![]()
![]()
 |
Masaru Emoto |
| 1943 | |
 |
Robert Nalbandyan is the co-discoverer of the photosynthetic protein plantacyanin and a pioneer in the field of free radicals |
| 1937 | |
 |
Robert Curl discoverer of fullerenes, wich are one of only four types of naturally occurring forms of carbon (the other three being diamond, graphite and ceraphite) |
| 1933 | |
 |
Neil Bartlett prepared the first noble gas compound, xenon hexafluoroplatinate, Xe+[PtF6]-. This contradicted all ideas chemists had of the nature of valency, as it was believed that xenon, like all noble gases, was totally inert to chemical combination |
| 1932 | |
 |
Stanley L. Miller showed in the Miller-Urey experiment that, if a mixture of ammonia, methane and hydrogen be exposed to ultraviolet radiation and to water, it can interact to produce amino acids, the building blocks of life |
| 1930 | |
 |
Ilya Prigogine was a Belgian physicist and chemist noted for his work on dissipative structures, complex systems, and irreversibility |
| 1917-2003 | |
|
Robert Burns Woodward was an American organic chemist, widely regarded as the preeminent organic chemist of the century. He made many outstanding contributions to modern organic chemistry, especially through the synthesis and structure determination of complex natural products |
|
| 1917-1979 | |
 |
Glenn Theodore Seaborg was prominent in the discovery and isolation of many transuranic elements (including plutonium, during the Manhattan Project) |
| 1912-1999 | |
 |
Melvin Calvin was a chemist most famed for discovering the Calvin cycle |
| 1911-1997 | |
 |
Roy J. Plunkett was the chemist who accidentally invented Teflon |
| 1910-1994 | |
 |
Willard Frank Libby was an American chemist, famous for his role in the development of radiocarbon dating, a process which revolutionised archaeology |
| 1908-1980 | |
| Dr. Albert Hofmann is best known as the father of LSD | |
| 1906-2008 | |
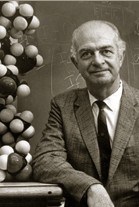 |
Linus Carl Pauling was a pioneer in the application of quantum mechanics to chemistry, and was one of the founders of molecular biology |
| 1901-1994 | |
 |
Robert Sanderson Mulliken was primarily responsible for the elaboration of the molecular orbital method of computing the structure of molecules |
| 1896-1986 | |
 |
Henrik Carl Peter Dam was awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine in 1943 for his work in discovering vitamin K and its role in human physiology |
| 1895-1976 | |
 |
John Lennard-Jones computational chemistry |
| 1894-1954 | |
| Henry Gilman organometallic chemistry | |
| 1893-1986 | |
 |
Harold Clayton Urey peformed the Miller-Urey experiment with Stanley L. Miller |
| 1893-1981 | |
 |
Victor Goldschmidt was a chemist considered to be the founder of modern geochemistry and crystal chemistry, developer of the Goldschmidt Classification of elements |
| 1888-1947 | |
 |
Irving Langmuir advanced several basic fields of physics and chemistry, invented the gas filled incandescent lamp, the hydrogen welding technique, and did work in surface chemistry |
| 1881-1957 | |
 |
Lise Meitner studied radioactivity and nuclear physics |
| 1878-1968 | |
 |
Gilbert Newton Lewis coined the term "photon" for the smallest unit of radiant energy, published several papers on relativity, in which he derived the mass-energy relationship in a different way from Albert Einstein's derivation, defined the term odd molecule, formulated the Lewis theory of acids and bases, invented the chemical notation system called the Lewis dot structure |
| 1875-1946 | |
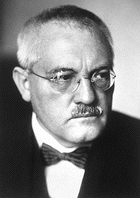 |
Carl Bosch developed the Haber-Bosch process together with Fritz Haber, the Haber Process (also Haber-Bosch process) is the reaction of nitrogen and hydrogen to produce ammonia |
| 1874-1940 | |
 |
Richard Wilhelm Heinrich Abegg was the pioneer of valence theory |
| 1869-1910 | |
 |
Felix Hoffmann is best known for having synthesized acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) for the first time in a stable form usable for medical applications, which Bayer then started marketing as Aspirin |
| 1868-1946 | |
 |
S°ren Peder Lauritz S°rensen introduced the chemical concept pH |
| 1868-1939 | |
 |
Maria Skłodowska-Curie and Pierre Curie isolated and named the radioactive elements polonium and radium, and pioneered the science of radiology |
| 1867-1934, 1859-1906 | |
 |
Alfred Werner developed the basis for modern coordination chemistry and proposed the octahedral configuration of transition metal complexes |
| 1866-1919 | |
 |
Vladimir Vernadsky |
| 1863-1945 | |
 |
Paul Ehrlich is noted for his work in hematology and immunology, and coined the term chemotherapy |
| 1854-1915 | |
 |
Wilhelm Ostwald invented the Ostwald process used in the manufacture of nitric acid, leading to mass production of fertilizers and explosives. He also did significant work on dilution theory leading to his discovery of the law of dilution which is named after him |
| 1853-1932 | |
 |
William Ramsay published several notable papers on the oxides of nitrogen and followed these up with the discovery of argon, helium, neon, krypton, and xenon |
| 1852-1916 | |
 |
Hermann Emil Fischer his name can still be found in the names of many chemical reactions and concepts |
| 1852-1919 | |
 |
Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff accounted for the phenomenon of optical activity by assuming that the chemical bonds between carbon atoms and their neighbors were directed towards the corners of a regular tetrahedron. This three-dimensional structure perfectly accounted for the isomers found in nature |
| 1852-1911 | |
 |
Henry Louis Le Chatelier is most famous for Le Chatelier's principle, which is used by chemists to predict the effect of a change in conditions on a chemical equilibrium |
| 1850-1936 | |
 |
Sir James Dewar discovered a process to produce liquid oxygen in industrial quantities, developed an insulating bottle, Dewar flask, still named after him, to study low temperature gas phenomena, and observed that cold charcoal could produce a vacuum |
| 1842-1923 | |
 |
Johannes Diderik van der Waals was the first to realise the necessity of taking into account the volumes of molecules and the intermolecular forces (now generally called "van der Waals forces") in establishing the relationship between the pressure, volume and temperature of gases and liquids |
| 1837-1923 | |
|
Alexander Mitscherlich his most important work was in the field of processing wood to create cellulose |
|
| 1836-1918 | |
 |
Dmitri Ivanovich Mendeleev was the creator of the Periodic Table of Elements |
| 1834-1907 | |
 |
Angelo Mariani started marketing a wine called Vin Mariani which had been treated with coca leaves |
| 1832-1914 | |
 |
Julius Lothar Meyer was contemporary and competitor of Dmitri Mendeleev to draw up the first periodic table of chemical elements. Some five years apart, both Mendeleev and Meyer worked with Robert Bunsen |
| 1830-1895 | |
 |
Friedrich August KekulÚ von Stradonitz discovered the ring shape of the benzene molecule after dreaming of a snake seizing its own tail |
| 1829-1896 | |
 |
Emil Erlenmeyer formulated the Erlenmeyer Rule: All alcohols in which the hydroxyl group is attached directly to a double-bonded carbon atom become aldehydes or ketones |
| 1825-1909 | |
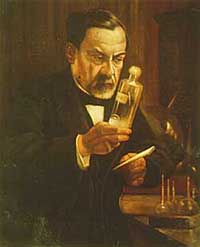 |
Louis Pasteur is known for his demonstration of the germ theory of disease and his development techniques of inoculation, most notably the first vaccine against rabies; he also made a major discovery in the field of chemistry, regarding asymmetric molecules and the polarization of light |
| 1822-1895 | |
 |
Robert Wilhelm Bunsen perfected the burner that was named after him, invented by British chemist/physicist Michael Faraday, and worked on emission spectroscopy of heated elements |
| 1811-1899 | |
 |
Thomas Graham discoverd the medical method known as dialysis |
| 1805-1869 | |
 |
Justus von Liebig made major contributions to agricultural and biological chemistry, and worked on the organization of organic chemistry |
| 1803-1873 | |
 |
Friedrich W÷hler is best-known for his synthesis of urea, but was also the first to isolate several of the elements |
| 1800-1882 | |
 |
Jean Baptiste AndrÚ Dumas is best known for his works on organic analysis and synthesis, as well as the determination of atomic weights (relative atomic masses) by measuring vapor densities
|
| 1800-1884 | |
 |
Friedrich Wilhelm SertŘrner isolated morphine from opium |
| 1783-1841 | |
 |
J÷ns Jakob Berzelius invented modern chemical notation and is considered one of the fathers of modern chemistry
|
| 1779-1848 | |
 |
Bernard Courtois discovered iodine |
| 1777-1838 | |
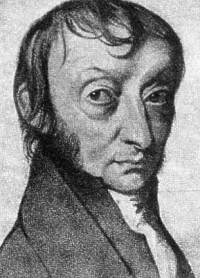 |
Amedeo Avogadro is most noted for his contributions to the theory of molarity and molecular weight. The number of molecules in one mole is called Avogadro's number is honor of him, as is Avogadro's law |
| 1776-1856 | |
 |
John Dalton is most well known for his advocacy of the atomic theory |
| 1766-1844 | |
 |
Johan Gadolin discovered the element yttrium, the first rare earth element |
| 1760-1852 | |
 |
Antoine-Laurent de Lavoisier is often referred to as the father of modern chemistry, stated the first version of the Law of Conservation of Matter, recognized and named oxygen, disproved the phlogiston theory, and helped to reform chemical nomenclature |
| 1743-1794 | |
 |
Carl Wilhelm Scheele was the discoverer of many chemical substances, most notably discovering oxygen before Joseph Priestley |
| 1742-1786 | |
 |
Joseph Priestley his most important achievement was the isolation of oxygen by heating mercuric oxide |
| 1733-1804 | |
 |
Henry Cavendish is credited with having discovered hydrogen |
| 1731-1810 | |
 |
Joseph Black discovered carbon dioxide (which he called `fixed air┤) |
| 1728-1799 | |
 |
Robert Boyle is largely regarded today as the first modern chemist and among his works "The Sceptical Chemist" is seen as a cornerstone book in the field of chemistry |
| 1627-1691 | |
 |
Jan Baptist van Helmont |
| 1580-1644 | |
|
|
Michal Sedziwˇj |
| 1566-1636 | |
 |
John Dee |
| 1527-1609 | |
| Georg Agricola | |
| 1490-1555 | |
 |
Nicholas Flamel |
| 1330-1419 | |
| Arnaldus de Villanueva | |
| 1235-1313 | |
 |
Abu Bakr al Razi |
| 854-925 | |
 |
Jabir Ibn Hayyan |
| 721-815 |