![]()

Pop art (late 1950s) David LaChapelle, 2004
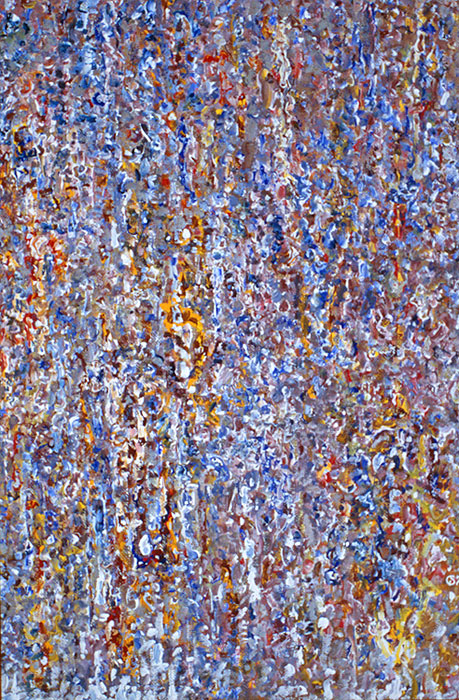

Abstract expressionism (1946) Anatoly Sokolov, the Biginning, 2002
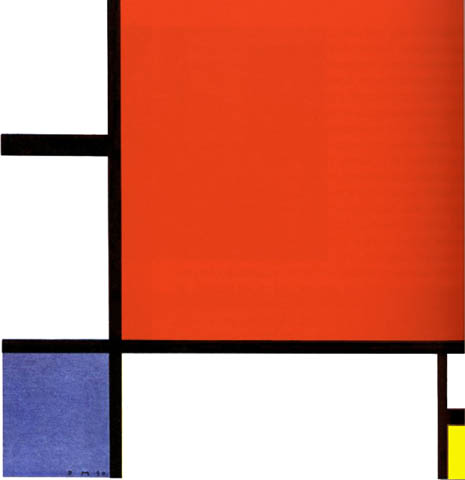
Postmodernism (1933) Piet Mondrian, Composition with Red, Blue, and Yellow
the fire in the Glaspalast (July 6, 1931)

American art (1930) American Gothic by Grant Wood

Art Deco (1925)
New Objectivity (1920s)
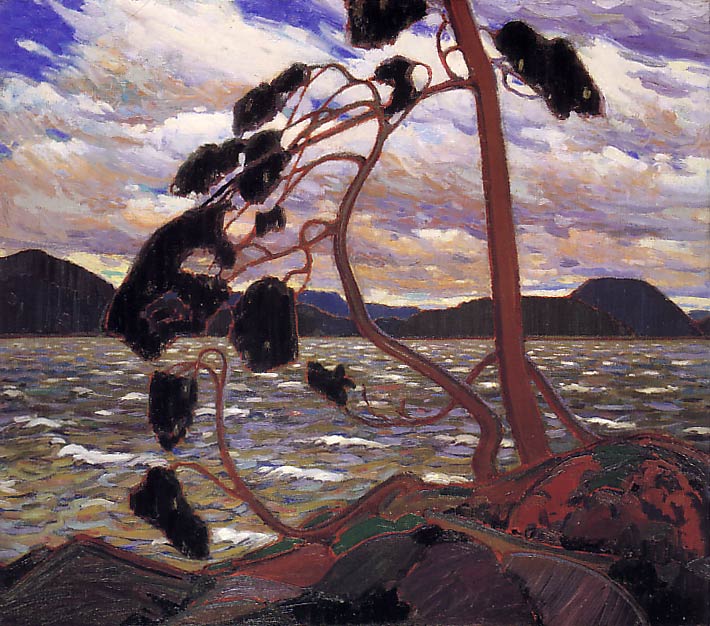

the Group of Seven (1917) Tom Thomson, the West Wind
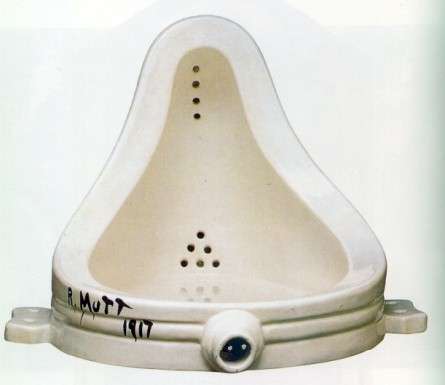
objet trouvé (1917) Marcel Duchamp

Metaphysical Painting (1917) Carlo Carrà

Surrealism (1910s) is an artistic movement and an aesthetic philosophy that aims for
the liberation of the mind by emphasizing the critical and imaginative powers of the unconscious
René Magritte, The Son of Man, 1964

Dadaism (1916-1920)

Suprematism (1913-1918) Kasimir Malevich, Black Circle, 1913
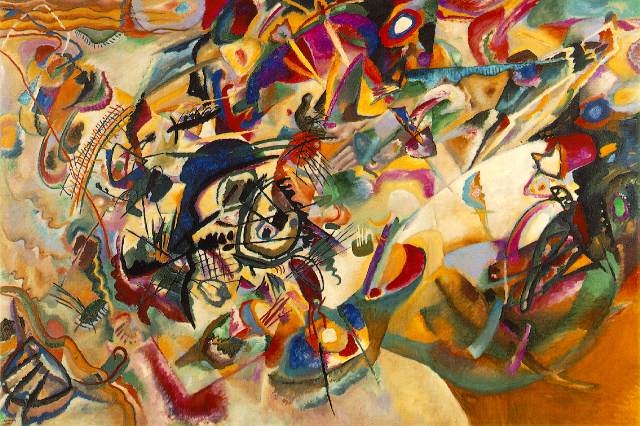

der Blaue Reiter (1911-1914) Wassily Kandinsky, Composition VI, 1913

Expressionism (1910) Franz Marc, Yellow Cow, 1911

Cubism (1908-1914) Pablo Picasso, Bather with Beach Ball, 1910
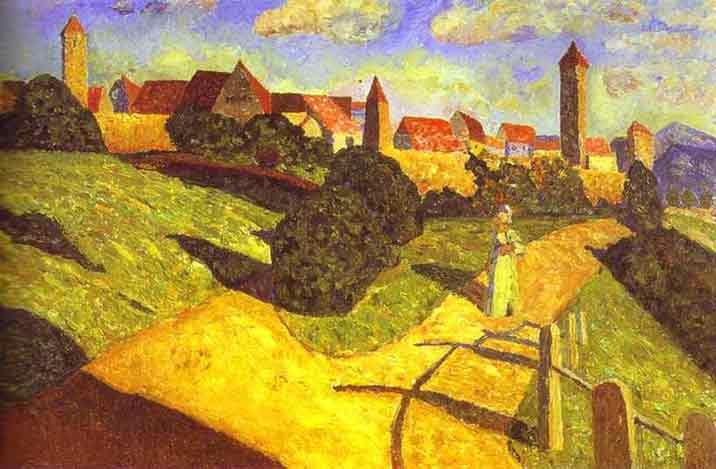

Modernism (1900) Wassily Kandinsky, Farewell, 1903
filmmaking (1898)
Cloisonnism (late 19th century)

Pointillism (late 1880s)


Fauvism (1888-1908) Henri Matisse, the Dessert: Harmony in Red, 1908

Art Nouveau (1892-1902) Alfons Mucha, Dancel, 1898
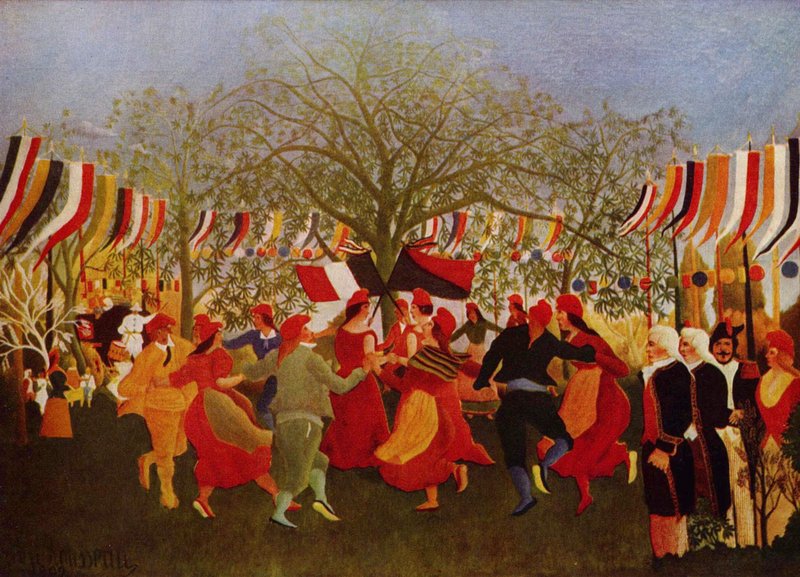

Post-impressionism (1890) Henri Rousseau, A Hundred Years of Independence, 1892
the Arts and Crafts movement (late 19th century)
Salon des Refusés (1863)

Impressionism (1860-1880) Oscar-Claude Monet, Nymphéas, 1890

Édouard Manet (1863) Le déjeuner sur l'herbe
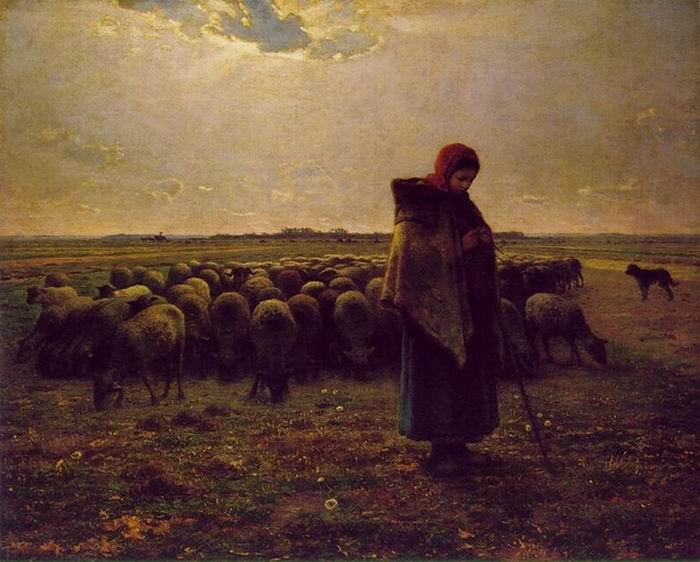

Realism (1840-1880) Jean-François Millet, La bergère gardant ses moutons, 1863

Barbizon school (1830-1870) Jean-François Millet, les glaneuses, 1857
Tableaux vivants (19th century) Joseph Wright of Derby, An Experiment on a Bird in an Air Pump
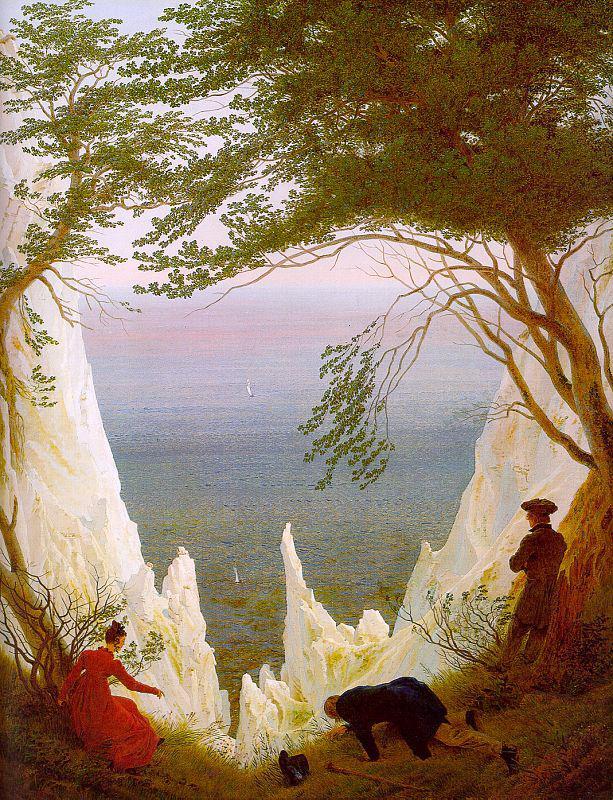

Romanticism (17??-18??) Caspar David Friedrich, Chalk Cliffs on Rügen, 1830
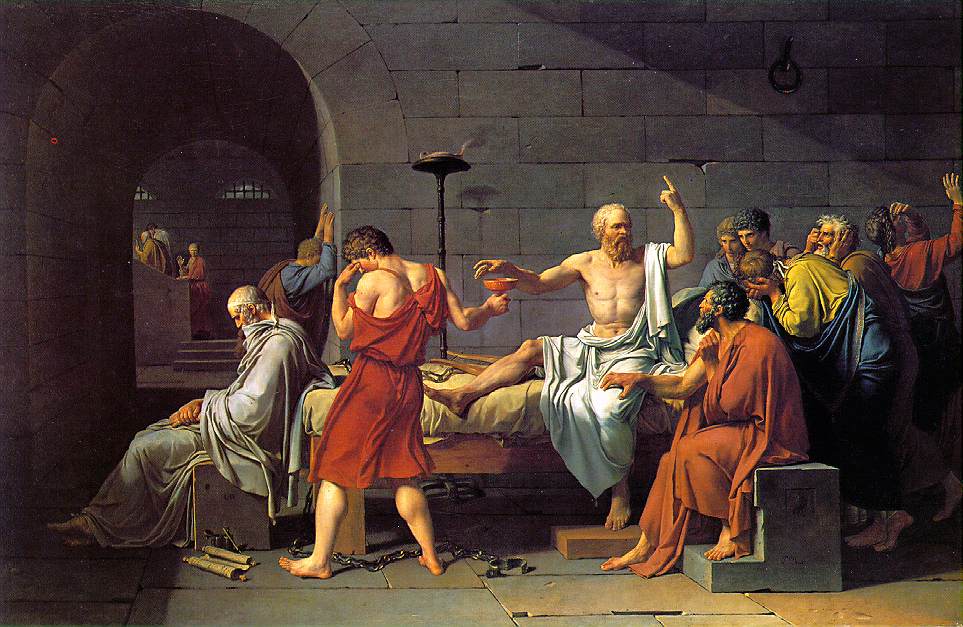

Neo Classicism (1765-1830) Jacques-Louis David, the death of Socrates, 1787

Classicism (1750-1820) in the arts, refers generally to a high regard for classical antiquity as setting standards
for taste which the classicist seeks to emulate. Classicism is usually contrasted with romanticism; the art of classicism
typically seeks to be formal, restrained, and Apollonian rather than Dionysian, in Friedrich Nietzsche's well known opposition.
Sir Lawrence Alma Tadema, Sappho and Alcaeus, 1881

Rococo (1700-1789) Francois Boucher, le Dejeuner, 1739
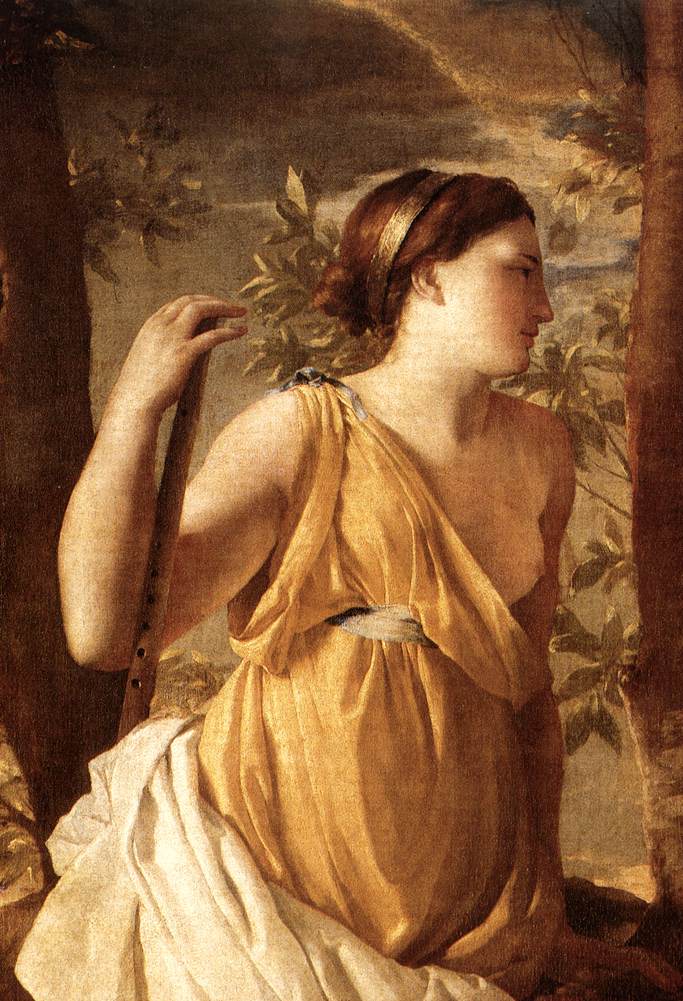

Baroque (1600-1700) Nicolas Poussin, the Poet's inspiration, 1638

Mannerism (1527-1600) Hans Baldung Grien, Virgin and Child, 1540
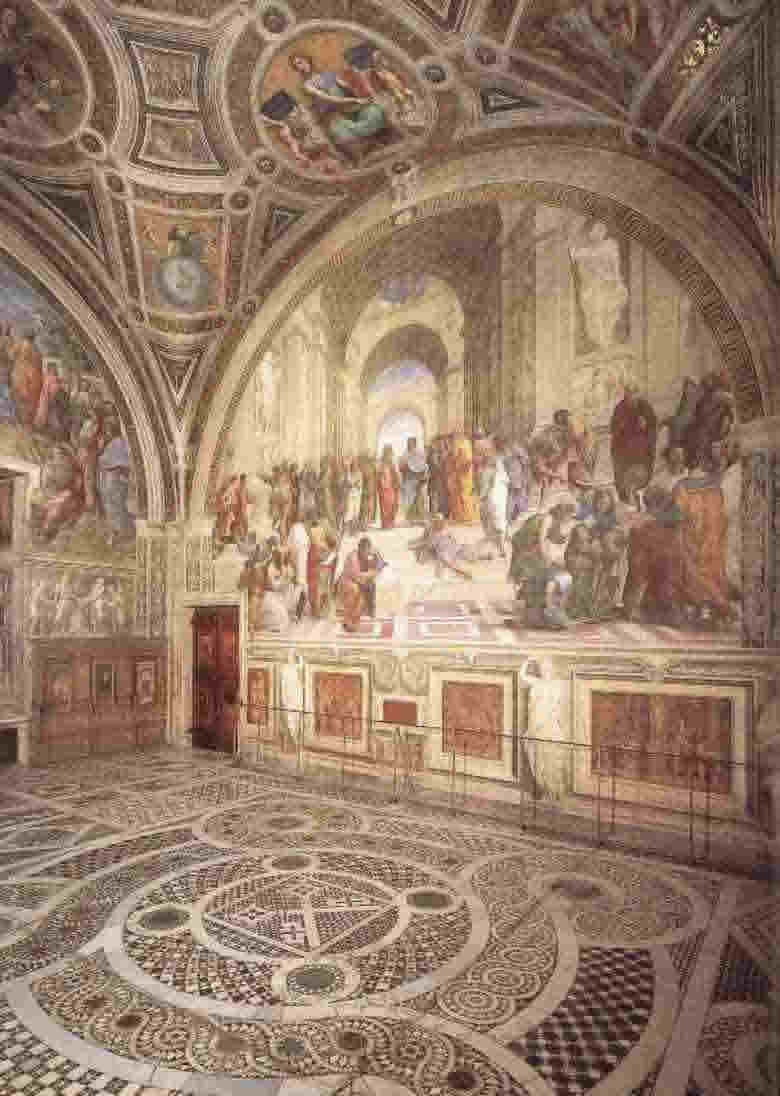

High Remaissance (1480s-1520s) Raphael, the School of Athens, 1509
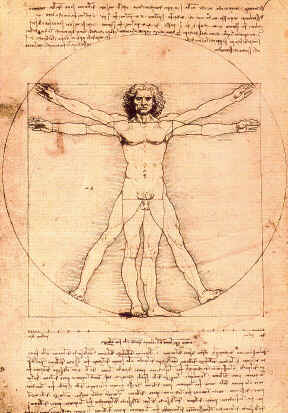
Renaissance (1500 in Italy, 1600 in northern Europe)

Gothic (1280-1515)
Italian Panel painting (13th century)

Illuminated manuscript (13th century)
Romanesque (11th, 12th century) attempts to link the architecture in medieval Europe
to Roman Architecture based on similarities of forms and materials
Ottonian (950-1050)
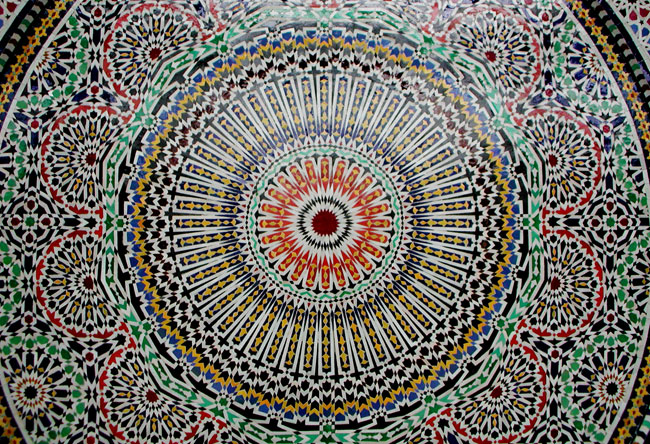

Arabesque (888)

Carolingian (780-900)

Byzantine (5th century)
Early Christian (200-500)

Roman (100 ad)

Greek (450 bc)

Chinese (1000 bc)

Babylonian (2000 bc)

Egyptian (3000 bc)

Cave painting (70,000 bc)