![]()
![]()
 |
Elizabeth Blackburn is the leading researcher in the field of telomeres, the 'telomerase' enzyme, and their effect on the aging of cells and propogation of cancer |
| 1948 | |
 |
Kary Mullis he invented the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), a central technique in molecular biology which allows the amplification of specified DNA sequences |
| 1944 | |
 |
Rupert Sheldrake |
| 1942 | |
 |
Richard Dawkins is best known for popularising the Williams Revolution in his book "The Selfish Gene" |
| 1941 | |
 |
Charles DeLisi succeeded to identify all 30000000000 genes in the human genome |
| 1941 | |
 |
Stephen Jay Gould was a paleontologist, evolutionary biologist as well as the most influential and widely read writer of popular science of his generation |
| 1941- 2002 | |
 |
Stuart Alan Kauffman is a biologist and complex systems researcher, and is most widely known for his promotion of self-organization as a factor that is at least as important as Darwinian natural selection in producing the complexity of biological systems and organisms |
| 1939 | |
 |
Daniel Janzen founded "Area de Conservación Guanacaste", probably the oldest, largest and most successful habitat restoration project in the world, 1.430 km2, located just south of the Costa Rica-Nicaragua border, between the Pacific Ocean and the Talamanca mountain range |
| 1939 | |
 |
David Suzuki is a geneticist who has attained prominence as a science broadcaster ("The Nature of Things") and an environmental activist |
| 1936 | |
 |
William Donald Hamilton can be seen as one of the forerunners of the discipline of sociobiology founded by Edward Osborne Wilson |
| 1936-2000 | |
 |
Robert Rosen focused his scientific work on the question: "what is life?" ("why are organisms alive?") |
| 1934-1998 | |
 |
Allan Wilson is best known for his "Mitochondrial Eve" hypothesis |
| 1934–1991 | |
 |
Richard Alexander his scientific pursuits integrate the fields of systematics, ecology, evolution, natural history and behaviour |
| 1930 | |
| Edward Osborne Wilson coined the term biodiversity | |
| 1929 | |
 |
Desmond Morris author of " the Naked Ape" |
| 1928 | |
 |
Carl Woese is an American microbiologist famous for defining the Archaea (a new domain or kingdom of life) in 1977 by phylogenetic analysis of 16S ribosomal RNA, a technique pioneered by Woese which is now standard practice, he was also the originator of the RNA world hypothesis in 1967 |
| 1928 | |
 |
George Christopher Williams is noted for starting the Williams revolution, presenting a gene-centric basis for biology with his book "Adaptation and Natural Selection" |
| 1926 | |
 |
John Maynard Smith was instrumental in the application of game theory to evolution and theorised on other problems such as the evolution of sex and signalling theory |
| 1920-2004 | |
 |
Rosalind Elsie Franklin made important contributions to the understanding of the fine structures of coal, DNA and viruses |
| 1920-1958 | |
 |
Francis Crick, James Dewey Watson are the discoverers of the structure of the DNA molecule |
| 1916-2004, 1928 | |
 |
Eugene Odum is often referred to as "the father of ecosystem ecology" |
| 1913-2002 | |
 |
George Emil Palade described the structure and function of organelles in cells |
| 1912 | |
|
○
|
Lucien Lison |
| 1908-1979 | |
 |
Marjorie Courtenay-Latimer was the South African museum official who in 1938 brought to the attention of the world the existence of the coelacanth, a fish thought to have been extinct for seventy million years |
| 1907-2004 | |
 |
Rachel Louise Carson was a zoologist and biologist whose landmark book, Silent Spring is often credited with having launched the global environmental movement |
| 1907-1964 | |
 |
Ernst Mayr helped develop the modern evolutionary synthesis of Mendelian genetics and Darwinian evolution |
| 1904-2005 | |
 |
Konrad Lorenz founder of ethology |
| 1903-1989 | |
 |
Louis Seymour Bazett Leakey was an archaeologist whose work was important in establishing human evolutionary development in Africa |
| 1903-1972 | |
 |
George Gaylord Simpson was the most influential scientists in paleontology (the study of the developing history of life on earth based on the fossil record) of the twentieth century |
| 1902-1984 | |
 |
Ronald Fisher has been described by Richard Dawkins as "the greatest of Darwin’s successors," was one of the founders of the neo-Darwinian modern evolutionary synthesis |
| 1890-1962 | |
 |
Sir Albert Howard is an organic farming pioneer, and a principal figure in the early organic movement |
| 1873-1947 | |
 |
David Grandison Fairchild was responsible for the introduction of more than 20,000 exotic plants and varieties of established crops into the United States, including mangos, alfalfa, nectarines, dates, horseradish, bamboos and flowering cherries |
| 1869-1954 | |
 |
James Mark Baldwin |
| 1861-1934 | |
 |
Wilhelm Ludvig Johannsen coined the word gene |
| 1857-1927 | |
 |
Hermann Müller |
| 1850-1927 | |
 |
Robert Koch is considered one of the founders of bacteriology, he became famous for the discovery of the tubercle bacillus and the cholera bacillus and for his development of Koch's postulates |
| 1843-1910 | |
|
○
|
Gustav Heinrich Theodor Eimer is credited with popularizing the term "Orthogenesis" to describe an intrinsic drive in life towards perfection, a form of directed evolution |
| 1843-1898 | |
 |
Anton Dohrn was a prominent Darwinist |
| 1840-1909 | |
 |
Ernst Haeckel popularized Charles Darwin's work in Germany |
| 1834-1919 | |
 |
John Lubbock was responsible for inventing the names Palaeolithic and Neolithic to denote the Old and New Stone Ages respectively |
| 1834-1913 | |
 |
Anton de Bary is considered a founding father of plant pathology (phytopathology) and coined the term symbiosis |
| 1831-1888 | |
 |
Charles Wyville Thomson chief scientist on the Challenger expedition |
| 1830-1882 | |
 |
George Jackson Mivart author of "the Origin of Human Reason" |
| 1827-1900 | |
 |
Armand David found in China altogether 200 species of wild animals, of which 63 were hitherto unknown to zoologists (such as the Giant Panda or the Père David's Deer), and 807 species of birds, 65 of which had not been described before |
| 1826-1900 | |
 |
Thomas Henry Huxley known as "Darwin's Bulldog" for his defence of Charles Darwin's theory of evolution. He also coined the term "agnosticism" to describe his stance on religious belief |
| 1825-1895 | |
 |
Alfred Russel Wallace his independent proposal of a theory of evolution by natural selection prompted Charles Darwin to reveal his own more developed and researched, but unpublished, theory sooner than he had intended |
| 1823-1913 | |
 |
Gregor Mendel is often called the "father of genetics" for his study of the inheritance of traits in pea plants |
| 1822-1884 | |
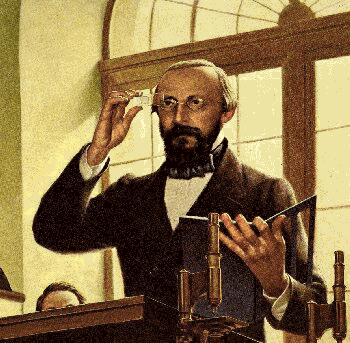 |
Rudolf Virchow one of his most famous rules is Omnis cellula e cellula ("every cell originates from another cell") |
| 1821-1902 | |
 |
Karl Wilhelm von Nägeli discovered what would later become known as chromosomes |
| 1817-1891 | |
 |
Henry David Thoreau |
| 1817-1862 | |
 |
Claude Bernard is the father of the concept of homeostasis |
| 1813-1878 | |
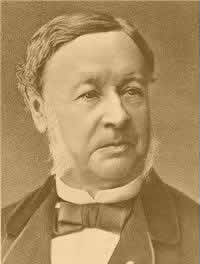 |
Theodor Schwann was the co-founder of cell theory and invented the term metabolism |
| 1810-1882 | |
 |
Charles Darwin achieved lasting fame as originator of the theory of evolution through natural selection |
| 1809-1882 | |
 |
Louis Agassiz was the first to come up with the idea that the Earth had been subject to a past ice age |
| 1807-1873 | |
 |
Richard Owen gave a spur to the inception of Darwin's theory of natural selection |
| 1804-1892 | |
 |
Matthias Jakob Schleiden was the first to formulate the cell theory |
| 1804-1881 | |
 |
Alcide d'Orbigny was the first scientist to describe geological timescales and defined numerous geological strata |
| 1802-1857 | |
 |
David Douglas |
| 1799-1834 | |
|
Christian Gottfried Ehrenberg German naturalist, zoologist, comparative anatomist, geologist, and microscopist, was one of the most famous and productive scientists of his time |
|
| 1795-1876 | |
 |
Karl Ernst von Baer formulated what would later be called the Baer's laws for embryology |
| 1792-1876 | |
 |
Carl Gustav Carus |
| 1789-1869 | |
 |
Christian Jürgensen Thomsen related the classification of artifacts to technology, that is, according to the materials in which they were made (stone, bronze, and iron), thereby defining the Stone Age, the Bronze Age, and the Iron Age |
| 1788-1865 | |
|
John James Audubon American ornithologist. He painted, catalogued, and described the birds of North America |
|
| 1786-1851 | |
 |
Lorenz Oken defined five animal classes: Invertebrates, Fish, Reptiles, Birds and Mammals |
| 1779-1851 | |
 |
Georges Cuvier his system of zoological classification led him toward the development of paleontology |
| 1769-1832 | |
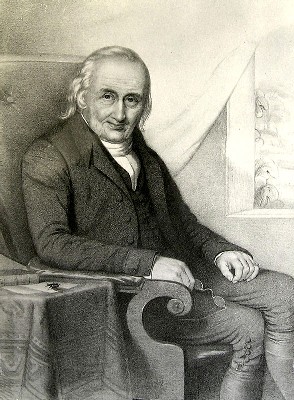 |
William Kirby entomology |
| 1759-1850 | |
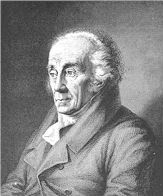 |
Johann Friedrich Blumenbach was a German physiologist and anthropologist.on the basis of his craniometrical research (analysis of human skulls), he divided the human species into five races: the Caucasian or white race, the Mongolian or yellow, the Malayan or brown race, the Negro or black race, and the American or red race |
| 1752-1840 | |
 |
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe known for his literary works but also a scientist. In biology his theory of plant metamorphosis stipulated that all plant formation stems from a modification of the leaf |
| 1749-1832 | |
 |
Jean-Baptiste Lamarck coined the term biology and taught that evolution fuctions by inheritance of acquired characteristics |
| 1744-1829 | |
 |
Sir Joseph Banks was the English naturalist and botanist on Cook's first great voyage (1768-1771) and some 75 species bear Banks' name. He is credited with the introduction to the West of eucalyptus, acacia, mimosa, and the genus named after him, Banksia |
| 1743-1820 | |
 |
Erasmus Darwin his most important scientific work is his Zoönomia, which contains a system of pathology, and a treatise on "generation," in which he, anticipated the views of Jean-Baptiste Lamarck, who in turn is regarded to have foreshadowed the theory of evolution |
| 1731-1802 | |
 |
Jan Ingenhousz is best known for his discovery of the process of photosynthesis |
| 1730-1799 | |
 |
Johann Reinhold Forster made contributions to the early ornithology of Europe and North America. He is best known as the naturalist on James Cook's second Pacific voyage, when he was accompanied by his son Georg Forster |
| 1729-1798 | |
 |
Charles Bonnet |
| 1720-1793 | |
 |
Georges-Louis Leclerc, Comte de Buffon influenced the next two generations of naturalists, including Jean-Baptiste Lamarck and Charles Darwin with his views such as the high similarity between humans and apes, and the possibility of a common ancestry |
| 1707-1788 | |
 |
Carolus Linnaeus laid the foundations for the modern scheme of taxonomy |
| 1707-1778 | |
 |
Pierre Louis Maupertuis |
| 1698-1759 | |
 |
Mark Catesby produced the first published account of the flora and fauna of North America. It included 220 plates of birds, reptiles and amphibians, fish, insects, and mammals |
| 1683-1749 | |
 |
Robert Hooke coined the biological term cell |
| 1635-1703 | |
 |
Marcello Malpighi was an Italian doctor, who gave his name to several physiological features. He was pioneer in using a microscope and he has also been described as a founder of comparative physiology and microscopic anatomy |
| 1628-1694 | |
 |
John Ray |
| 1627-1705 | |
 |
Gaspard Bauhin introduced binomial nomenclature into taxonomy, which was much later taken up by Linnaeus |
| 1560-1624 | |
 |
Andrea Cesalpino |
| 1519-1603 | |
 |
Rembert Dodoens Dodoens' herbal Cruydeboeck with 715 images (1554) was influenced by that of Leonhart Fuchs. He divided the plant kingdom in six groups |
| 1517-1585 | |
 |
Conrad Gessner his three-volume Historia Animalium is considered the beginning of modern zoology |
| 1516-1565 | |
|
Leonardo da Vinci is known as an artist but was also an anatomist. He dissected hundreds of specimens and drew exact copies of them |
|
| 1452-1519 | |
 |
Gaius Plinius Secundus |
| 23-79 | |
 |
Theophrastus was the successor of Aristotle in the Peripatetic school, the most important of his books are two large botanical treatises, On the History of Plants and On the Causes of Plants |
| 372-287 bc | |
 |
Aristotle |
| 384-322 bc | |
|
○
|
Speusippus wrote books on biological classification before Aristotle |
| 408-339 bc | |
 |
Xenophanes examined fossils |
| 570-475 bc |