese colonized Brazil (1532) Governor of the São Vicente settlement, Martim Afonso de Sousa, established
the fazenda system. He distributed to noblemen large parcels of land, which formed the basis for the plantation system in Brazil
Francisco Pizarro was appointed Governor of Peru (July 26, 1529)
the Narváez expedition (1527-1528) was a Spanish attempt
to install Pánfilo de Narváez as adelantado (governor) of Florida
Aztec defenders under Cuauhtémoc attacked Hernán Cortés (June 30, 1520) and his troops on the Noche Triste,
forcing them to evacuate the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlán. Over half the Spanish soldiers are killed, and all of their
cannons are lost. Cortés and his remaining men retreat to the city of Tlaxcala to regroup
the Spanish conquest of Yucatán (1520-1697) brought Mexcio, that is the former Aztec empire,
under Spanish rule in 1521. The territory of the Mayas in the south was conquered up until 1697
Goa (1510) was conquered by Afonso de Albuquerque
Santa Maria de la Antigua (1510) was established by Spanish explorer Vasco Núñez
de Balboa on the Caribbean coast of what is now Darién Province, Panama
the Battle of Diu (1509)
Queen Isabella approved the Encomienda System (1503)
King Ferdinand established La Casa de Contratación (1503) a Board of Trade to regulate commerce in
Spanish America, which developed the colonial economy according to principles later called mercantilism
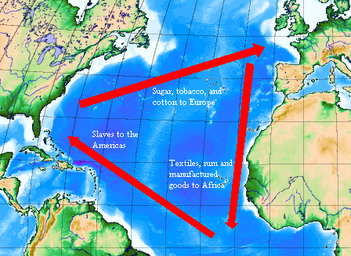
the triangular Atlantic trade (1500-1808)
Jamaica was claimed for Spain (1494) after Christopher Columbus
first landed there. Later it was used it as his family's private estate

the Treaty of Tordesillas
(June 7, 1494) divided the world outside of Europe in
an
exclusive duopoly between the Spanish and the Portuguese along a north-south
meridian 370 leagues (1770 km; 1100 miles) west of the Cape Verde Islands
Inter caetera (1493)
the Colonization of the Americas

Columbus first reached land at Guanahani, an island in the Bahamas (October 12, 1492)
Boabdil, the last Moorish King of Granada, surrendered the city (January 2, 1492) to the army of Ferdinand and Isabella after a lengthy siege
the Queen of Cyprus, Catherine Cornaro (March 14, 1489) sold her
kingdom to Venice which already owned Dalmatia, Corfu and Crete
the Treaty of Alcaçovas (September 4, 1479)
the Portuguese Armada (August 21, 1415) managed to conquer the North African trade centre Ceuta, thus
founding the Portuguese Empire: the earliest and longest lived of the western european colonial empires (1415-1999)
the Battle of Aljubarrota (August 14, 1385)
Crusades (1096-1291) were Roman Catholic endeavors to re-capture the Holy Land from the Muslims